Scalars & Vectors
Brook Edgar
Teacher

Explainer Video
Scalars & Vectors
Scalar quantities have magnitude only, whereas vector quantities have both magnitude and direction.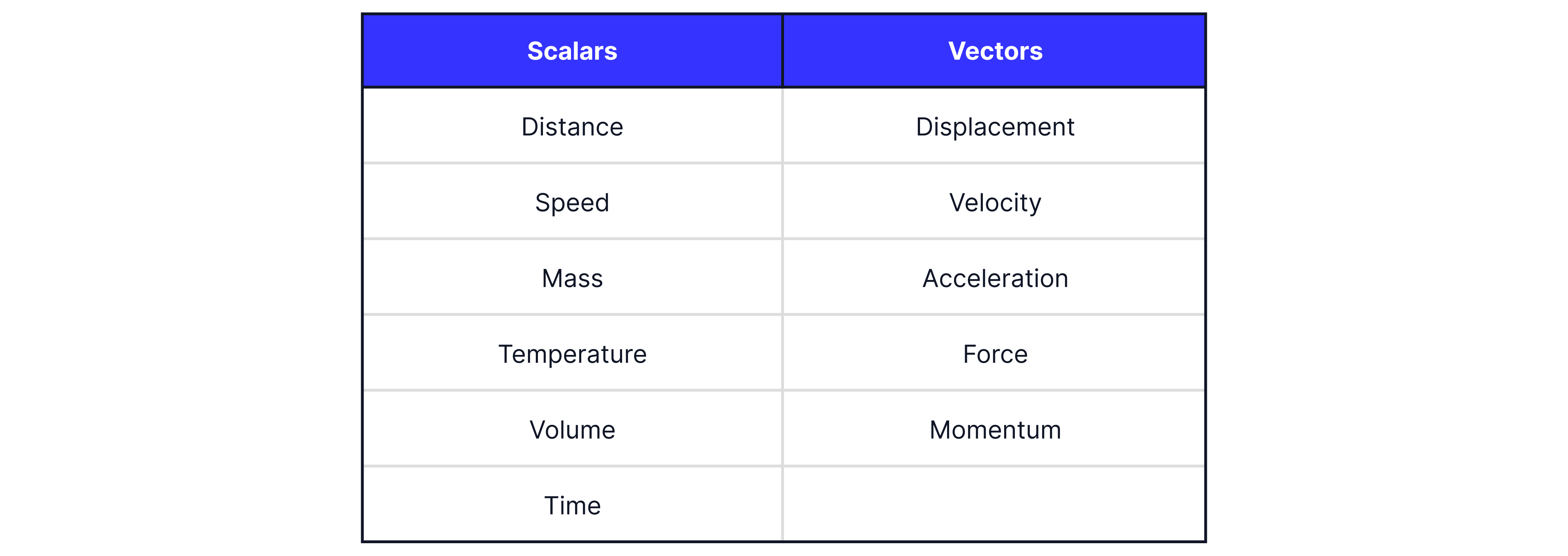
Speed
Speed is the rate of change of distance; it is a scalar.
Formula:
Remember: Units in A-level Physics need to be written in index form -> =
Velocity
Velocity is the rate of change of displacement; it is a vector as it has both magnitude and direction.
