Triple Science Only - Uses of Monoclonal Antibodies (Higher Tier)
Laura Armstrong & Joe Wolfensohn
Teachers


Contents
Recall Questions
This topic requires prior knowledge of how monoclonal antibodies are produced and how the immune system recognises specific antigens.
What is a monoclonal antibody?
A monoclonal antibody is an antibody produced from a single clone of white blood cells that binds to one specific antigen.
What is the role of an antibody in the immune system?
Antibodies bind to specific antigens on pathogens to help destroy them.
How are monoclonal antibodies produced?
They are produced by fusing a mouse lymphocyte with a tumour cell to create a hybridoma. The hybridoma will divide by mitosis forming many clones that produce identical antibodies.
Topic Explainer Video
Check out this @JoeDoesBiology video that explains the uses of monoclonal antibodies, then read the study notes. Once you’ve gone through them, don’t forget to try the practice questions!
Uses of Monoclonal Antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies are highly specific, meaning they will only bind to one specific antigen. This makes them incredibly useful in medicine and research.
Diagnostic Uses
- Pregnancy Tests: Monoclonal antibodies detect the hormones in a woman’s urine, indicating pregnancy.
- Blood Tests: They can measure hormone levels (e.g. insulin or thyroid hormones) and detect pathogens like viruses or bacteria by testing for the antigens.
- Research: Used to locate or identify specific molecules in cells or tissues by binding to them and attaching a fluorescent dye for visibility under a microscope.
How does a pregnancy test work?
Pregnant women produce the hormone HCG.
HCG is excreted in urine and so can be detected using a pregnancy test.
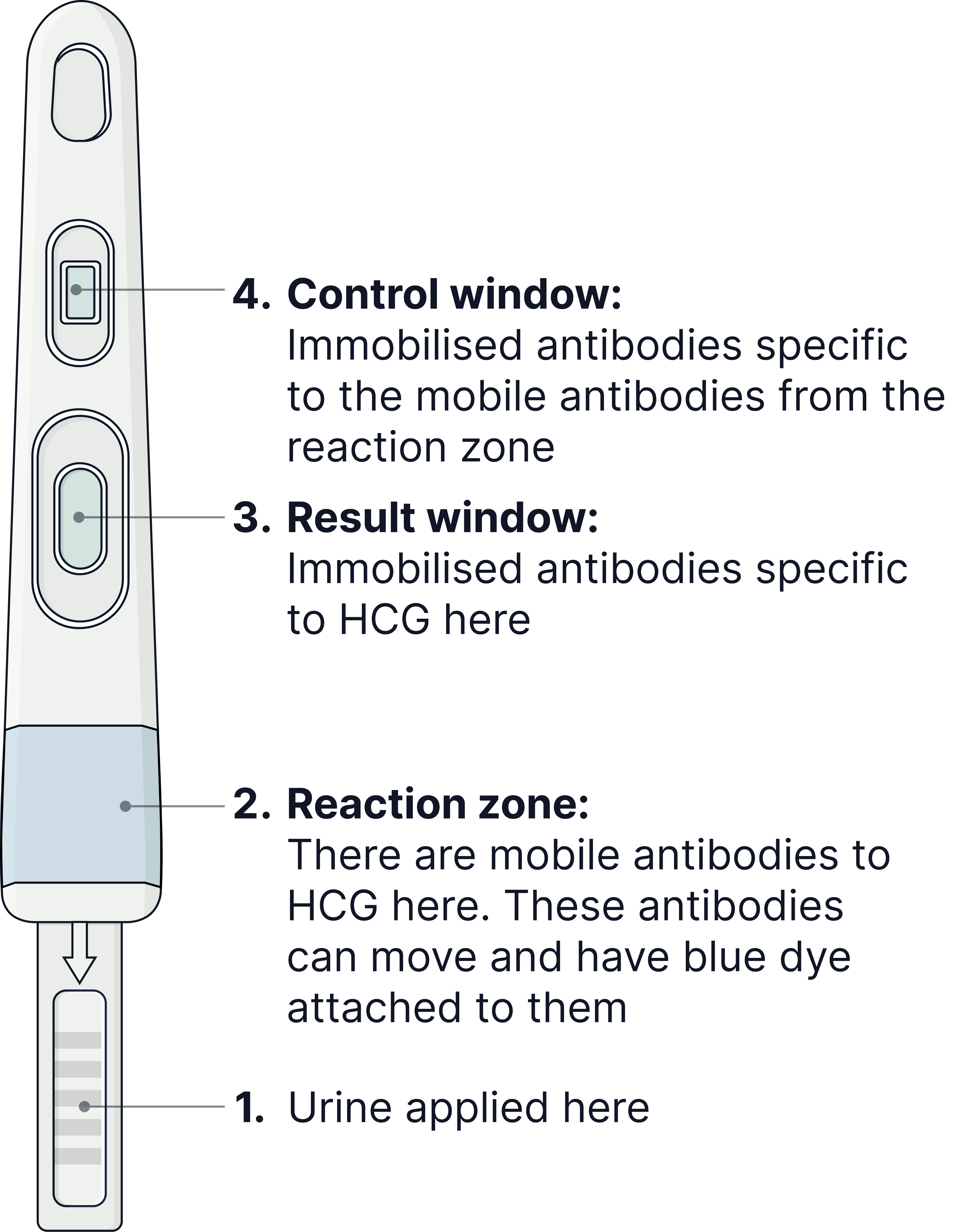
- Urine passes through the reaction zone.
- The HCG hormone (if present in the woman's urine) binds to the mobile HCG antibodies that are present in the reaction zone.
- The mobile antibodies with HCG attached continue to pass up the pregnancy test stick and into the results zone.
In the results zone the HCG hormone binds to the immobilised HCG antibodies. - Other mobile antibodies that did not have HCG attached will bind to immobilised antibodies in the control zone.
Blue dye appears in both control and results zones to show a positive result.
Note- if the test is negative (as there was no HCG hormone in the urine) mobile antibodies will only be able to bind to antibodies in the control zone. Only one blue line in the control zone will be seen.
Therapeutic Uses
- Cancer Treatment:
- Monoclonal antibodies can be designed to bind only to cancer cell antigens.
- They are combined with a radioactive substance, toxic drug, or chemical that kills the cancer cell.
- This allows for targeted treatment, killing only cancerous cells while leaving healthy cells unharmed.
Ethical, Social, and Scientific Considerations
- Monoclonal antibodies were expected to be a ‘miracle treatment’, but they have not become as widely used as hoped. Production can be complex and costly.
- Side effects have been greater than expected in some patients.
- Ethical issues may arise, particularly around the use of animals (mice) to produce the original antibodies.
Key Terms and Definitions
|
Key Term |
Definition |
|
Monoclonal antibody |
Identical antibodies that bind to one specific antigen. |
|
Antigen |
A molecule on a pathogen that triggers an immune response. |
|
Hybridoma |
A fused cell made from a lymphocyte and a tumour cell. |
|
Targeted therapy |
Treatment aimed specifically at diseased cells, e.g. cancer, using antibodies. |
Exam Tip
You do not need to memorise the names of specific tests or treatments but should be able to explain how monoclonal antibodies work if provided with information.
Practice Question
Explain how monoclonal antibodies can be used to treat cancer. (4 marks)
Model Answer:
- Monoclonal antibodies are made to bind to specific antigens found on cancer cells.
- A toxic drug or radioactive substance is attached to the antibody.
- The monoclonal antibody binds to the antigens on the surface of the cancer cell and delivers the substance directly to the cancer cell.
- This kills the cancer cells without affecting healthy cells nearby.
More Practice
Try to answer these practice questions from the TikTok videos on your own, then watch the videos to see how well you did!