Discriminants and how to determine the number of real roots of a quadratic equation
When working with quadratic equations, the discriminant is the key to unlocking the mystery of real roots. For any quadratic equation written in the standard form
the discriminant is given by
The Key to Determining Real Roots (and No Real Roots)
The value of the discriminant tells you everything you need to know about the nature of the quadratic's roots:
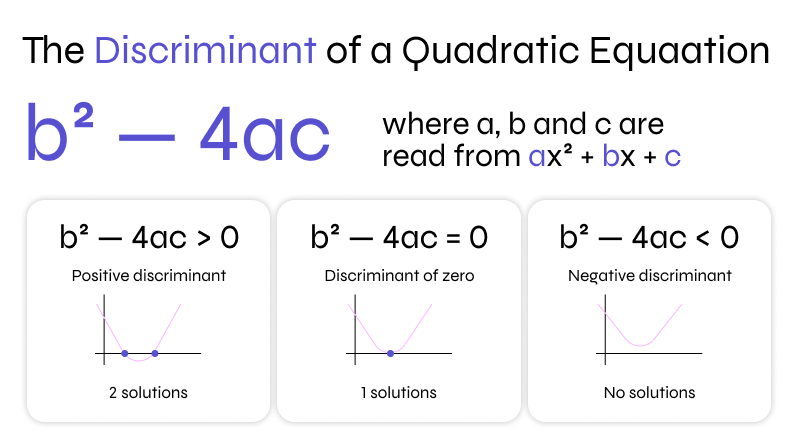
Two Distinct Real Roots
A positive discriminant means the quadratic equation has two different real solutions. These roots can be found using the quadratic formula and will lie at two separate points on the graph of the equation.
One Real Repeated Root
When the discriminant is zero, the quadratic equation has exactly one real root, but it is repeated. This situation is often referred to as a "double root" and graphically represents a parabola that just touches the x-axis at a single point.
No Real Roots
A negative discriminant indicates that the quadratic equation has no real roots. Instead, it has two complex roots that are conjugates of each other. In this case, the parabola does not cross the x-axis at all.
Putting It All Together
Understanding the discriminant is crucial because it provides a quick and efficient way to predict the behavior of quadratic equations without necessarily solving them completely. Whether you're analyzing the graph of a quadratic function or solving a real-world problem, the discriminant offers a snapshot of what to expect.
Example
Consider the quadratic equation
Calculate the discriminant:
Since Δ>0, we know that this equation has two distinct real roots.