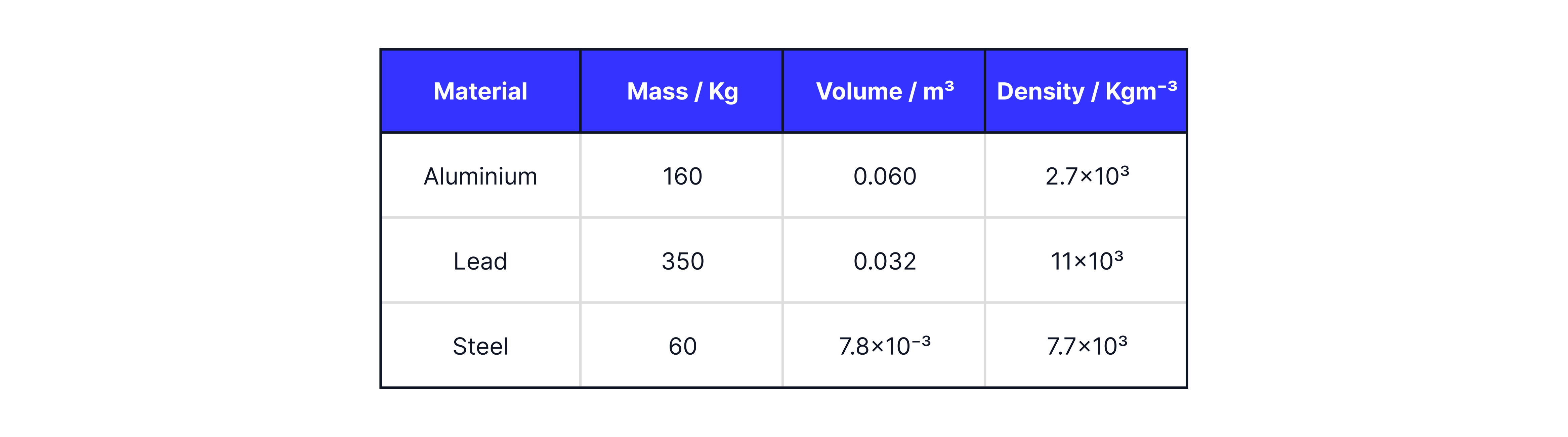
Density and Hooke's Law
Brook Edgar
Teacher

Explainer Video
Density
Density is defined as mass per unit volume.
Formula:
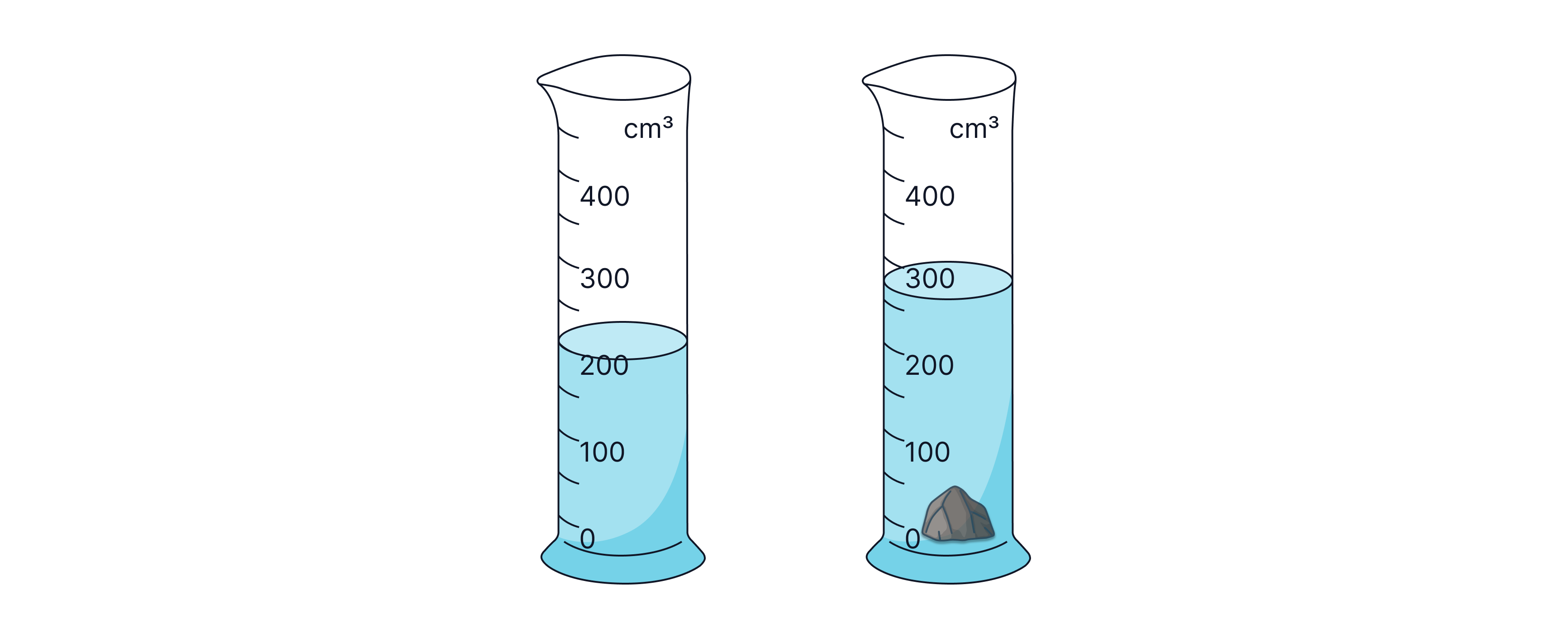

To find the density of an irregularly shaped object, like this rock:
Record the mass using a balance, ensuring there is no zero error.
Add water to the measuring cylinder and record the initial volume.
Place the object into the measuring cylinder and record the final volume.
The difference in the volume of water is the volume of the object.
Use the equation to calculate the density, mass divided by volume.
If the irregularly shaped object is less dense than water and floats, you would need to attach a sinker to the object. A sinker is a weight with a known volume that is denser than water. If one is needed, in step four above, you would subtract the sinker's volume from the water's displacement to find the final volume of the irregularly shaped object.
Note: The upthrust on the ball is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced.
Worked Example
The density of water is . Calculate this in ?
Answer:
There are in a , so therefore,
Teacher Tip: In a metre cubed, there would be much more mass than in a centimetre cubed for the same density.
Worked Example
How would you change the standard method to measure the density of a liquid, for example if you wanted to find the density of milk?
Answer:
Record the mass by placing the empty measuring cylinder on the balance and zeroing it.
Then fill the measuring cylinder with the liquid (milk) and record the mass on the balance.
Record the volume from the measuring cylinder.
Calculate the density of the liquid by doing mass/volume.
Worked Example
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, made of % by volume of copper and % by volume of zinc.
Density of copper =
Density of zinc =
A rod of brass, volume, is made. Calculate the mass of copper and the mass of zinc required to make it.
Calculate the density of brass.
Answer:
Worked Example
A scaffolding pole has an external radius of and an internal radius of . It is made of Aluminium. Calculate the mass of a length pole.
Answer:
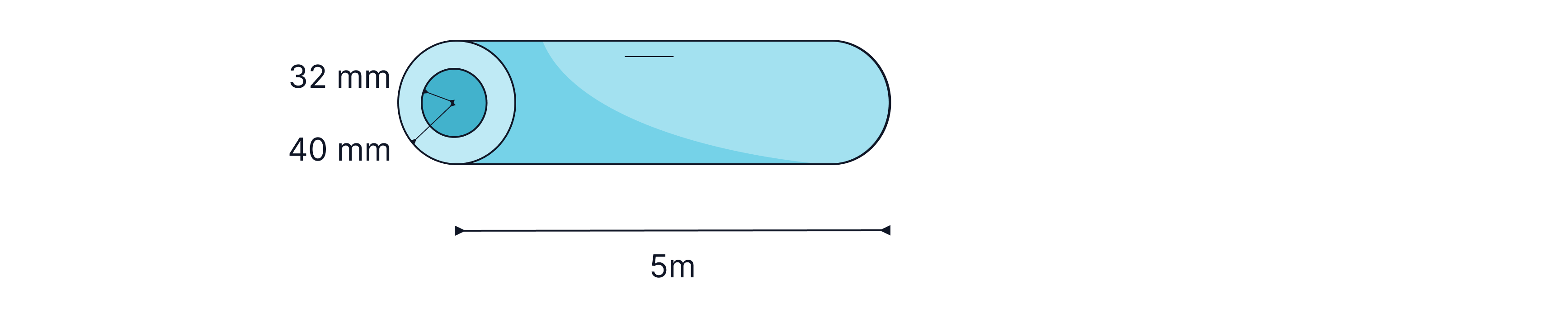
Volume of the hollow cylinder = the volume of the larger radius solid cylinder - the volume of the inner radius solid cylinder.
Volume of a cylinder =
Hooke's Law
Every spring has a characteristic value we call the spring constant, .
The spring constant depends on the material's properties and the spring's geometry.

If the spring obeys Hooke's law, the extension of the spring is directly proportional to the applied force up until the limit of proportionality.
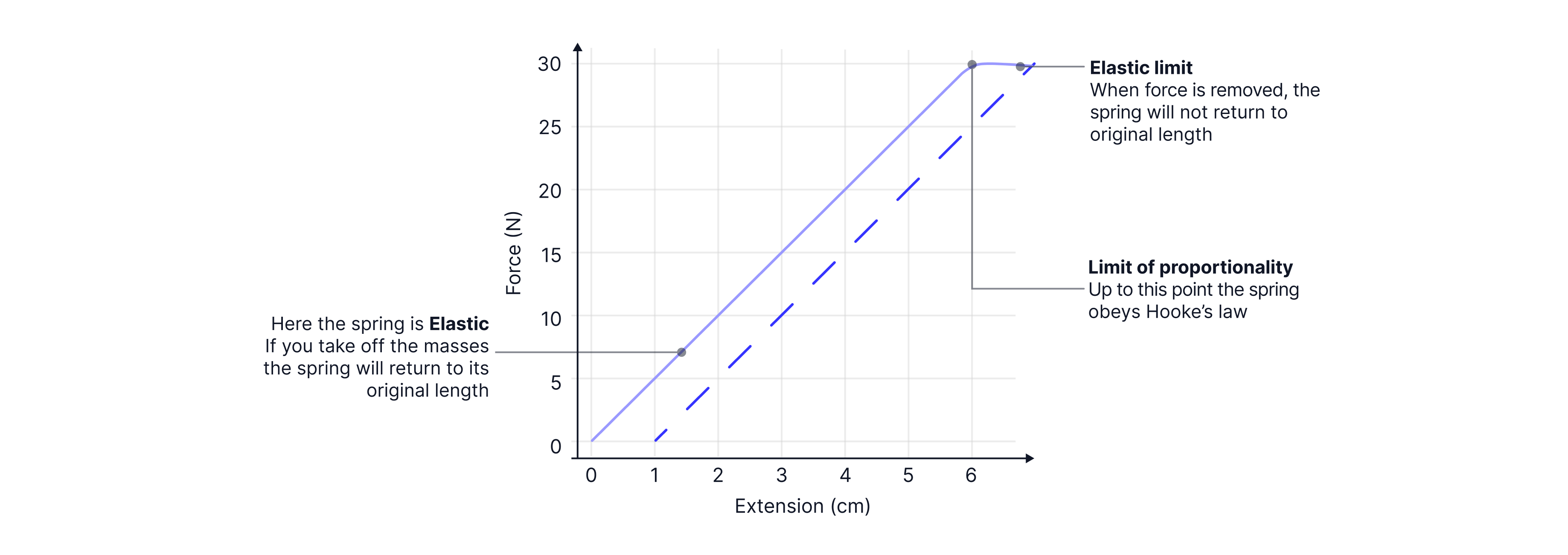
Beyond the limit of proportionality, the graph begins to curve, but the spring may still return to its original length once the force is removed; it is elastic.
Once you have gone beyond the spring's elastic limit, the spring will no longer return to its original length and is now permanently deformed (plastic deformation).
Key difference:
The limit of proportionality is the point up to which the force applied is directly proportional to the extension.
The elastic limit is the point beyond which the spring will no longer return to its original length when the applied force is removed..
Worked Example
The image shows identical springs in series and in parallel, each spring has a spring constant .
Calculate the effective spring constant (), the spring constant if the two springs were modelled as one spring.
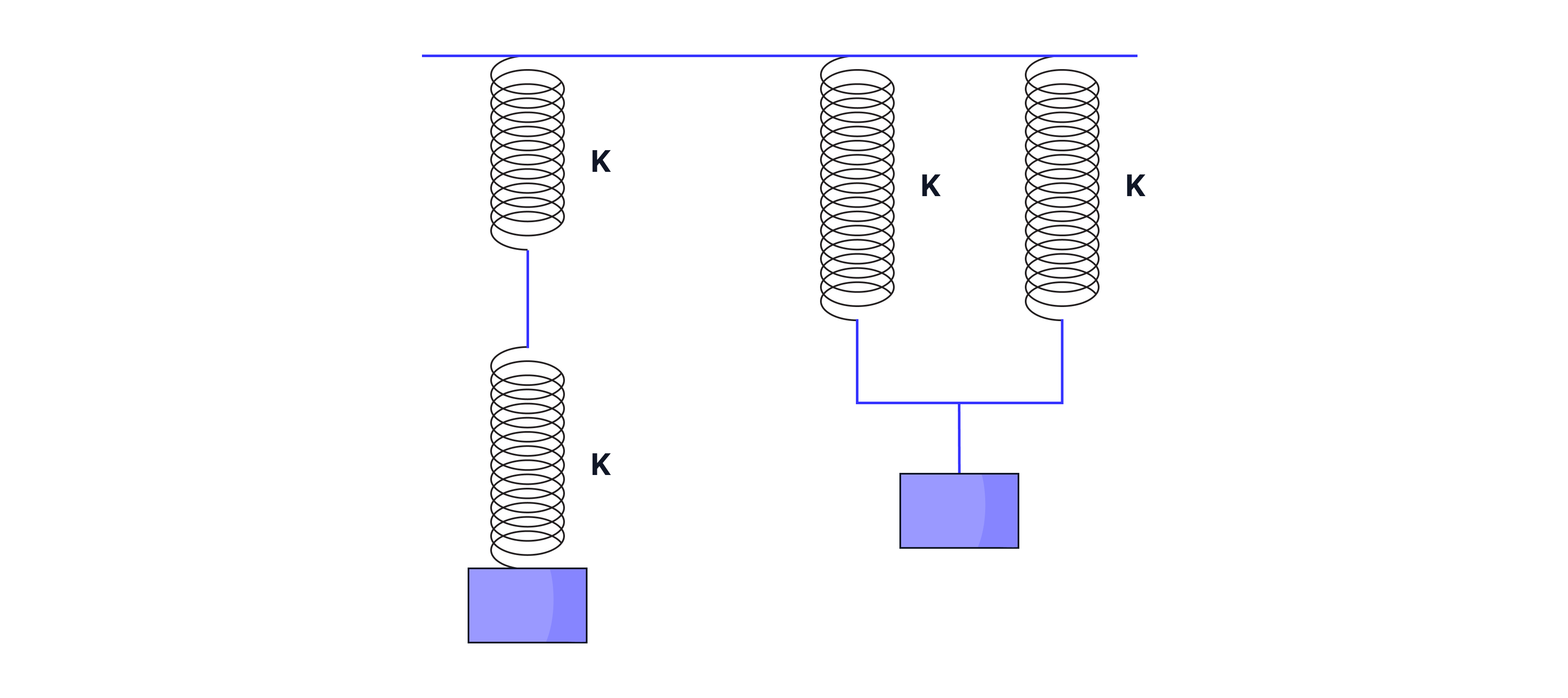
Answer:
When two springs are placed in series, the effective spring constant is half the spring constant of each individual spring.
When two springs are placed in parallel, the effective spring constant is double the spring constant of each individual spring.
Practice Questions
A steel scaffolding pole has an external radius of and an internal radius of .What is the mass of a length pole? The density of steel is =
-> Check out Brook's video explanation for more help.
Answer:
Mass =
A spring has an original length of . When a ball is added, the spring extends to .
Volume of ball = .
Calculate the spring constant.
The equipment is now lowered in water, so the ball is submerged. Calculate the upthrust on the ball, knowing the new length of the spring is .
Calculate the density of the liquid.
-> Check out Brook's video explanation for more help.
Answer: