Units
Brook Edgar & Hannah Shuter
Teacher


Explainer Video
SI Units
An SI unit is an abbreviation of the French word Système International. The International System Of Units (SI) is used universally as a standard for measurements. An SI base unit is a fundamental unit that is defined arbitrarily and not by combinations of other units. There are seven SI base units you need to know:
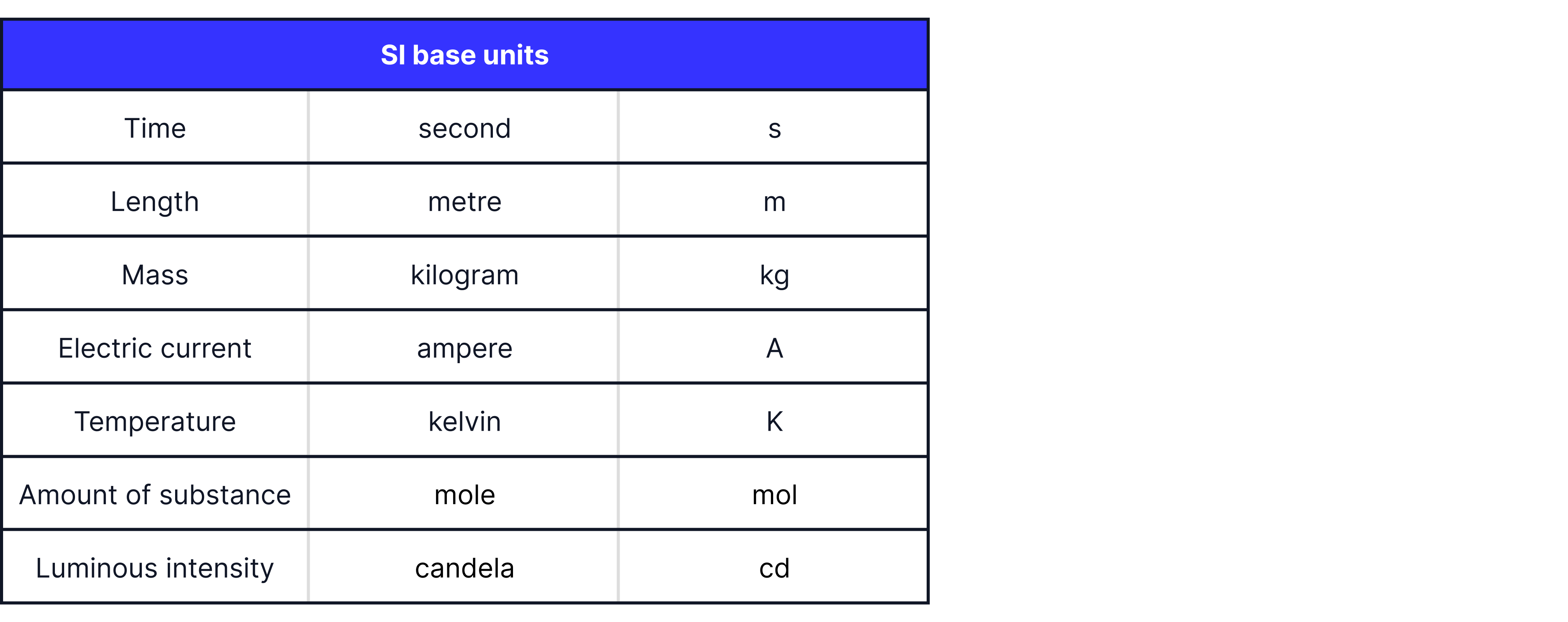
You need to know how to write other units in terms of their SI base units.
For example, if we want to write the SI base units for energy, we want to use an equation that allows us to easily convert the standard unit of joule into its SI base units. The best equation for this is the work done equation, as work done is another way to define energy.
Metre is an SI base unit, but newton is not, so we need to use another equation to define the newton.
Therefore:
Remember: When multiplying indices with the same base, you add the indices -> When dividing indices with the same base, you subtract the indices ->
Worked Example:
Which row has the fundamental units correctly matched to the physical quantity?
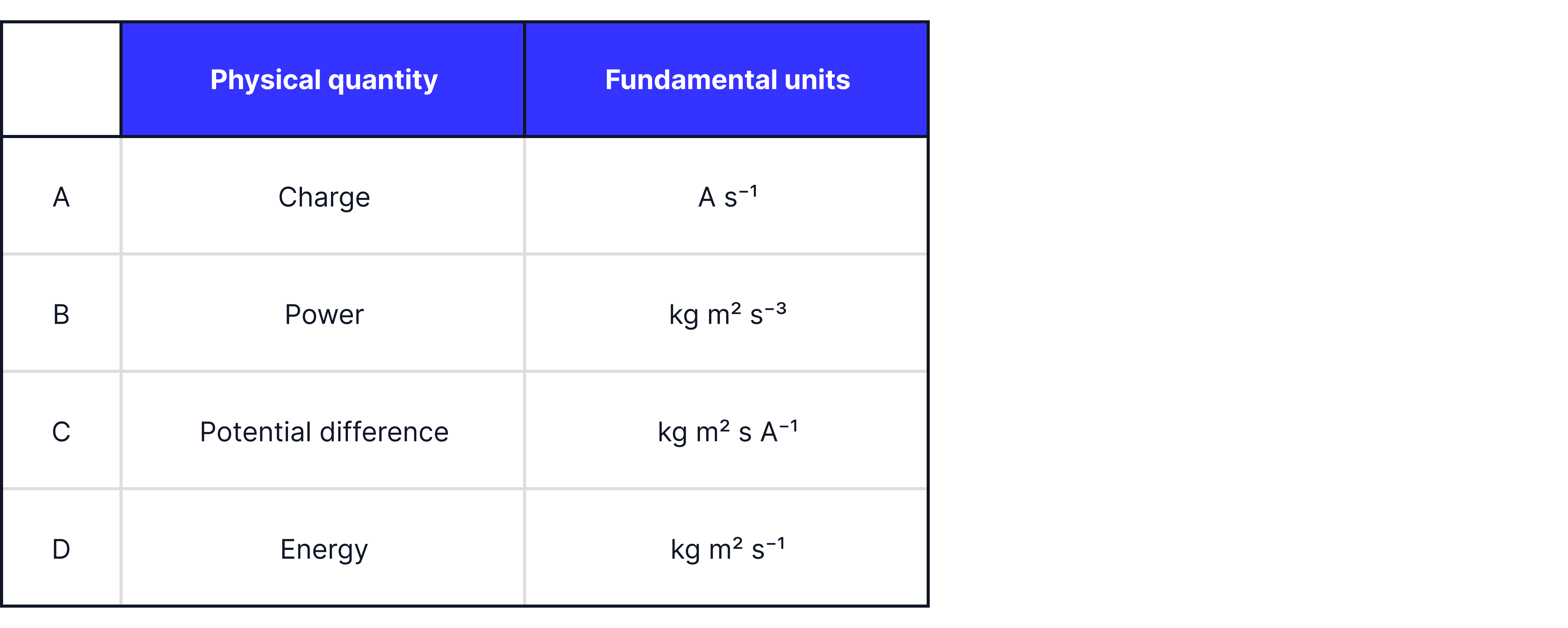
Answer:
It is not option A as the unit for charge written in terms of its SI base units would be:
It is option B as:
Joule, J, is not a fundamental unit, so we need to use another equation to write J, in terms of its SI base units -> :
Newton, N, is not an SI base unit, so we need to use another equation -> :
It is not answer C as potential difference in terms of its SI base units would be:
It is not answer D as energy in terms of its SI base units, as solved before is:
Prefixes
To save time and space, units are often expressed with prefixes.
From GCSE, you already know that is and that , which can be written as is . There are many more that are used throughout A-level physics that you need to memorise:
Worked Example:
Sort the below from largest to smallest:
1. Micrometre
2. Gigametre
3. Kilometre
4. Nanometre
5. Picometre
6. Femtometre
7. Megametre
8. Centimetre
9. Terametre
10. Millimetre
Answer:
Terametre
Gigametre
Megametre
Kilometre
Centimetre
Millimetre
Micrometre
Nanometre
Picometre
Femtometre
Worked Example:
Which row gives a distance travelled of ?
| Speed | Journey time |
A | ||
B | ||
C | ||
D |
Answer:
Practice Questions
Write and in terms of SI base units.
-> Check out Brook's video explanation for more help.
Answer:
Write the standard units of the following quantities in terms of their SI base units.
Magnetic flux density, which has the unit Tesla
, which has the unit Volts
-> Check out Brook's video explanation for more help.
Answer:
Which row gives SI prefixes in descending order of magnitude?
-> Check out Brook's video explanation for more help.
Answer:
Which of the following are SI base units?
-> Check out Brook's video explanation for more help.
Answer: