Gas Exchange in the Alveoli
Laura Armstrong & Joe Wolfensohn
Teachers


Recall Questions
This topic requires prior knowledge of diffusion to understand how oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged efficiently.
How does increasing surface area affect the rate of diffusion?
It Increases the rate of diffusion
State an example of a substance that diffuses into cells.
Oxygen / Glucose / Amino acids
Why are exchange surfaces 1 cell thick?
To reduce the diffusion distance, to increase the rate of diffusion
Topic Explainer Video
Check out this @JoeDoesBiology video that explains gas exchange in the alveoli, then read the study notes. Once you’ve gone through them, don’t forget to try the practice questions!
Gas Exchange in the Alveoli
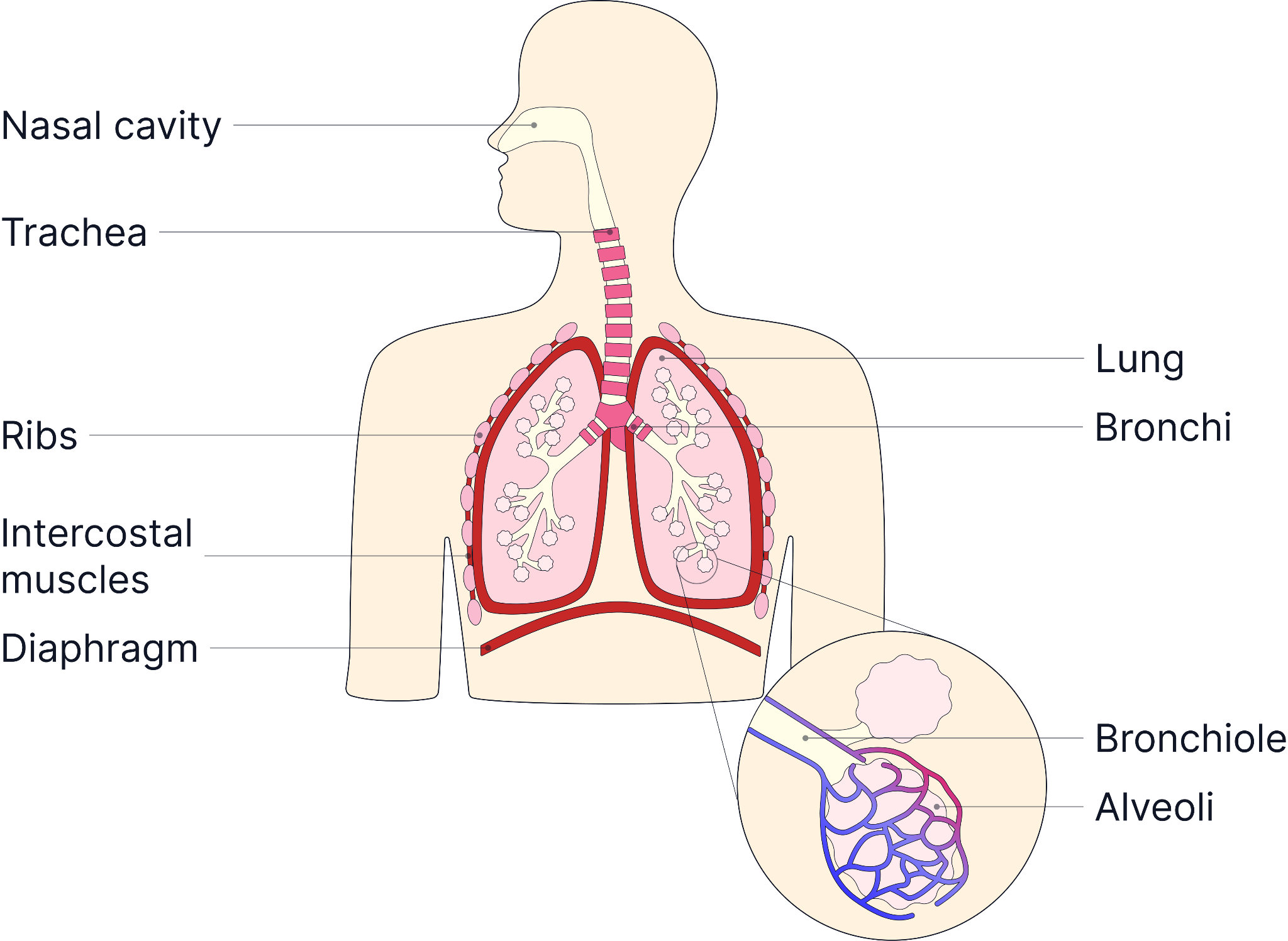
What are Alveoli?
- Alveoli are tiny (0.2mm) air sacs in the lungs.
- They are the site of gas exchange between the air and the blood.
- Found at the ends of bronchioles in clusters.
- There are millions of alveoli in the lungs.
Gases Involved in Exchange
- Oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into the blood.
- Carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the alveoli to be exhaled.
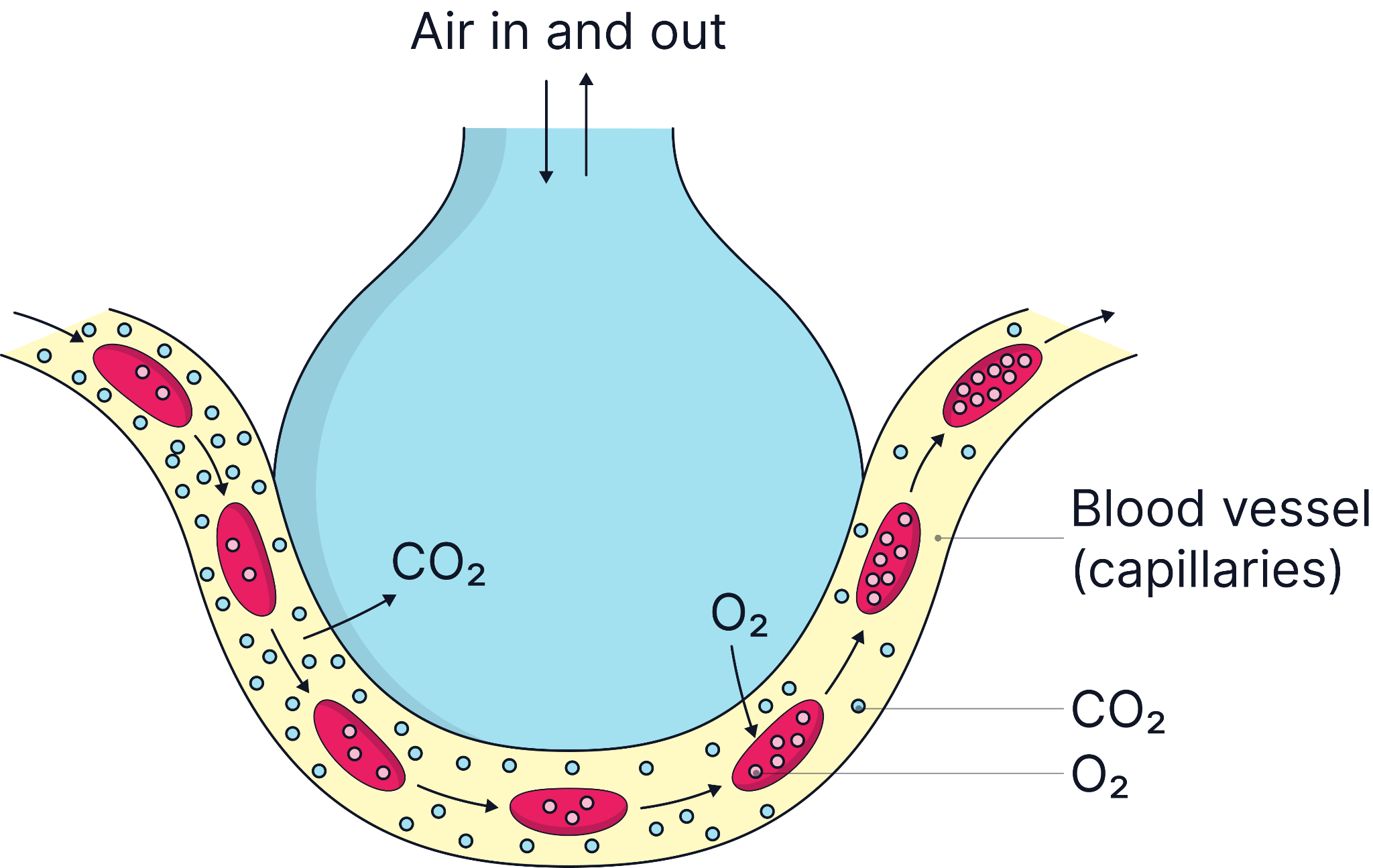
Adaptations of the Alveoli (to maximise diffusion)
|
Adaptation |
Explanation |
|
Large surface area |
Millions of alveoli provide a huge surface area for diffusion. |
|
Thin walls |
Walls are one cell thick, reducing the diffusion distance. |
|
Good blood supply |
Maintains a steep concentration gradient for oxygen and carbon dioxide with constant blood flow. For example, blood moving into the capillary will be deoxygenated, so there will always be a higher concentration of oxygen in the air in the alveolus than in the blood. |
|
Continuous ventilation |
Breathing in fresh air means there will always be air with a higher concentration of oxygen in the alveoli than in the blood, maintaining a steep concentration gradient for oxygen. |
Key Terms
- Alveolus (plural: alveoli) – tiny air sac in the lungs.
- Diffusion – net movement of particles from a higher to a lower concentration.
- Capillary – small blood vessels surrounding alveoli.
- Ventilation – movement of air in and out of the lungs.
Exam Tips
- Link the factors that affect the rate of diffusion to the adaptations of the alveoli.
- Do not say the alveoli are thin, it is the walls of the alveoli which are thin!
Practice Question
Explain how the alveoli are adapted to maximise gas exchange. (3 marks)
- Alveoli have a large surface area to increase diffusion.
- The walls are 1 cell thick, reducing the diffusion distance.
- A rich blood supply maintains a steep concentration gradient for oxygen / carbon dioxide.
More Practice
Try to answer these practice questions from the TikTok videos on your own, then watch the videos to see how well you did!