Triple Science Only - Required Practical- Rate Of Decay
Laura Armstrong & Joe Wolfensohn
Teachers


Recall Questions
This topic requires prior knowledge of the conditions affecting microbial activity and how to measure rates of biological processes.
What is decay in biology?
Decay is the breakdown of organic material by microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi.
What conditions affect the rate of decay?
Temperature, water availability, and oxygen availability.
What are lipid molecules broken down into?
Glycerol and fatty acids.
Topic Explainer Video
Check out this @JoeDoesGCSEBiology video that explains the required practical- rate of decay, then read the study notes. Once you’ve gone through them, don’t forget to try the practice questions!
Investigating Rate of Decay (pH change in milk)
Aim
- To investigate how temperature affects the rate of decay of fresh milk by observing the change in pH.
Method Overview
- Set up several test tubes or boiling tubes containing fresh milk mixed with a pH indicator (such as cresol red or phenolphthalein).
- Add a small quantity of lipase enzyme to each tube to speed up decay.
- Place the tubes in water baths at different temperatures (e.g. 5°C, 20°C, 35°C, 50°C).
- Record how long it takes for the pH to drop (indicated by colour change of the pH indicator). A pH probe could also be used for a more accurate and continuous measurement.
- Repeat and take a mean time for each temperature.
- Calculate rate of decay using the formula: Rate = 1 / time taken.
Variables
|
Type |
Variable |
|
Independent |
Temperature of the milk (controlled using water baths) |
|
Dependent |
Time taken for milk to decay (pH to drop) |
|
Control |
Volume of milk, volume of lipase, same pH indicator, type of milk (eg. full fat) |
You could also investigate other independent variables, such as: the type of milk or the volume of milk.
Why Measure pH?
- As milk decays, bacteria break down lipids and release fatty acids. Fatty acids are acidic and therefore will lower the pH. The more fatty acids produced, the lower the pH will become.
- A faster pH drop = faster decay.
- Eventually the pH will stop changing. This is most likely because all the lipids have been digested and therefore the reaction has stopped. But it is possible that the change in pH has also caused the lipase enzymes to denature.
Results & Interpretation
- You would expect the fastest pH change (and highest decay rate) at around 35–40°C.
- At low or high temperatures, the rate of decay will be slower:
- Too cold: enzyme activity is slow.
- Too hot: enzymes denature.
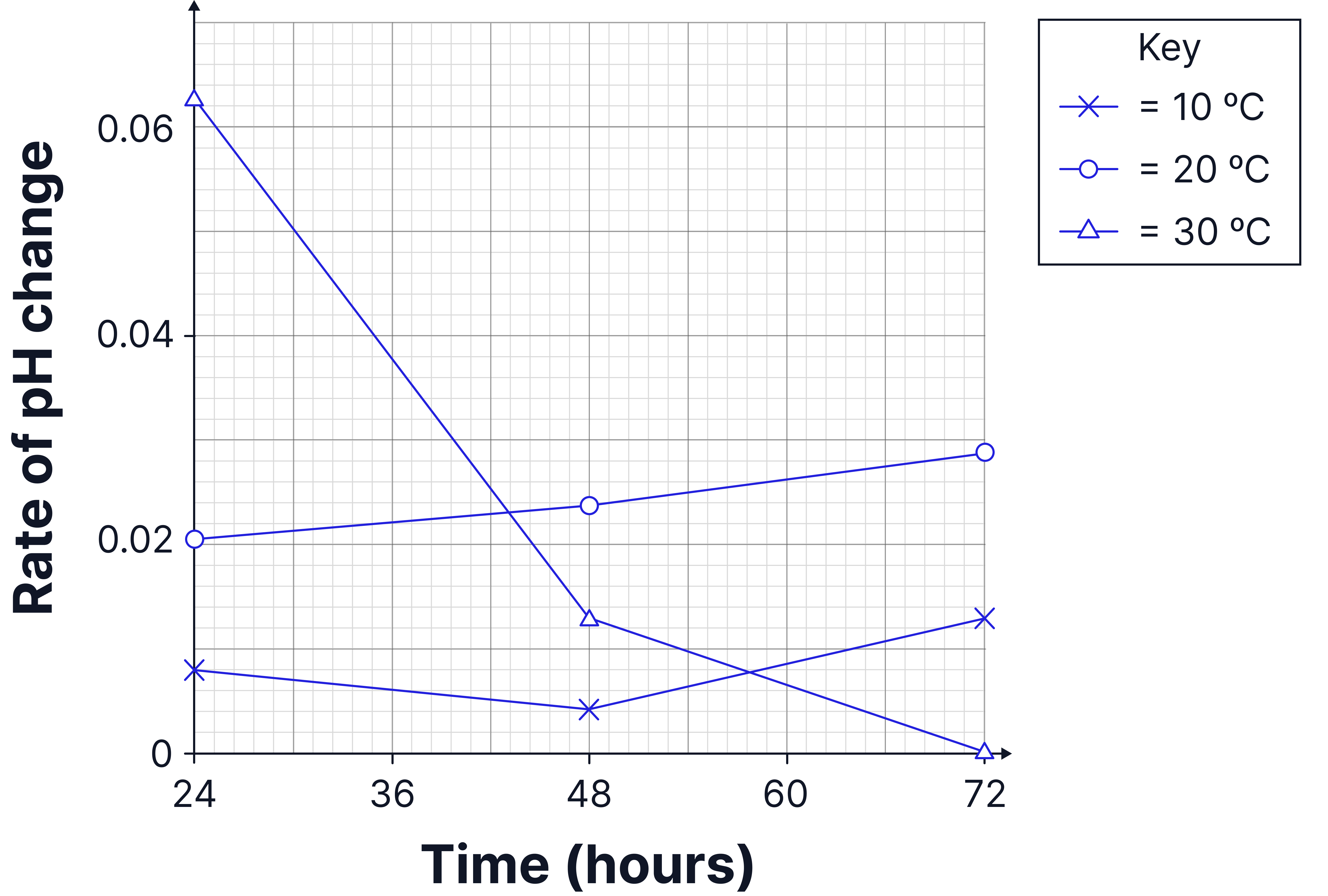
The rate of decay can also be calculated from the graph.
For example: Calculate the rate of decay at 30°C in the first 48 hours.
Rate = change in y / change in x
Rate = 0.063 - 0.013 / 48
Rate = 0.001 units / hour.
Key Terms and Definitions
Decay - The breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms.
pH indicator - A chemical that changes colour depending on pH (used to detect acid production).
Rate of decay - How quickly organic material is broken down.
Exam Tip:
- Questions on this practical may also link to your knowledge of bile. If bile were added to the milk this would emulsify the lipids, increasing their surface area. This would speed up the breakdown of the lipids by enzymes and increase the rate of decay even further.
Practice Questions
A student investigated the effect of temperature on the rate of milk decay. The colour of the pH indicator changed from purple to yellow. The student found the rate of decay increased up to 45°C then decreased.
Explain why temperature affects the rate of decay. (4 marks)
Model Answer:
- Decay is carried out using enzymes (in microorganisms).
- Higher temperatures increase the kinetic energy of the enzymes.
- This increases enzyme activity up to an optimum, speeding up decay.
- Above the optimum temperature, enzymes denature and the rate of decay decreases.
More Practice
Try to answer these practice questions from the TikTok videos on your own, then watch the videos to see how well you did!