Loop of Henle
Laura Armstrong
Teacher

Contents
What is the function of the kidneys?
To filter blood, remove urea, and regulate water and salt balance.
What is ultrafiltration and where does it occur?
It’s the filtration of small molecules; such as glucose, amino acids and ions from the blood under high pressure in the glomerulus/Bowman’s capsule.
What is osmosis?
The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane from a region of high water potential to low water potential.
Topic Explainer Video
Why Is the Loop of Henle Important?
The Loop of Henle plays a vital role in water conservation by creating a concentration gradient in the medulla, which allows the collecting duct to reabsorb water by osmosis.
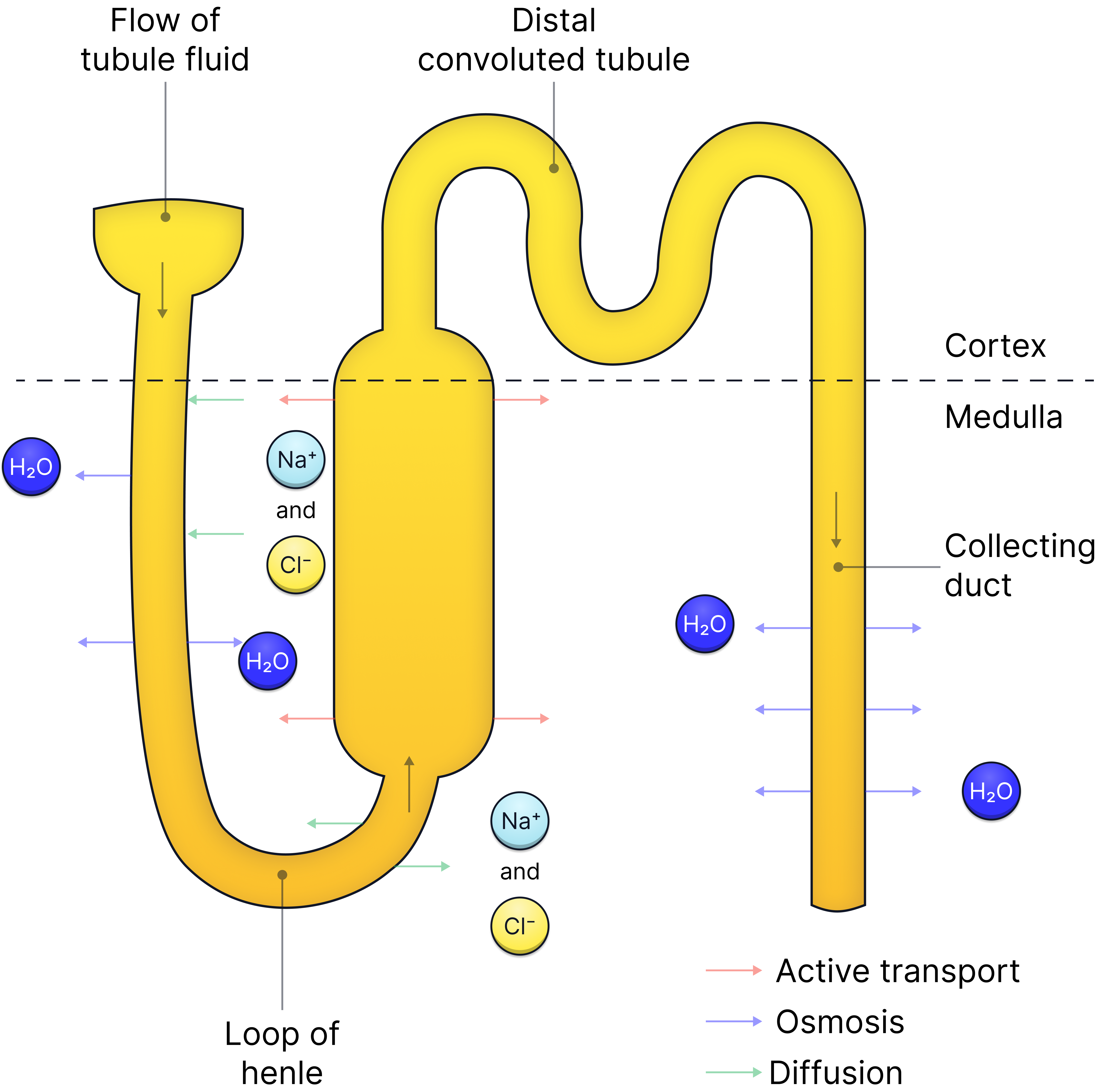
Structure of The Loop of Henle
| Region | Structure | Function |
| Descending limb | Thin walls, permeable to water. | Water leaves filtrate by osmosis into medulla (high salt). |
| Ascending limb | Thick walls, impermeable to water, permeable to ions. | Actively transports Na⁺ and Cl⁻ into medulla, maintaining gradient. |
The Countercurrent Multiplier Mechanism
Why “countercurrent”?
Because the flow of filtrate in the ascending and descending limbs is in opposite directions, which maximises the efficiency of water reabsorption.
How it works:
- Na⁺ and Cl⁻ are actively pumped out of the ascending limb into the medulla.
- This lowers the water potential of the medulla.
- Water moves out of the descending limb into the salty medulla by osmosis.
- This creates increasingly concentrated filtrate as it moves down the descending limb.
- Some Na⁺ and Cl⁻ will also diffuse out of the filtrate at the botom of the ascending limb.
- As filtrate moves up the ascending limb, more ions are removed by active transport, further concentrating the medulla.
Net Result:
- A steep water potential gradient in the medulla.
- Even though the concentration of filtrate in the collecting duct is high (and it therefore has a low water potential) the water potential of the surrounding medulla will always be lower, therefore water will continue to move out by osmosis and be reabsorbed back into the blood.
- More water reabsorbed from the collecting duct → concentrated urine.
Adaptations of Desert Animals
Animals in arid environments (e.g. kangaroo rat, camel) must conserve water. Their kidneys are highly specialised:
| Adaptation | Function |
| Very long loops of Henle | Deeper into medulla = steeper water potential gradient = more water reabsorbed. |
| More mitochondria in cells of ascending limb | Supports more active transport of Na⁺ and Cl⁻ into medulla. |
| Thicker medulla | Indicates longer loops = steeper water potential gradient. |
| Highly concentrated urine | Less water lost — crucial in dry habitats. |
| Nocturnal behaviour | Reduces water loss via evaporation during heat of day. |
Key Terms
- Countercurrent multiplier: Mechanism that maintains medullary concentration gradient using opposite flow and ion pumping.
- Medulla: Inner region of the kidney where the Loop of Henle and collecting duct create and use a low water potential.
- Osmoregulation: Regulation of water and solute concentrations in the body.
- Collecting duct: Final site of water reabsorption, dependent on ADH and the medullary gradient.
Exam Tips
Always specify direction of osmosis (water) and active transport (ions) when describing the mechanism.
Mention water potential gradients instead of just “saltiness”.
Explain how the structure of the Loop of Henle enables the kidney to produce concentrated urine. (4 marks)
- The Loop of Henle creates a low water potential in the medulla via the countercurrent multiplier.
- The ascending limb actively transports Na⁺ and Cl⁻ into the medulla, lowering its water potential.
- The descending limb is permeable to water, so water leaves the filtrate by osmosis.
- This maintains a steep gradient, allowing more water to be reabsorbed from the collecting duct.
Practice Question 1
Try to answer the practice question from the TikTok on your own, then watch the video to see how well you did!
Practice Question 2
If you want to try out another one, check this video out and see how you do!