Capacitance
Brook Edgar
Teacher

Contents
Explainer Video
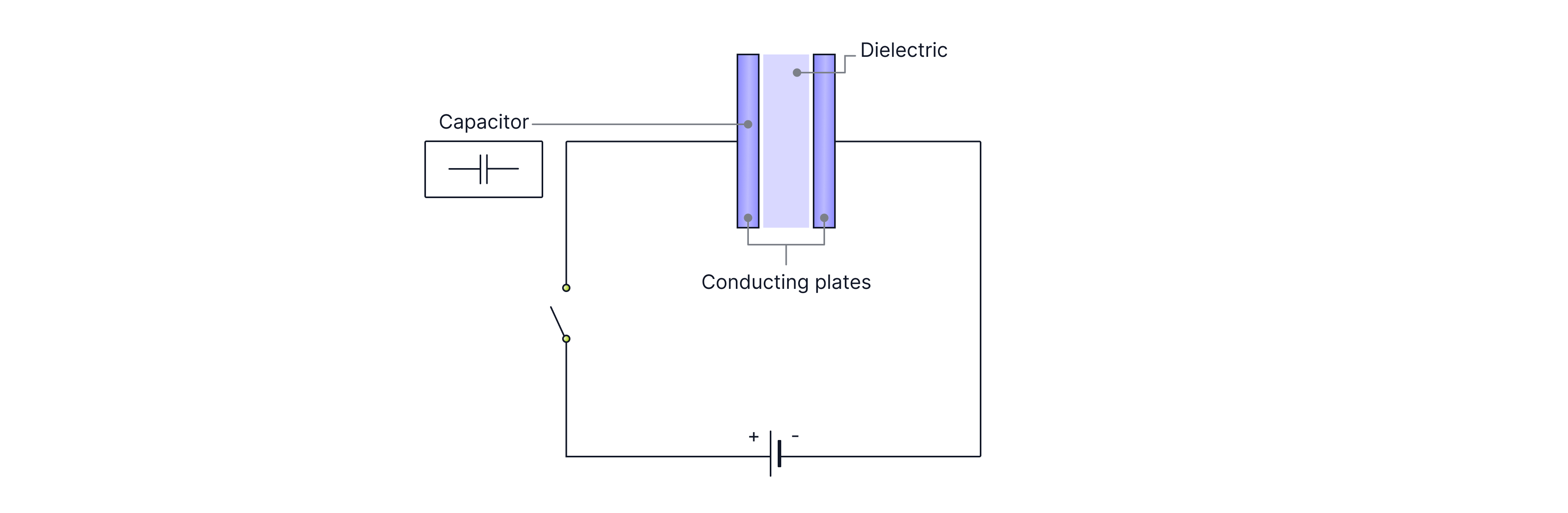
Capacitors
Capacitors are devices that store electrical energy in the electric field between the plates by storing charge on the plates.
Capacitance is defined as the charge stored per unit voltage. It is measured in farads, F.
Formula:
 A fully discharged capacitor, with a terminal voltage of zero, will initially act as a short circuit when attached to a source of voltage, drawing maximum current as it begins to build charge. Negative charges from the negative terminal of the cell move onto one plate, building up a negative charge on that plate. Negative charges on the other plate of the capacitor are repelled off, and attracted to the positive terminal of the cell. Current flows around the circuit.
A fully discharged capacitor, with a terminal voltage of zero, will initially act as a short circuit when attached to a source of voltage, drawing maximum current as it begins to build charge. Negative charges from the negative terminal of the cell move onto one plate, building up a negative charge on that plate. Negative charges on the other plate of the capacitor are repelled off, and attracted to the positive terminal of the cell. Current flows around the circuit.
Over time, the capacitor's terminal voltage rises to meet the applied voltage from the source. The current through the capacitor decreases correspondingly as it becomes harder to push more negative electrons onto an already negative plate.
Once the capacitor has reached the full voltage of the source, the current will become zero, essentially acting like an open circuit.
A capacitor is usually charged through a fixed resistor to slow down the charging time.
