Triple Science Only - The Role Of Biotechnology
Laura Armstrong & Joe Wolfensohn
Teachers


Contents
Recall Questions
This topic requires prior knowledge of genetic modification and enzymes in biological processes.
What is meant by genetic modification?
Changing the DNA of an organism to give it new characteristics.
Which biological molecules act as catalysts in living organisms?
Enzymes.
What are the reactants for aerobic respiration?
Glucose and oxygen.
Topic Explainer Video
Check out this @JoeDoesGCSEBiology video that explains the role of biotechnology, then read the study notes. Once you’ve gone through them, don’t forget to try the practice questions!
The Role of Biotechnology
Modern biotechnology helps solve global challenges, such as:
- Feeding a growing population.
- Producing medical treatments.
- Reducing the environmental impact of farming.
1. Mycoprotein – Food from Fungi
- Mycoprotein is a high-protein, low-fat meat substitute.
- It is produced using the fungus Fusarium.
- The fungus is grown in aerobic conditions (with oxygen) in large fermenters.
- It is fed a glucose syrup as an energy source to be used in aerobic respiration.
- After growth, the biomass is harvested, purified, and dried into mycoprotein.
- It is used in vegetarian products like Quorn.
- The mycoprotein can be produced anywhere and is very energy efficient.
- The conditions inside the fermenter are ideal for the growth of microorganisms.
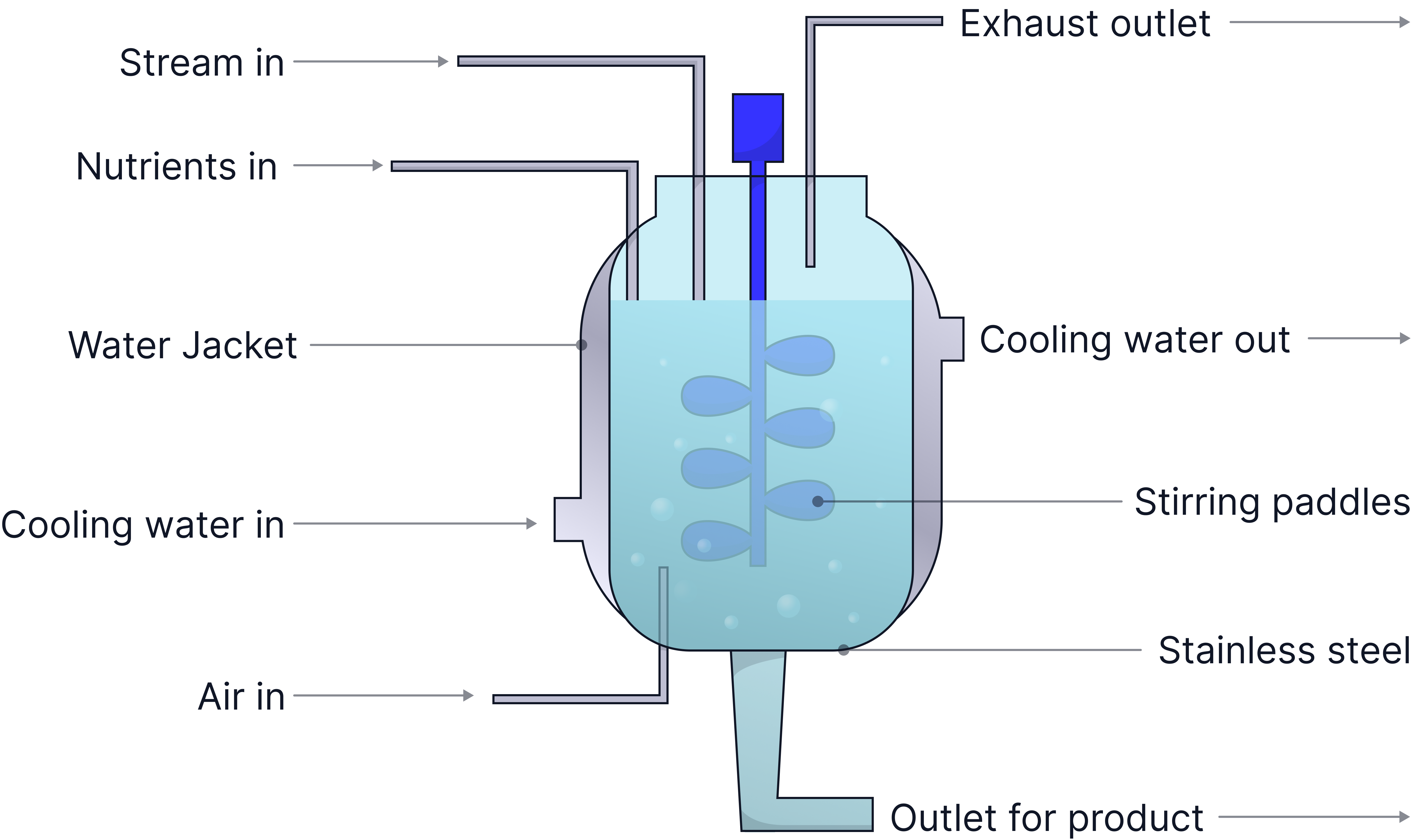
A fermenter used to produce microorganisms.
The fermenter is sterilised before use using hot steam. This will kill any microorganisms that would compete with the growing fungus for oxygen and glucose and lead to contamination.
The cooling water jacket will prevent the fermenter from overheating and help to maintain a constant temperature inside the fermenter.
The stirring paddles will help to distribute glucose and oxygen evenly throughout the fermenter as well as making sure the temperature is constant and even.
Air containing oxygen is pumped in to provide the growing fungus with oxygen for aerobic respiration.
Nutrients, including glucose are added for aerobic respiration.
Benefits of mycoprotein
- Mycoprotein is suitable for vegetarians.
- It is cheaper than getting food from farming animals.
- It is quicker than getting food from farming animals.
- It requires less space / land than farming animals.
- No animals are killed to produce the food.
- Mycoprotein is lower in fat than some meat.
- Mycoprotein is lower in calories than some meat.
2. Genetically Modified Bacteria – Producing Insulin
- Human insulin is needed by people with Type 1 diabetes.
- A gene for human insulin is inserted into a bacterium using genetic engineering.
- The bacteria are cultured in fermenters and produce insulin as they grow.
- The insulin is harvested and purified for medical use.
- This method is cheaper, faster, and more ethical than using animal insulin (e.g. from pigs).
3. GM Crops – Feeding the World
- Genetically modified (GM) crops can be altered to:
- Grow in harsh climates.
- Resist pests and disease.
- Produce higher yields.
- Contain improved nutritional content (e.g. Golden Rice, which contains lots of vitamin A).
- GM crops are seen as a way to increase global food supply, but some people have concerns about the long term effect on human health.
Key Terms & Definition
- Biotechnology - The use of organisms or biological systems to make useful products.
- Mycoprotein - Protein-rich food produced from fungi, used as a meat alternative.
- GM crops - Crops genetically engineered to have beneficial traits like higher yield.
Exam Tip:
- Make sure you can describe how mycoprotein is produced using a fermenter and the advantages of getting food from mycoprotein instead of from farming animals.
Practice Question
Describe how mycoprotein is produced. (4 marks)
Model Answer:
- Mycoprotein is made from the fungus Fusarium.
- The fungus is grown in fermenters with oxygen (aerobic conditions).
- It is fed glucose syrup as an energy source.
- The biomass is harvested and purified to make mycoprotein.
More Practice
Try to answer the practice question from the TikTok video on your own, then watch the video to see how well you did!