HR Diagram
Brook Edgar
Teacher

Explainer Video
The H-R Diagram
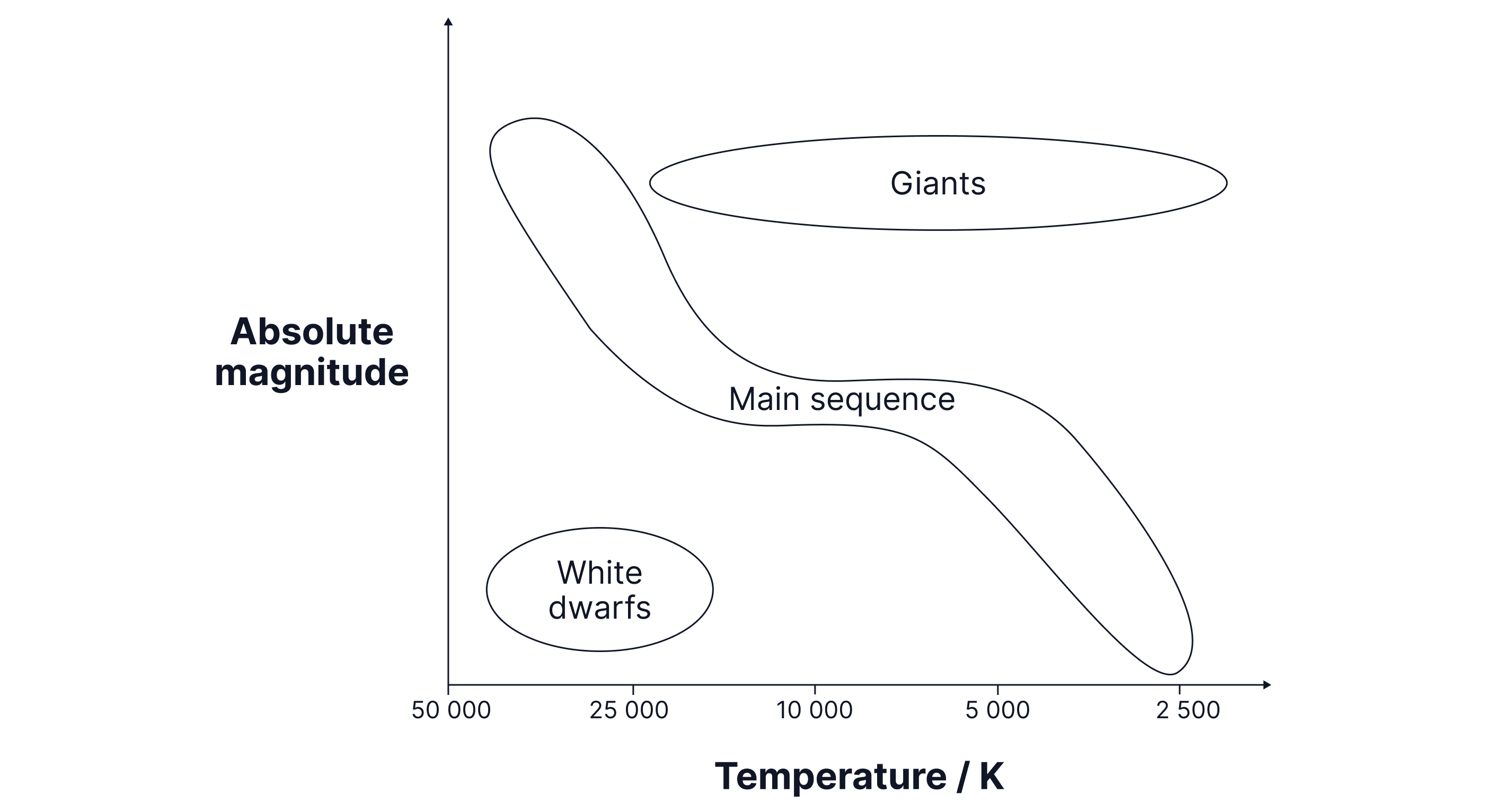
The Hertzsprung-Russell (HR) diagram plots the absolute magnitude (luminosity) of stars against their spectral types (temperatures). It's a fundamental tool in astronomy for studying the evolution of stars.
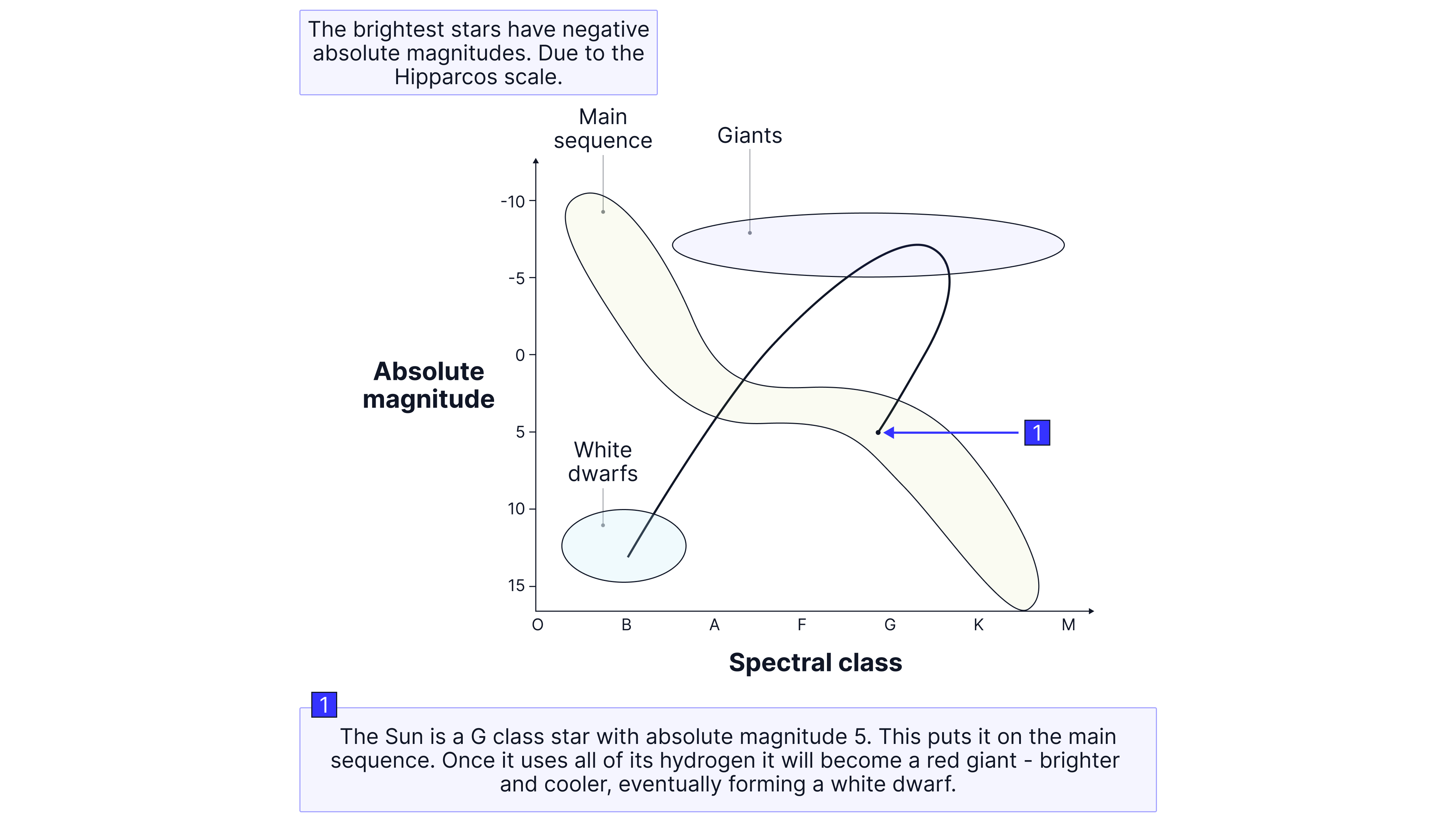
The main-sequence is where stars spend most of their lifetimes fusing hydrogen into Helium.
The Sun is a G-type main sequence star. It has an absolute magnitude of . The Sun will evolve into a red giant star once it has consumed all the hydrogen in its core. It swells and cools, turning redder and larger. The Sun will eventually form a white dwarf, which is hotter but dimmer due to its small size.
Stefan’s law can be used to explain why some stars are referred to as giants or dwarfs. For example, a dim (absolute magnitude ) star in spectral class A must be much smaller than a much brighter star (absolute magnitude ) in the same spectral class (i.e. at the same temperature) as .
Remember: The brightest stars have negative absolute magnitudes due to the Hipparcos scale.
Worked Example
A much larger star than the Sun may supernova and become a black hole. Suggest whether supernovae and black holes could be placed on the HR diagram.
Answer:
Supernovae would not fit onto the HR diagram because their absolute magnitude lies around (type 1a supernovae); the scale only goes to a luminosity of . The temperature of a supernova would also be greater than , off the scale.
