Aerobic respiration - Glycolysis
Laura Armstrong
Teacher

Contents
Recall Questions
This topic requires prior knowledge of respiration from GCSE. You can test your knowledge on this below.
What is the word equation for aerobic respiration you learnt at GCSE?
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water (+ Energy)
Where in the cell does aerobic respiration take place?
Mainly in the mitochondria.
What is the main purpose of aerobic respiration?
To release energy in the form of ATP for cellular processes.
Topic Explainer Video
What Is Aerobic Respiration?
Aerobic respiration is a metabolic pathway in which energy stored in glucose is released to form ATP. It requires oxygen and occurs in four main stages:
|
Stage |
Location |
|---|---|
|
1. Glycolysis |
Cytoplasm |
|
2. Link reaction |
Mitochondrial matrix |
|
3. Krebs cycle |
Mitochondrial matrix |
|
4. Oxidative phosphorylation |
Inner mitochondrial membrane |
Stage 1: Glycolysis – Breakdown of Glucose
Where it Happens:
-
In the cytoplasm
-
Does not require oxygen, so occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration
Step-by-Step Summary of Glycolysis
- Phosphorylation of glucose
-
-
Glucose (6 carbons) is phosphorylated using 2 molecules of ATP
-
This forms hexose bisphosphate (6 carbons)
-
-
Splitting of hexose bisphosphate
-
Hexose bisphosphate splits into two molecules of triose phosphate (each with 3 carbons)
-
-
Oxidation of triose phosphate
-
Triose Phosphate is oxidised (loses hydrogen) to form pyruvate (with 3 carbons)
-
The hydrogens are transferred to a coenzyme called NAD, forming 2 reduced NAD (NADH)
-
-
ATP generation
-
4 molecules of ATP are produced from ADP and Pi via substrate-level phosphorylation
-
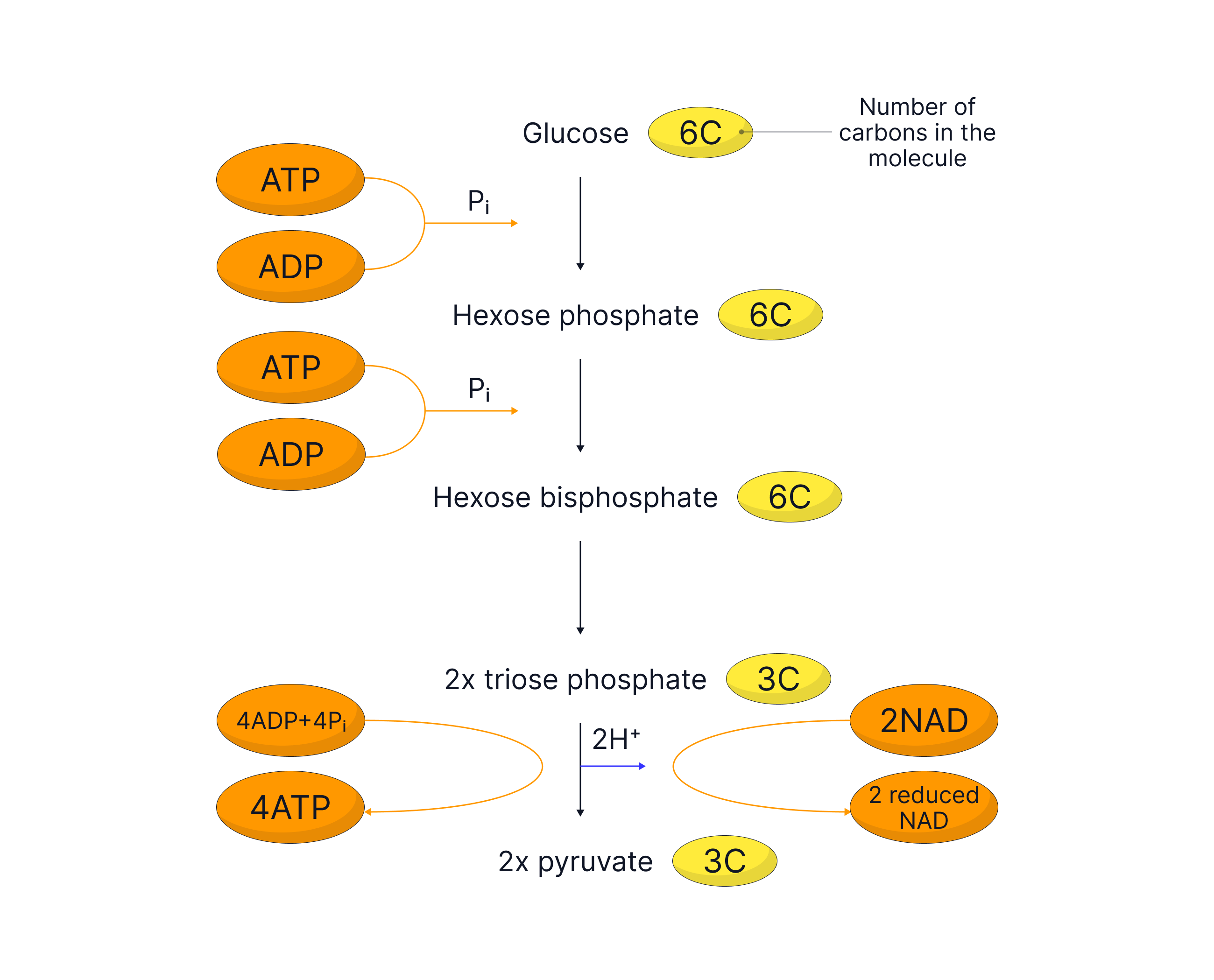
Net Products of Glycolysis (per glucose molecule)
|
Molecule |
Amount |
|---|---|
|
ATP (net gain) |
2 (4 made – 2 used) |
|
Reduced NAD |
2 |
|
Pyruvate |
2 |
These products are used in the next stages of aerobic respiration:
-
Pyruvate enters the mitochondria for the link reaction
-
NADH carries electrons to the electron transport chain in oxidative phosphorylation
Key Terms
-
Glycolysis: The first stage of respiration where glucose is broken down into pyruvate in the cytoplasm.
-
Phosphorylation: The addition of a phosphate group to a molecule (e.g., ATP → ADP + Pi and the phosphate is used to phosphorylate glucose).
-
NAD: A coenzyme that accepts hydrogen atoms to become reduced NAD (NADH).
-
Substrate-level phosphorylation: Direct production of ATP from a reaction involving a molecule that donates phosphate.
Exam Tip
In questions on glycolysis:
-
Make sure you distinguish between gross ATP production (4 ATP) and net gain (2 ATP).
-
Use correct terminology like “oxidation of triose phosphate to form pyruvate”
-
Glycolysis occurs in aerobic and anaerobic respiration—don’t say it requires oxygen!
Describe what happens during glycolysis. (5 marks)
-
Glucose is phosphorylated using 2 ATP molecules.
-
This produces two molecules of triose phosphate.
-
Each triose phosphate is oxidised to form pyruvate.
-
2 NAD are reduced to form 2 NADH
-
4 ATP are produced via substrate-level phosphorylation, with a net gain of 2 ATP
Practice Question
Try to answer the practice question from the TikTok on your own, then watch the video to see how well you did!