The Water Cycle
Laura Armstrong
Teacher

Contents
Recall Questions
This topic requires prior knowledge of transpiration and evaporation.
What is evaporation?
A change of state from a liquid to a gas, such as when liquid water changes into water vapour (gas) due to heating.
What is transpiration?
The loss of water vapour from plant leaves through tiny holes called stomata.
Topic Explainer Video
Check out this @lauradoesGCSEbiology video that explains the water cycle, then read the study notes. Once you’ve gone through them, don’t forget to try the practice questions!
The Water Cycle
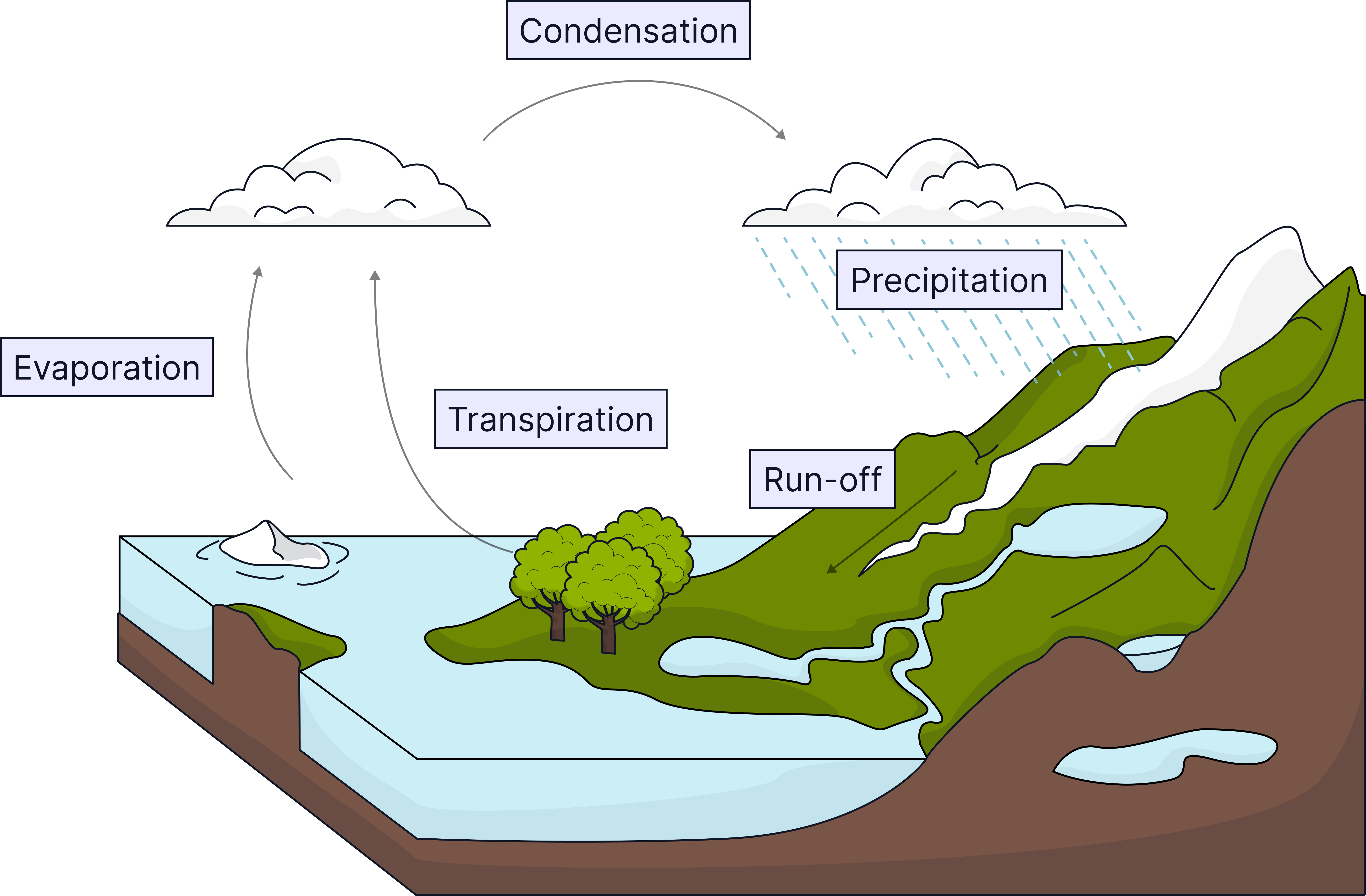
What is the Water Cycle?
- The water cycle recycles water between the land, sea, and atmosphere.
- It provides fresh water for plants and animals on land.
- Water is constantly evaporating, condensing, and falling as precipitation.
Key Processes in the Water Cycle
1. Evaporation:
- Energy from the Sun heats water in rivers, lakes, and oceans.
The water evaporates, changing from a liquid to water vapour in the air.
2. Condensation:
- Water vapour cools as it rises and condenses into clouds (tiny water droplets).
3. Precipitation:
- Water droplets in clouds grow and fall as rain, snow or hail, returning water to the ground.
4. Transpiration:
- Plants take up water from the soil through their roots via osmosis.
Water moves up through the plant in the xylem vessels and evaporates from the leaves, mainly via the stomata.
This loss of water vapour is called transpiration.
5. Run-off and infiltration:
- Water runs off the surface of the land - for example, soil, hills, fields, and hard surfaces like roads.
Run-off water flows into rivers, streams, and lakes.
Some water soaks into the ground (this is called infiltration) and becomes groundwater, which plants can use or which can feed into rivers later.
Why Is the Water Cycle Important?
- It makes sure fresh water is always available for plants, animals, and humans.
- It helps plants grow by pulling water up the xylem vessels from roots to leaves.
- It links to other cycles like the carbon cycle, as plants need water for photosynthesis as well as carbon dioxide.
Key Terms & Definitions
- Evaporation - When liquid water changes into water vapour (gas).
- Transpiration - Loss of water vapour from plant leaves, mainly via stomata.
- Condensation - When water vapour cools and changes back to liquid droplets.
- Precipitation - Water falling from clouds as rain, snow, sleet, or hail.
- Run-off - Water flowing over the ground into rivers, lakes or oceans.
Exam Tip:
- Use key words like evaporation, transpiration, condensation, precipitation and run-off.
Practice Question
Name the five processes shown on the diagram (5 marks)
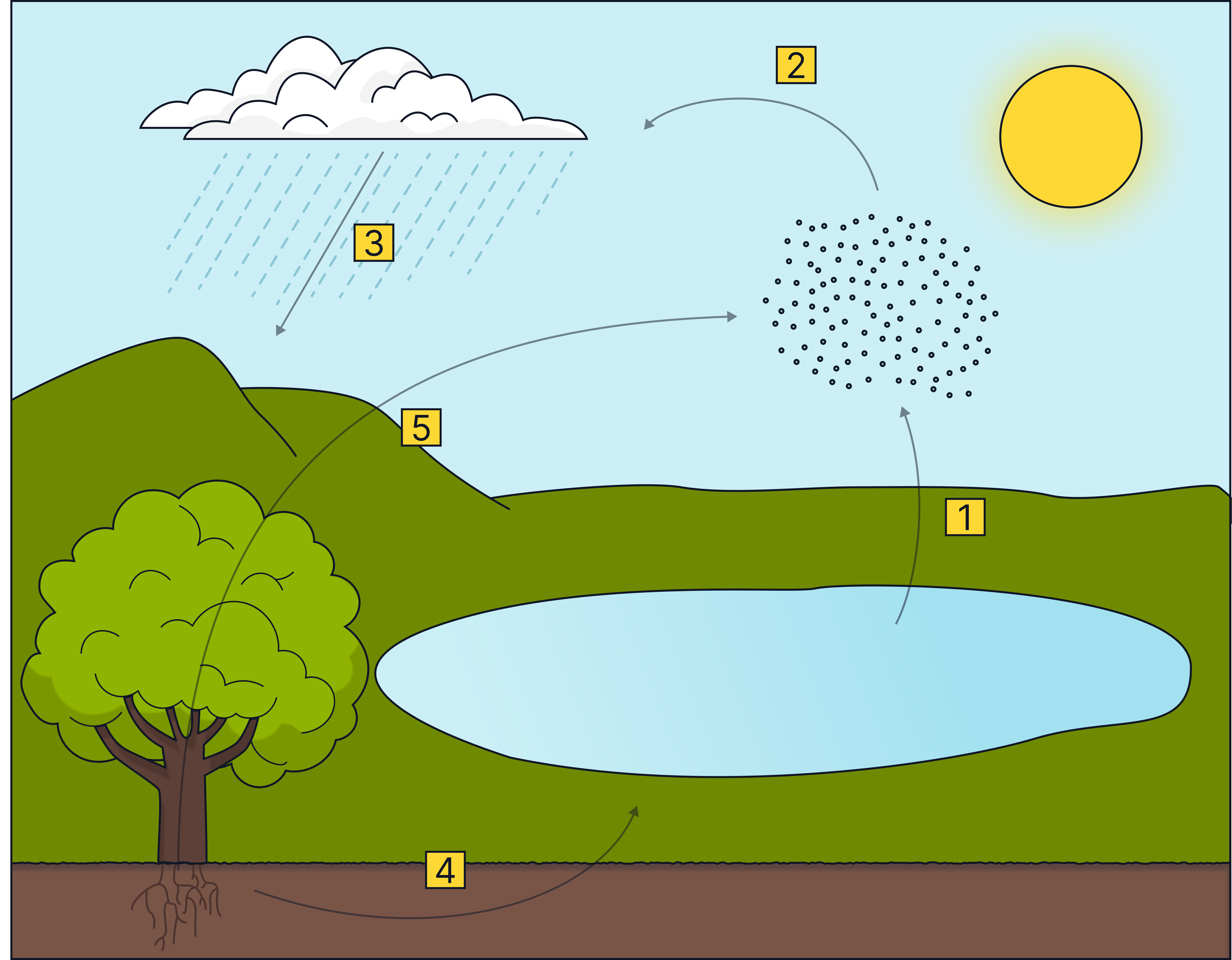
Model Answer:
1. Evaporation
2. Condensation
3. Precipitation
4. Run-off / infiltration / percolation
5. Transpiration
More Practice
Try to answer the practice question from the TikTok video on your own, then watch the video to see how well you did!