Capacitor Charging Graphs
During charging, the current is initially high and decreases over time. is the maximum current. We can see from the equation that it is an exponential decay. is the resistance of the fixed resistor in the circuit that is there to slow the charging process. is the capacitance of the capacitor.

During charging, the potential difference (pd) is low and increases until it equals the pd of the source,

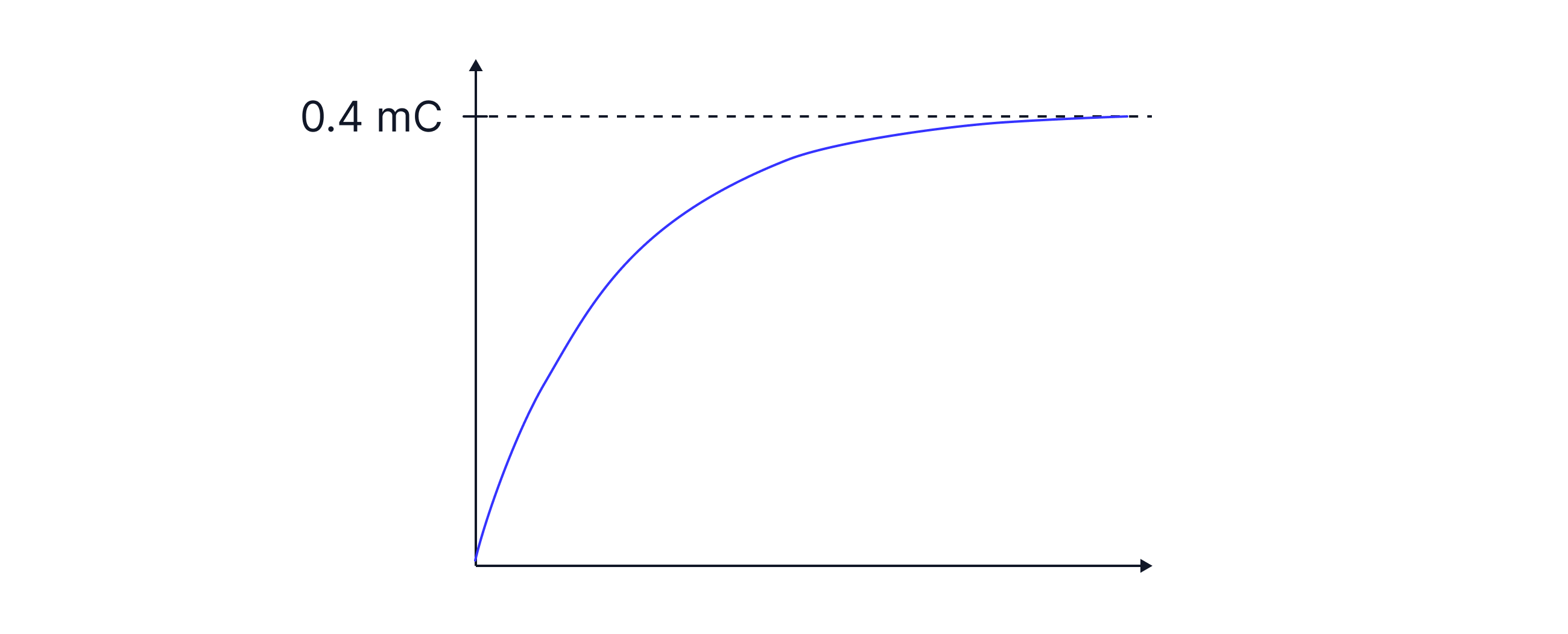
During charging, the charge on the plates is zero to begin with and increases over time until it reaches the maximum charge stored, .