Formula:
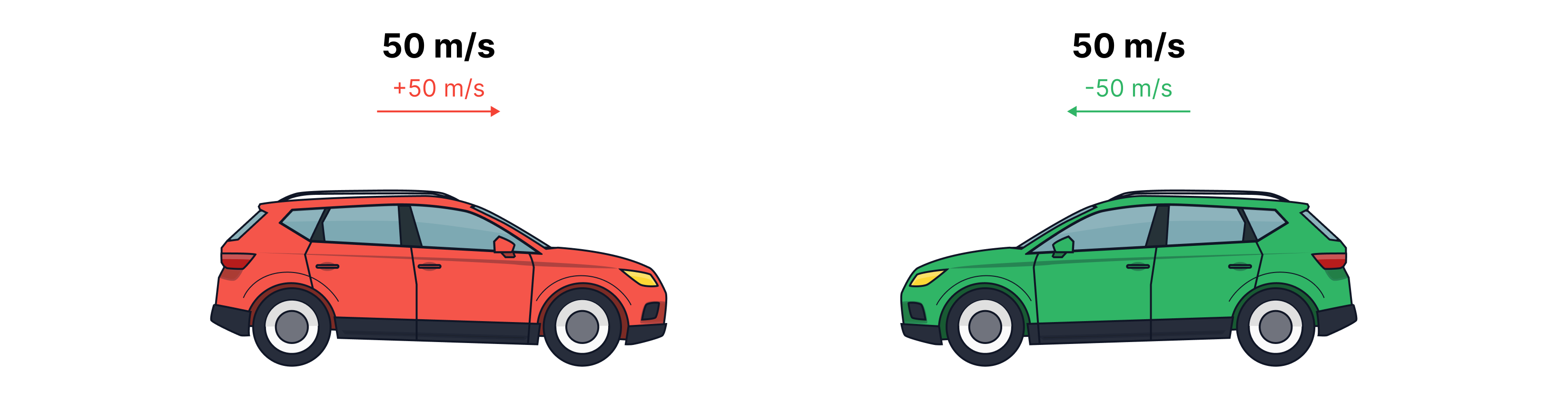
Two moving objects can have the same speed but different velocities as they are travelling in different directions.

Other scalars include: distance, energy, mass, and time.
Other vectors include: weight, momentum, acceleration, force, and displacement.
Worked Example
An athlete runs from the start to the position shown on the track.
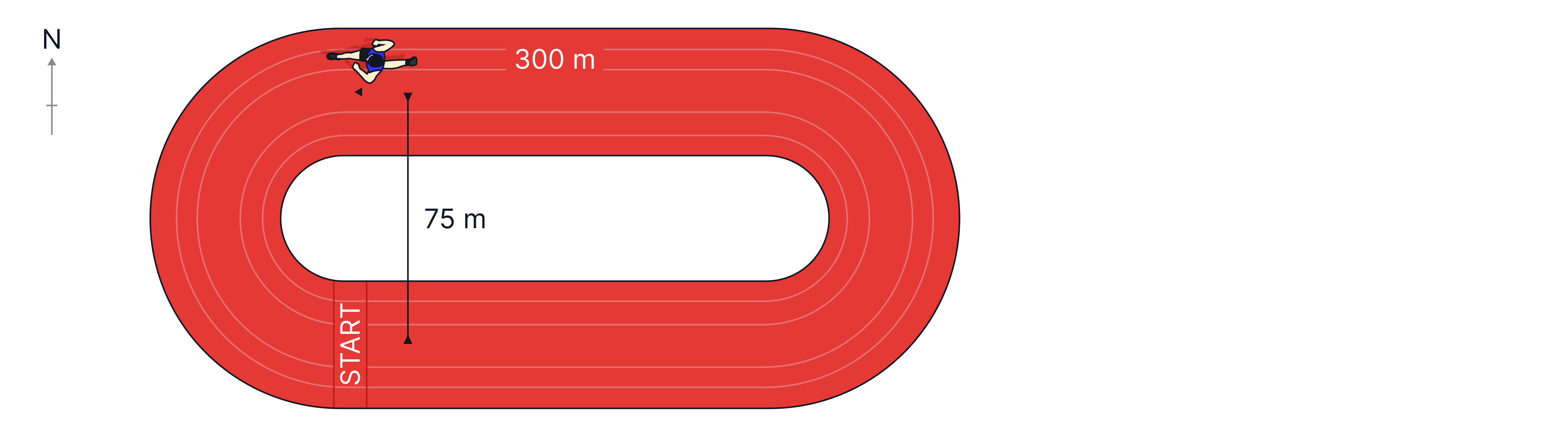
Calculate the distance travelled by the athlete.
State the displacement of the athlete.
If it took the girl half a minute to run , calculate her average speed.
Answer:
Distance =
Displacement = North
Teacher Tips: In question 1, distance is a scalar, so the question is asking for the total distance travelled by the athlete. In question 2, displacement is a vector, so the question is asking how far the runner has ended up relative to their starting position. They are to the North of where they started.
Acceleration
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity.
Formula:
Remember: In the alphabet, u comes before v; therefore, u is always the initial velocity (first in the alphabet), and v is the final velocity (second in the alphabet).
t u v w x y z
Worked Example
A man riding his bike accelerates from rest at a rate of .
If he does this for minute, what is his velocity?
He then continues at this speed for hours. Calculate the distance travelled in this time.
He stops suddenly. It took him seconds to come to rest. Calculate his acceleration.
Answer:
Practice Questions
Define Velocity
Answer:
Velocity is the rate of change of displacement.
Define Acceleration
Answer:
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity.
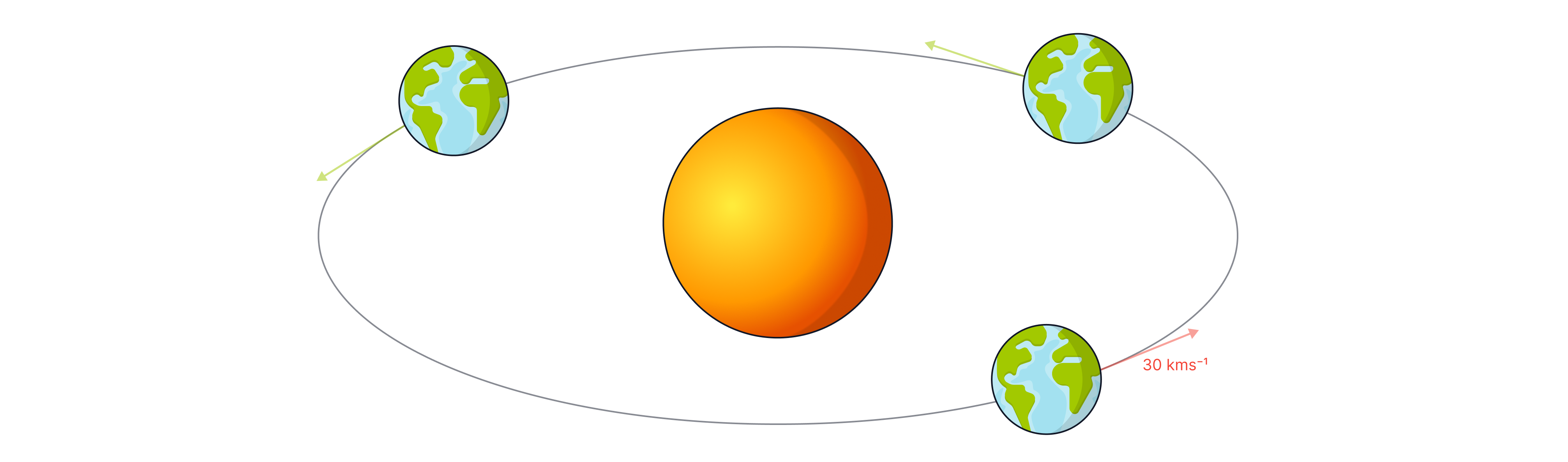
The Earth orbits the Sun at a constant velocity of .
Explain what is wrong with the sentence.
Answer:
The Earth orbits the Sun at a constant speed of .
Velocity is a vector that includes direction. The direction of motion of the Earth is constantly changing (at a tangent to the circle), so the velocity is not constant.
Complete the table below.
-> Check out Brook's video explanation for more help.
Vector or Scalar | SI Unit | |
|---|---|---|
Force | ||
Displacement | ||
Kinetic energy | ||
Power |
Vector or Scalar | SI Unit | |
|---|---|---|
Force | Vector | |
Displacement | Vector | |
Kinetic energy | Scalar | |
Power | Scalar |