(Stabilising, directional recap) Disruptive selection
Joe Wolfensohn
Teacher

Contents
Recall Questions
This topic requires prior knowledge of natural selection from Year 12. You can test your knowledge on this below.
What causes genetic variation within a population?
Mutations, meiosis (independent assortment & crossing over), and random fertilisation.
What is the definition of natural selection?
The process by which individuals with advantageous alleles survive, reproduce, and pass on their alleles to the next generation, leading to a change in allele frequency.
What is meant by a 'selective pressure'?
An environmental factor that affects the survival or reproductive success of individuals within a population.
Topic Explainer Video
Check out this @JoeDoesBiology video that explains (stabilising, directional recap) disruptive selection or read the full notes below. Once you've gone through the whole note, try out the practice questions!
What is Natural Selection?
Natural selection alters the allele frequency of a population depending on how individuals with different phenotypes survive and reproduce. There are three main types of natural selection, each with distinct effects on the population’s phenotype distribution.
Directional Selection
Graph:
- The mean phenotype shifts in the direction of the advantageous phenotype.
- The range of phenotypes and the standard deviation remains unaltered.
Definition:
- Occurs when one extreme phenotype is favoured over the mean or other extreme, causing a shift in the population’s phenotype distribution.
Example
Antibiotic resistance in bacteria - individuals with mutations that make them resistant to antibiotics survive and reproduce more, shifting the population towards resistance.
Stabilising Selection
Graph:
- The mean phenotype has the advantage and is selected for.
- Both extremes of phenotype are selected against.
- Happens in a stable / unchanging environment.
- Range of phenotypes and the standard deviation get reduced.
Definition:
- Favours the average phenotype and selects against extremes. Reduces variation and occurs in a stable environment.
Example
Human birth weight - very low or very high birth weights have higher mortality. Average-weight babies have a higher survival rate.
Disruptive Selection
Graph:
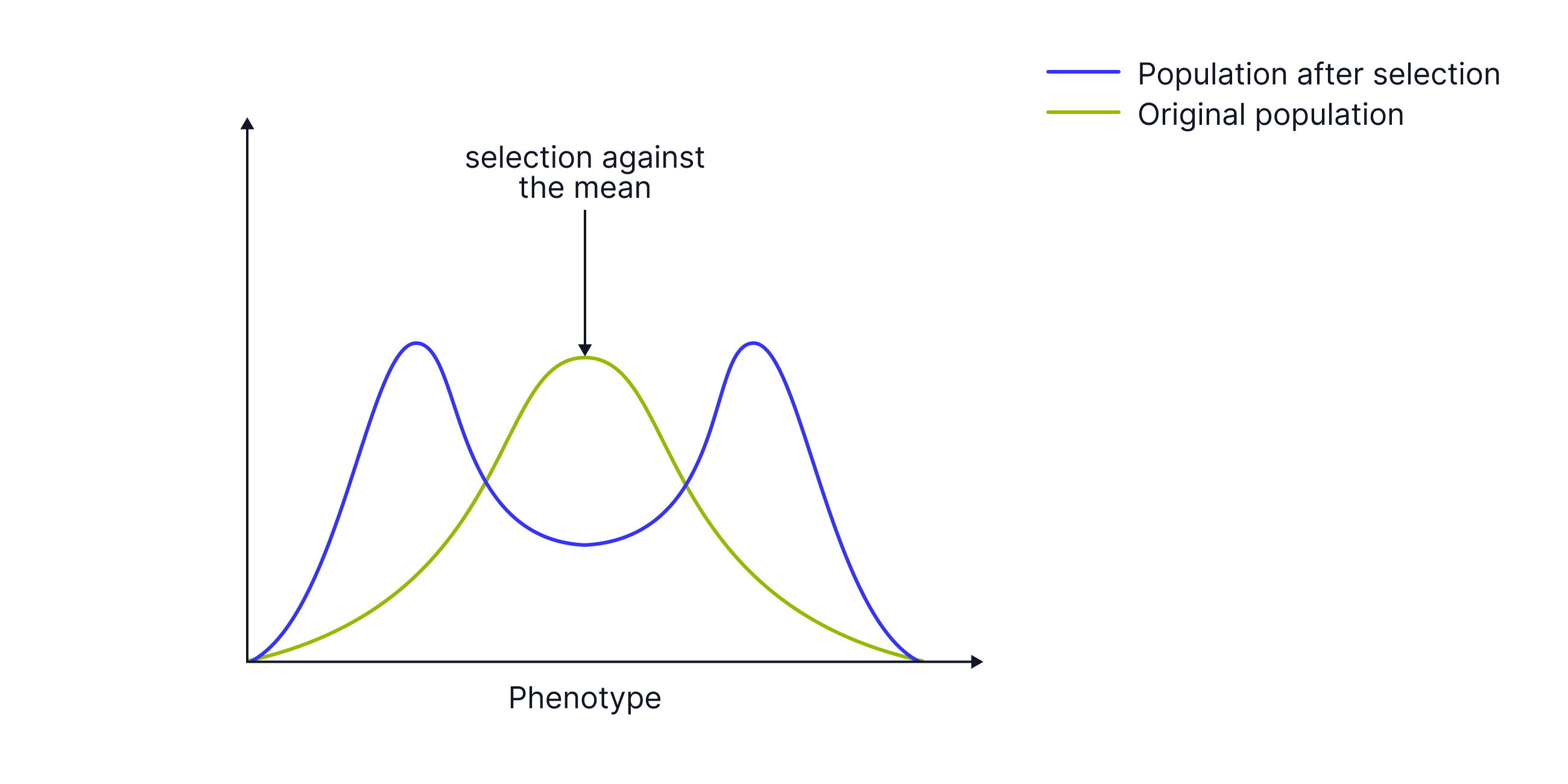
Definition:
- Favours both extreme phenotypes and selects against the mean. Can lead to the formation of two distinct groups - an early stage of speciation – eventually leading to the formation of two new species from a pre-existing species.
Example
Feather colour in male birds where females prefer either very dark or very light plumage, but not intermediate shades.
Key Terms
- Natural Selection: The process where individuals with advantageous traits survive and reproduce to pass on their alleles.
- Directional Selection: Selection that favours one extreme phenotype.
- Stabilising Selection: Selection that favours the average phenotype.
- Disruptive Selection: Selection that favours both extremes of a phenotype range.
- Phenotype: Observable traits or characteristics of an organism determined by both genotype and the environment.
- Allele Frequency: The proportion of a specific allele within a gene pool.
Exam Tip
Command words like "Describe" vs "Explain":
-
Describe: State what happens (e.g., “The curve shifts to the right”).
-
Explain: Give a biological reason why it happens (e.g., “Because individuals with the extreme phenotype are more likely to survive and reproduce”).
When describing graphs:
-
Reference changes in the mean, range, and standard deviation of the distribution.
Lactose is the main sugar in milk and is hydrolysed by the enzyme lactase. Lactase is essential to newborn mammals as milk is their only source of food. Most mammals stop producing lactase when they start feeding on other food sources. Humans are an exception to this because some continue to produce lactase as adults. The ability to continue producing lactase is known as lactase persistence (LP) and is controlled by a dominant allele.
One hypothesis for LP in humans suggests that the selective pressure was related to some human populations farming cattle as a source of milk.
Describe how farming cattle as a source of milk could have led to an increase in LP and name the type of selection taking place. (5 marks)
1. LP due to mutation
2. Milk provides named nutrient, e.g. glucose, galactose
3. Individuals with LP more likely to survive and reproduce
Accept pass on allele/LP for reproduce.
4. Frequency of allele increases
5. Directional selection
Practice Question
Try to answer the practice question from the TikTok on your own, then watch the video to see how well you did!