Hubble's Law
Brook Edgar
Teacher

Contents
Explainer Video
Hubble's Law
Hubble (an American astronomer) observed that light reaching Earth from distant galaxies was redshifted (the light was stretched out into longer regions of the spectrum). This showed us that these galaxies are moving away from us.
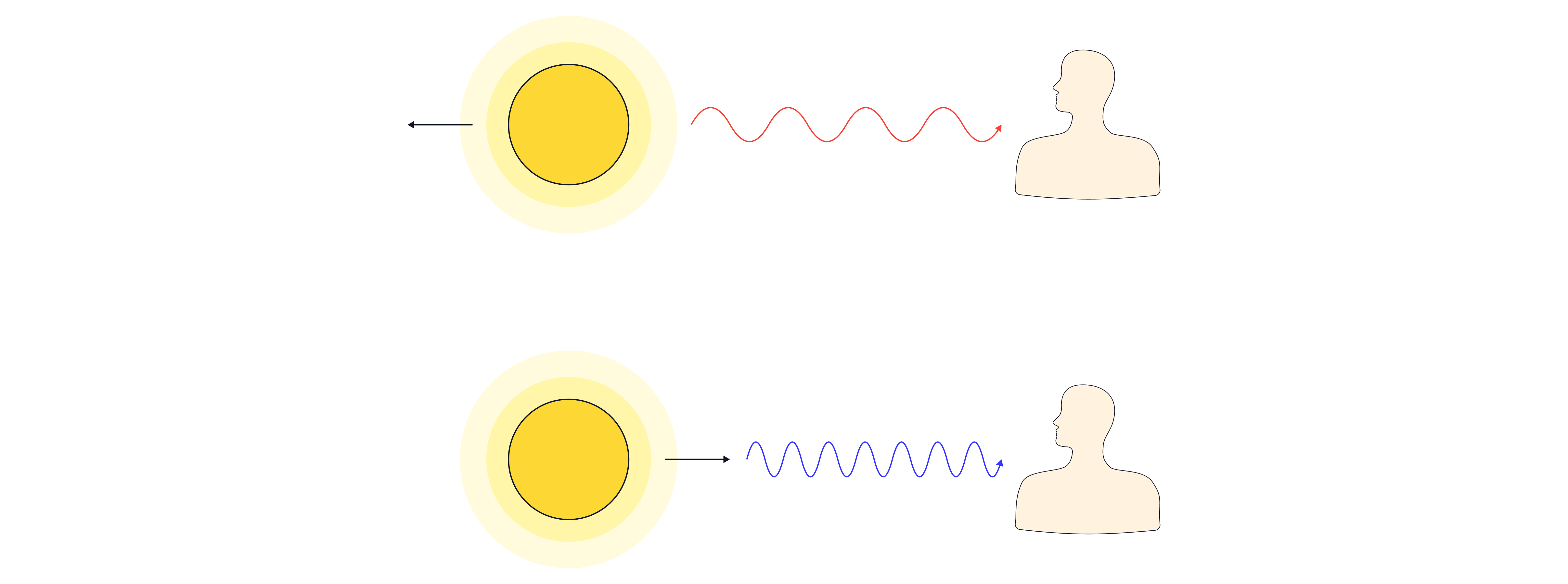
The farther away a galaxy is from us, the faster it recedes. The relationship is known as Hubble's Law:
Formula:
= recessional velocity
= Hubble constant
= distance to the galaxy
Remember: Hubble's law only applies to stars or systems that are redshifted. Most stars around Earth are redshifted because the universe is expanding; the distance between the star and Earth has increased since the light was first emitted, causing the wave to be “stretched”.
Redshift
The redshift of an object can be determined using its recessional velocity:
Formula:
= redshift
= velocity
= speed of light
towards us is a positive number, so to calculate the amount of redshift, as objects are moving away from us, we can often write:
Doppler Effect
As the light from an object is analysed, the shift in wavelength of one particular spectral line can be measured due to the object's motion towards or away from us. This slight change in wavelengths due to the changes in relative motion between the source and the observer is known as the Doppler effect.