Black holes also would not fit onto the HR diagram because they do not emit light. The escape velocity of a black hole is greater than the speed of light, so light cannot escape; it would therefore be extremely dim, having an absolute magnitude greater than .
Practice Questions
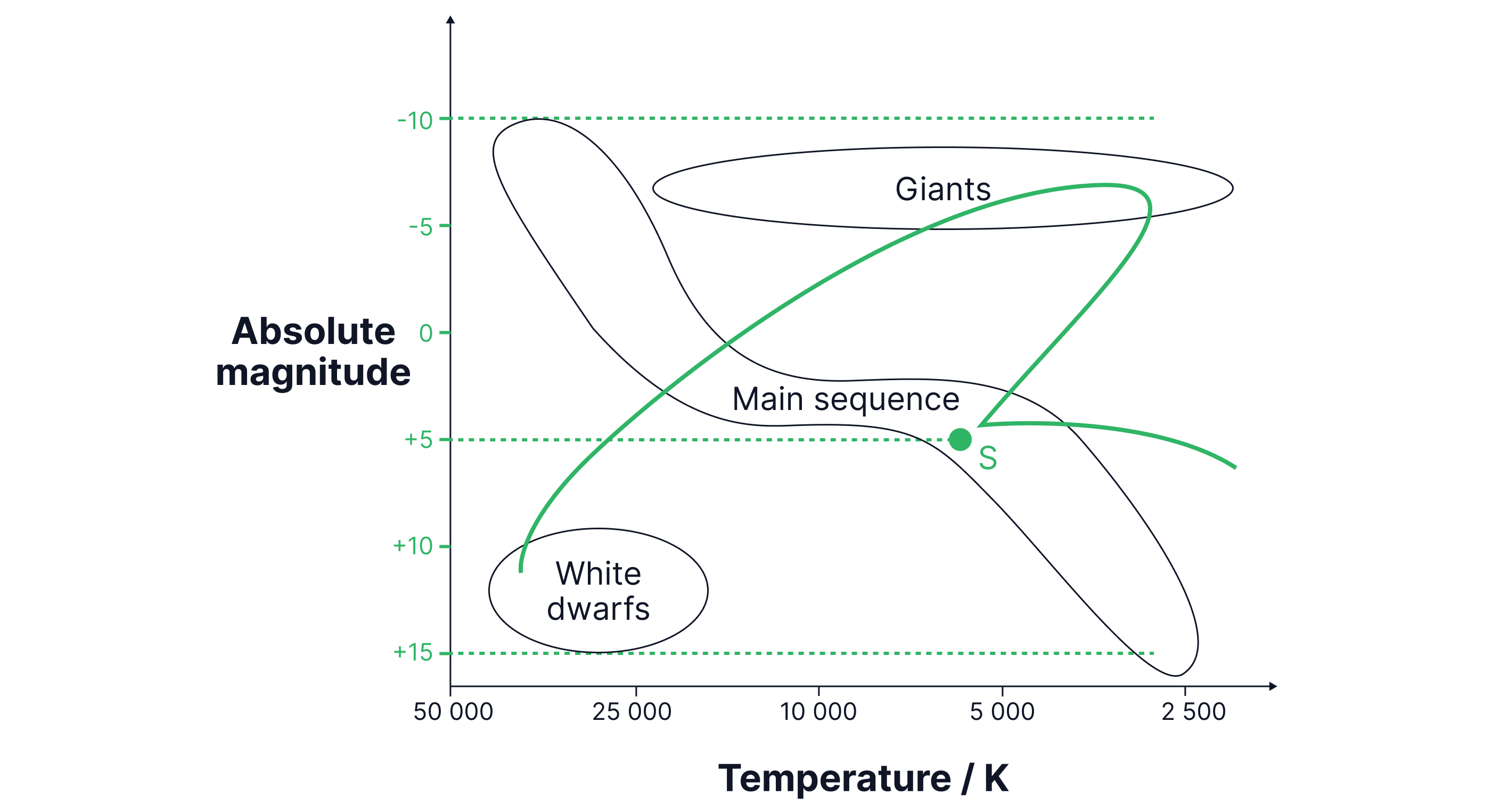
Use the Hertzsprung–Russell (HR) diagram to answer the following questions.
Label the absolute magnitude scale.
Label the position of the Sun with an S.
Draw a line on the HR diagram to show the evolution of a star similar to the Sun from formation.
-> Check out Brook's video explanation for more help.
Answer:
From to .
The Sun is a G-class star with absolute magnitude .
Line coming in from the RHS to the main sequence, up to the right to the giants and down to the left to the white dwarfs.