Worked Example
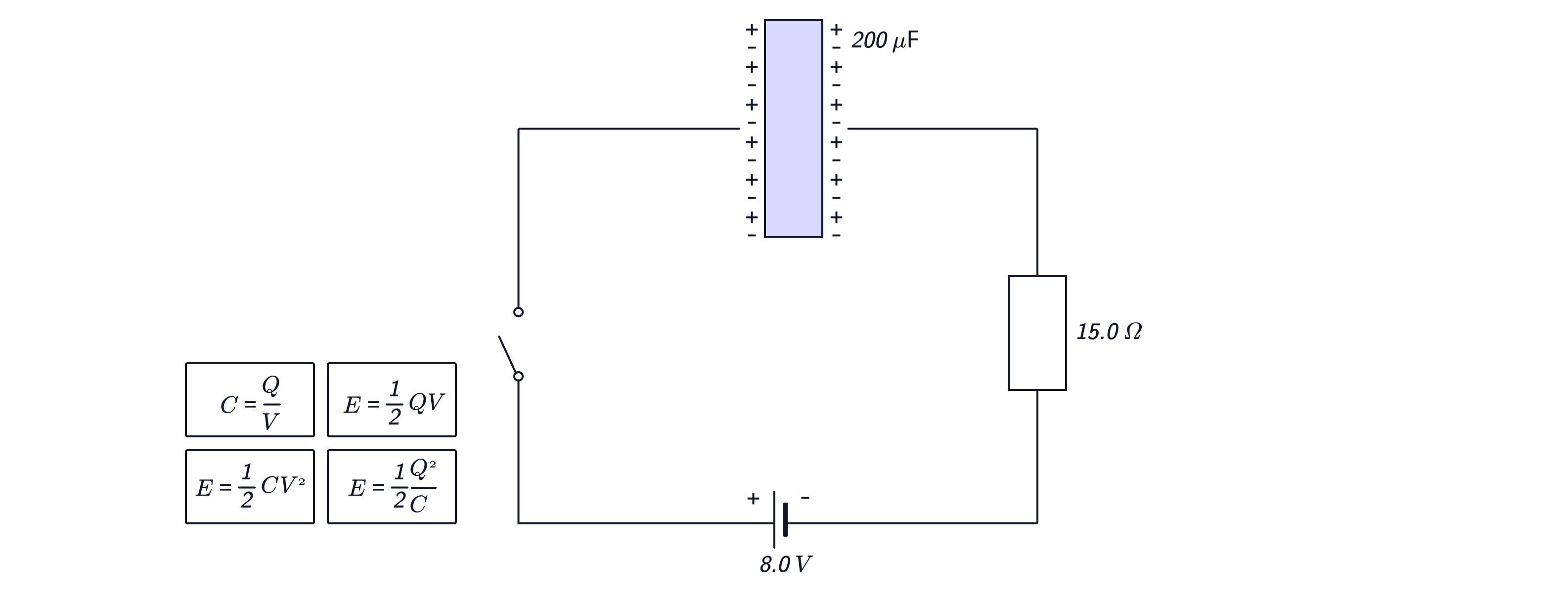
Calculate the maximum charge stored on the capacitor.
When the switch is closed, current flows quickly as there is no charge on the capacitor yet. Calculate this maximum current.
Calculate the current during charging when the voltage across the capacitor is 5.0 V.
Answer:
The capacitor is fully charged when the pd across it equals that of the source, V.
When the switch is closed, the pd across the capacitor is zero, so the pd across the fixed resistor equals that of the source, and we can use this to calculate the current through the fixed resistor.
When the voltage across the capacitor is five, the pd across the fixed resistor will be V. We can use this and the resistance of the fixed resistor to find the current through it and hence the whole circuit, as it is a series circuit.
Capacitor Discharging Graphs
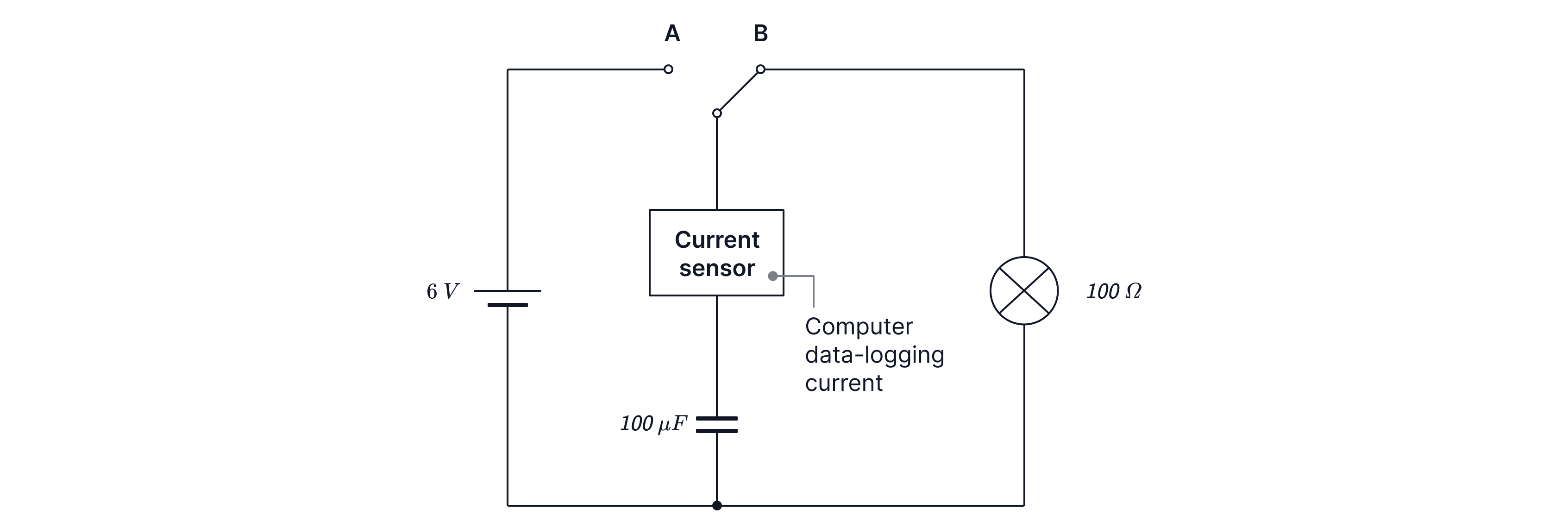
When a capacitor is discharging, with the switch in the position shown at point B, the current is initially high due to the high charge initially stored on the plates and decreases over time. It follows the same relationship as the charging process.

When discharging, the pd starts at the maximum value provided by the source during charging and decreases over time as charge is lost from the plates, causing the potential difference between them to fall over time.

During discharging, the charge on the plates decreases over time as electrons move off the negative plate and travel through the circuit to the positive plate, which reduces the negative charge on one plate and the positive charge on the other.

Time Constant
Capacitors discharge rapidly, often used in camera flashes, due to the sudden release of energy. To slow the discharge process, a fixed resistor is often placed into the circuit.
The time for the capacitor to discharge to -> of its initial charge is known as the time constant, .
Formula:
An alternative way to find the time constant is to plot a logarithmic graph by taking the natural log of each side of the equation:
Following the equation of a line, :
-> , we would plot a graph of the against . The negative reciprocal of the gradient will = , the time constant, .
Worked Example
A capacitor is fully charged by a supply. It is then discharged through a resistor.
Calculate how much charge remains on the capacitor after seconds.
Calculate the pd on the capacitor after seconds.
Calculate the discharge current after seconds.
Answer:
During discharging, the charge falls exponentially. We need first to calculate what the maximum charge stored on the capacitor is, and then use this to find the charge left after 20 seconds.
We know that the pd decreases over time and that the initial pd stored on the capacitor is equal to that of the source from the charging process.
The current drops exponentially. To find the initial current, we know that it is the same as the maximum current during the charging process. The maximum current during charging occurs at the start when the pd across the capacitor plates is zero and the pd across the fixed resistor is equal to that of the source. As we know the resistance of the fixed resistor, we can then solve for the maximum current.
Remember: The time constant measures the rate of discharging or charging of a capacitor. It is the time it takes for the current/charge/voltage to fall to of its initial value () or the time taken for the current/charge/voltage to rise to () of its maximum value.
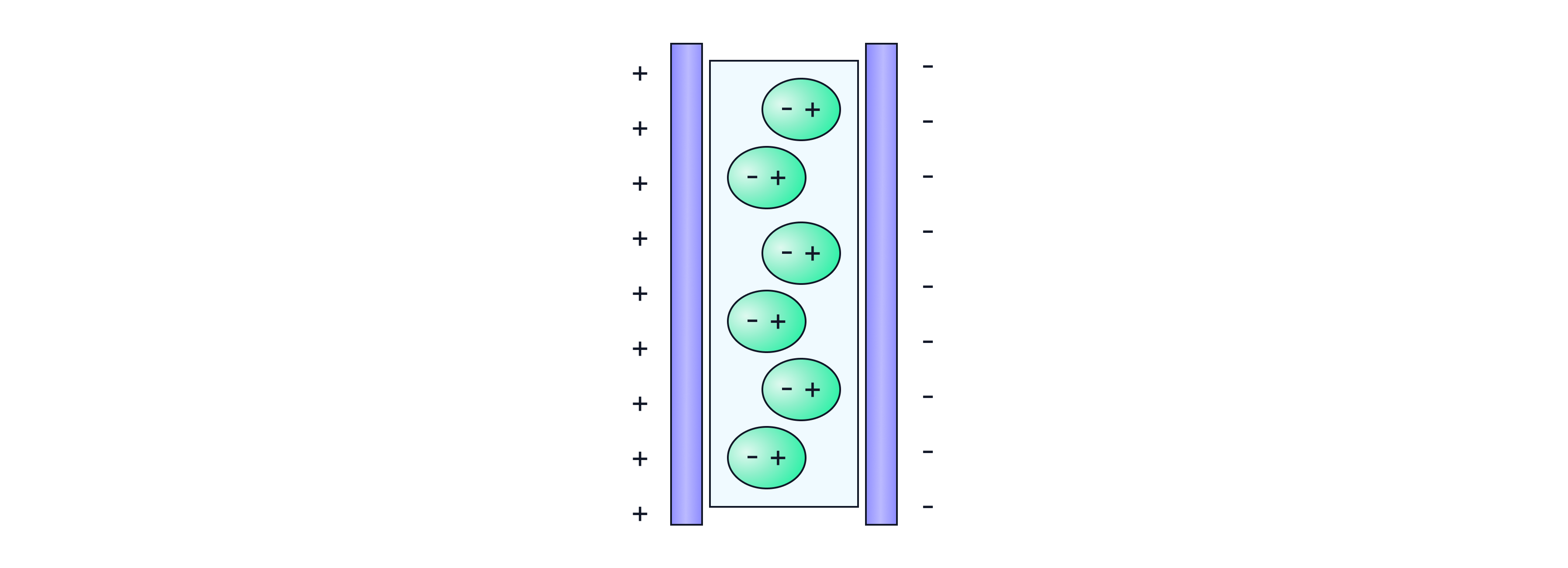
Dielectrics
Dielectrics allow more charge to be stored on the capacitor for the same voltage, thus increasing the capacitance of the capacitor. They are usually polar molecules that line up with the electric field between the capacitor plates. The negative sides of the polar molecules are attracted to the positive plate of the capacitor, and the positive side of the polar molecules to the negative plate. The polar molecules then create their own electric field, opposing that from the capacitor plates, thus reducing the overall electric field. The pd across the plates decreases, so more charge can be pulled onto the capacitor plates.
Formula:
Worked Example
An air-filled parallel-plate capacitor has a capacitance of . The space between the plates is filled with a dielectric of relative permittivity . Calculate the new capacitance of the capacitor and the energy stored when the pd across the capacitor is .
Answer:
The new capacitance is seven times the old capacitance as the dimensions of the capacitor have not changed.
We use the equation , as we know the new capacitance and the pd.
Practice Questions
A capacitor has a capacitance of and is in a circuit with a fixed resistor of resistance . Calculate the time for the charge to reach .
-> Check out Brook's video explanation for more help.
Answer:
The flash tube in a camera produced a flash when a capacitor, capacitance is discharged.

Calculate the energy stored on the capacitor.
Calculate the work done by the battery.
The discharged circuit has a resistance of . Emission of light stops when the p.d falls below Calculate the duration of the flash.
-> Check out Brook's video explanation for more help.
Answer: