Triple Science Only - Protein Synthesis (Higher Tier)
Laura Armstrong
Teacher

Contents
Recall Questions
This topic requires prior knowledge of DNA Structure.
Which base pairs with adenine (A) in DNA?
Thymine (T)
What are the components of a DNA nucleotide?
A sugar, a phosphate group, and a base (A, T, C, or G)
How do we describe the overall structure of DNA?
A double helix.
Topic Explainer Video
Check out this @lauradoesbiology video that explains protein synthesis, then read the study notes. Once you’ve gone through them, don’t forget to try the practice questions!
Protein Synthesis
What is Protein Synthesis?
Protein synthesis is the process by which cells make proteins, following instructions carried in DNA.
- DNA is found in the nucleus.
- The order of bases in DNA determines the order of amino acids in a protein.
- Three bases in DNA code for one amino acid.
- Proteins are made by joining amino acids in the correct order at the ribosomes.
Step-by-Step: Protein Synthesis
1. Template Made
- DNA remains in the nucleus.
- A template (a copy of the gene) is made and moves out of the nucleus to the ribosome in the cytoplasm.
2. Amino Acids Brought to Ribosome
- Carrier molecules bring specific amino acids to the ribosome.
- Each carrier molecule matches a section of the template to ensure the amino acids are joined in the correct order.
3. Chain of Amino Acids Assembled
- The ribosome joins the amino acids together to form a protein chain.
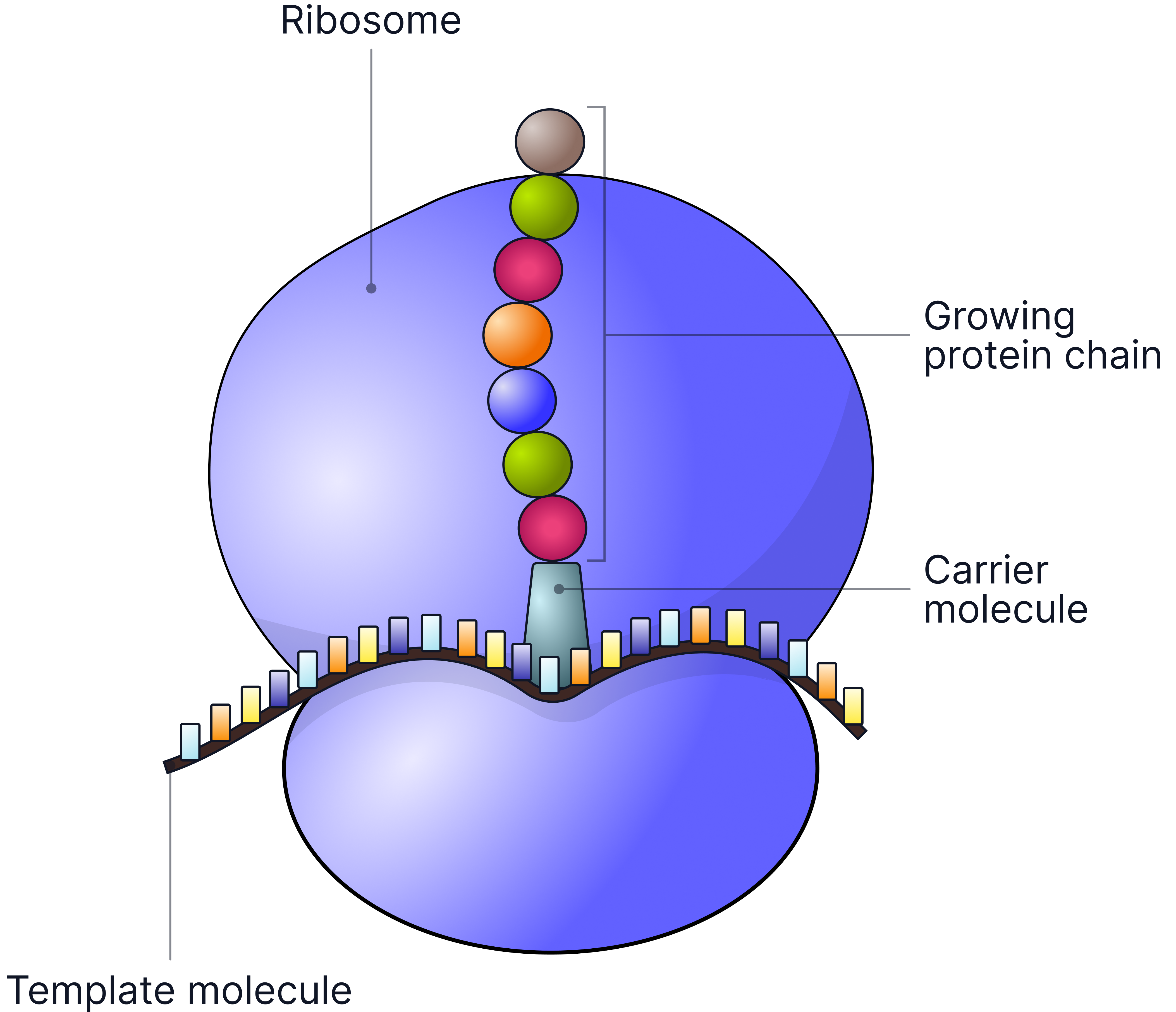
4. Protein Folding
- The chain folds into a unique 3D shape, allowing the protein to perform its specific function, e.g. as:
- An enzyme
- A hormone
- A structural protein (e.g., collagen)
How DNA Structure Affects the Protein
- The order of bases in DNA determines the order of amino acids in a protein.
- Each triplet of bases codes for one amino acid.
- A change (mutation) in the DNA base sequence can:
- Change the order of amino acids in a protein.
- Affect the overall shape of the protein.
- Change or stop the protein’s function.
Key Terms & Definitions
|
Term |
Definition |
|---|---|
|
Protein synthesis |
The process of making proteins using instructions from DNA. |
|
Gene |
A short section of DNA that codes for the order of amino acids in a protein. |
|
Template |
A copy of a gene that leaves the nucleus to guide protein synthesis. |
|
Carrier molecule |
Molecule that brings the correct amino acid to the ribosome. |
Exam Tip
For Higher Tier, focus on sequence → shape → function:
- The DNA base sequence determines the amino acid order in a protein.
- This affects the folding and therefore the shape and function of the protein.
- If the order of amino acids is not correct, the shape of the protein will be different and the protein may not be able to function. For example, the shape of an enzymes active site may be different and it will not be able to bind to its substrate.
Practice Question
Explain how a change in the DNA base sequence could lead to a change in the structure and function of a protein. (4 marks)
Model Answer:
- The DNA base sequence determines the order of amino acids in a protein.
- A change in the base sequence (a mutation) may change the sequence of amino acids.
- This can alter the way the protein folds, changing its shape.
- If the shape changes, the protein may not function properly, e.g. an enzymes active site may no longer bind to its substrate, or a hormone may not longer be able to bind to its receptor.
More Practice
Try to answer these practice questions from the TikTok videos on your own, then watch the videos to see how well you did!