The Doppler equation can be used to calculate the maximum recessional velocity and, therefore, its corresponding redshift.
Formula:
= change in wavelength
= recessional velocity
= speed of light
The emitted wavelength of light, when the source is at rest, is determined by using the laboratory value for that same element, also known as the rest wavelength. The Lab value represents the actual unshifted wavelength of a particular spectral line.
The Big Bang Theory
Hubble's Law, which demonstrates that the universe is expanding based on observations of redshifts, lays the foundation for the Big Bang theory. The Big Bang Theory suggests that the universe originated from a small, dense region known as a singularity, which expanded rapidly. Space, matter, and time were created in the Big Bang. It suggests that the Universe began about billion years ago.

We can use Hubble's constant to calculate the age of the universe.
The quoted value on the AQA formulae sheet of Hubble's constant is .
the unit of velocity needs to be in , and the unit of distance in (not megaparsec) in order for time to be in seconds.
As you can see, this is an overestimate. The value of Hubble's constant is a subject of ongoing research due to discrepancies in measurements, but the currently accepted value is ~. However, Hubble's law assumes the universe is expanding at a constant rate, which provides a quick estimate of the universe's age. To calculate the true value, other factors must be taken into consideration, as observations of distant Type 1a supernovae are dimmer than expected, suggesting that the universe is not expanding at a uniform rate but is accelerating. Dark energy is thought to be the reason behind this—it has an overall repulsive effect and is constant throughout the universe. It is controversial, as no one knows what it is yet.
Evidence for the Big Bang Theory
If the Big Bang theory were correct, radiation should have remained after the Big Bang, and if we could observe it, we would have evidence to support the theory.
This radiation was observed and named the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMBR). It is uniform in all directions of space, ~ K.
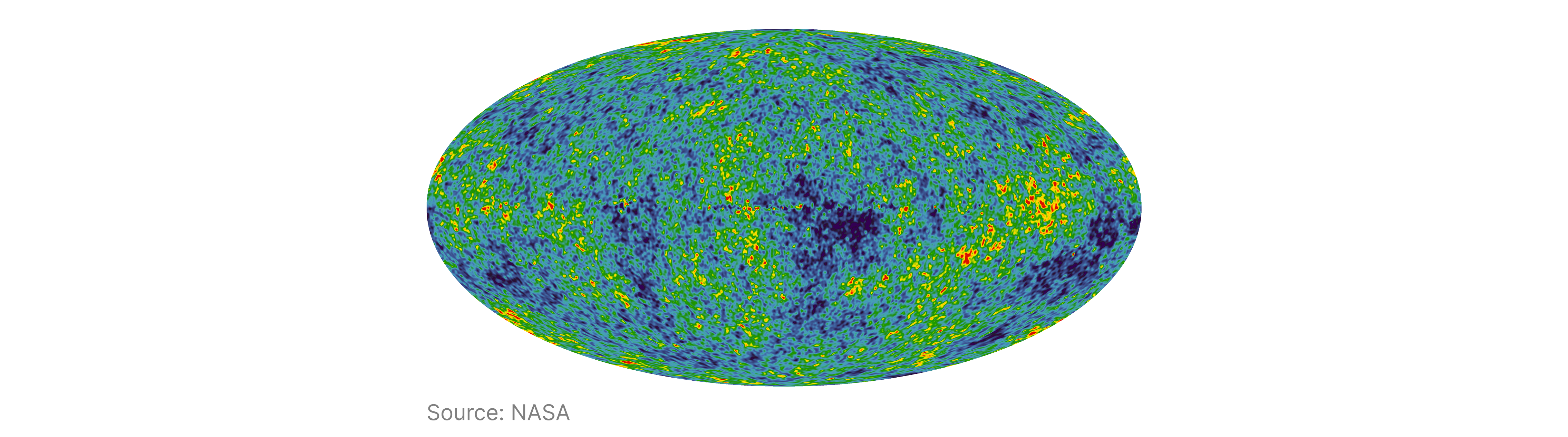
Further evidence supporting the Big Bang theory comes from the formation of nuclear matter. The Big Bang theory suggests that a brief period of fusion occurred when the universe was very young, resulting in the production of helium from hydrogen fusion. The universe then expanded and cooled too rapidly to create larger nuclei, resulting in a relative abundance of hydrogen and helium in the ratio of , spread uniformly throughout the universe, and a lack of larger elements, which is observed.
Remember: In exams, due to the value of Hubble's constant changing over time, they often will provide data on redshift or graphs for you to calculate the currently accepted value of Hubble's constant and then use this to calculate the age of the universe. Always take care that your units match to solve for time in seconds.
Worked Example
Markarian- is the closest known quasar to the Earth, million light years away. Redshift . Use this information to estimate the age, in seconds, of the universe.
Answer:
Orbital Motion and Doppler Shift
Sometimes, we are asked in exams to calculate the maximum recessional velocity of a star in orbit about a common centre of mass due to the presence of exoplanets using the Doppler effect (more on this in section ). At one point in its orbit, the star will be approaching us, exhibiting blueshift, and at another point in its orbit, it will be moving away from us, exhibiting redshift.
The key difference here is that we receive many different wavelengths of light during its orbit by observing the shift in wavelength of one particular spectral line as the star follows its circular orbit; therefore, we cannot simply compare the emitted wavelength and the observed wavelength as before.
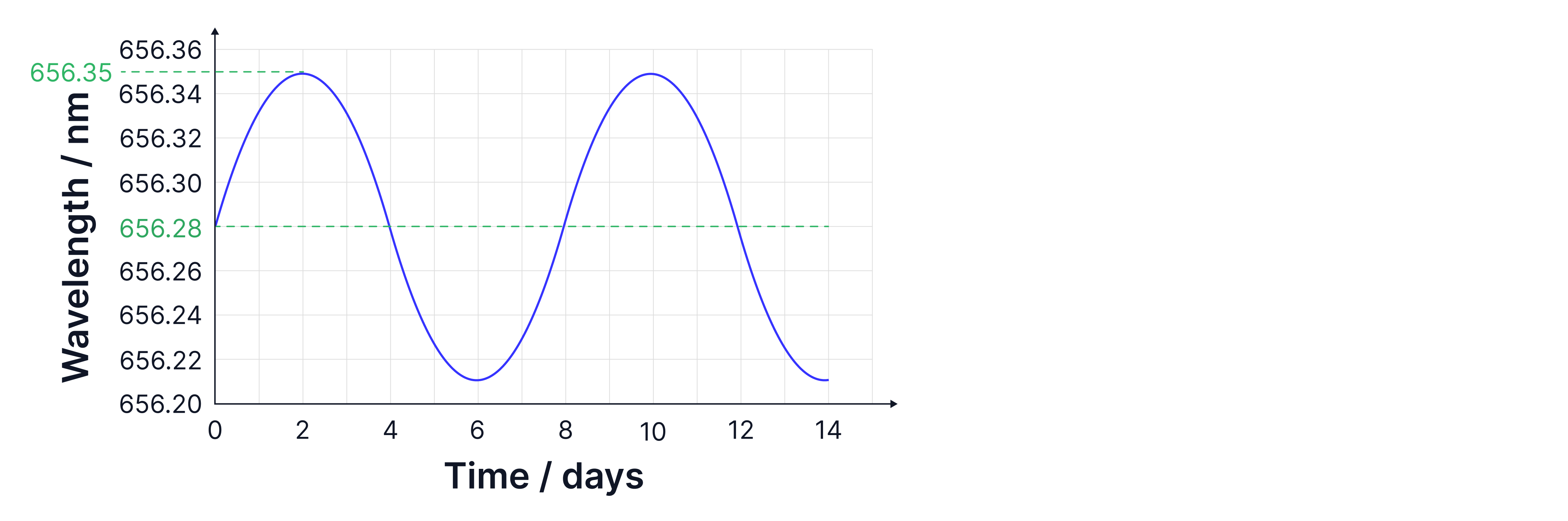
represents the wavelength emitted from the star when it is at rest /observed in the lab. The graph below illustrates the motion of the star as it moves towards us, resulting in blueshifted wavelengths, shorter wavelengths, and when it moves away from us, it exhibits redshifted wavelengths, longer wavelengths. The time for a full orbit is shown as 8 days.
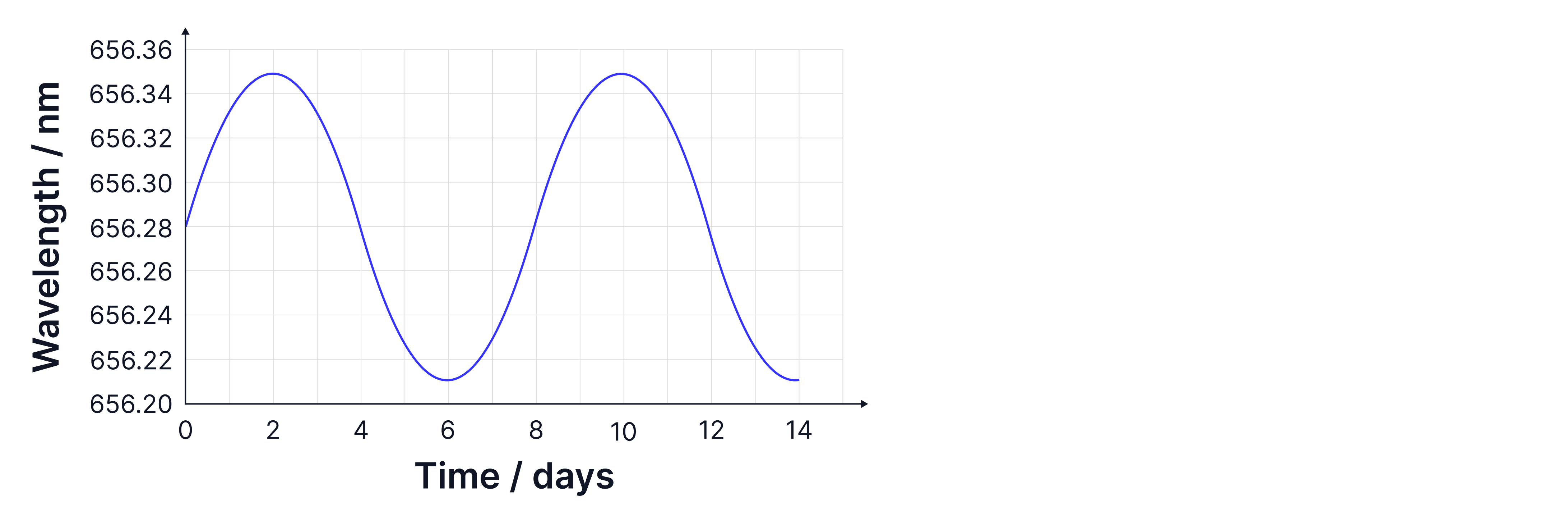
Here, the rest wavelength is the average of the redshifted and blueshifted wavelengths, and the change in wavelength is the change in wavelength from one extreme compared to the rest wavelength.
Practice Questions
Sketch the light curve for a Type 1a supernova.
Distances to Type 1a supernovae are known. How do we use them to determine Hubble's constant?
-> Check out Brook's video explanation for more help
Answer:
Sketch of absolute magnitude against time in days, peaking at abs at day and lasting around days.
Using their spectra, we can determine their redshift and thus their recessional velocity. We can then plot a graph of velocity against distance to determine Hubble's constant.
The redshift of a quasar is . It is away.
Estimate the age of the universe.
-> Check out Brook's video explanation for more help
Answer: