Blood vessels
Laura Armstrong
Teacher

Contents
Recall Questions
This topic requires prior knowledge of the overall structure of the circulatory system and the function of different vessel types from GCSE.You can test your knowledge on these below.
Name the three main types of blood vessels.
Arteries, veins, capillaries.
Describe the structure of the heart.
-
The heart has four chambers: two atria and two ventricles.
-
The right side pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs, while the left side pumps oxygenated blood to the body.
-
Valves prevent backflow of blood.
Topic Explainer Video
Check out this @LauraDoesBiology video that explains blood vessels or read the full notes below. Once you've gone through the whole note, try out the practice questions!
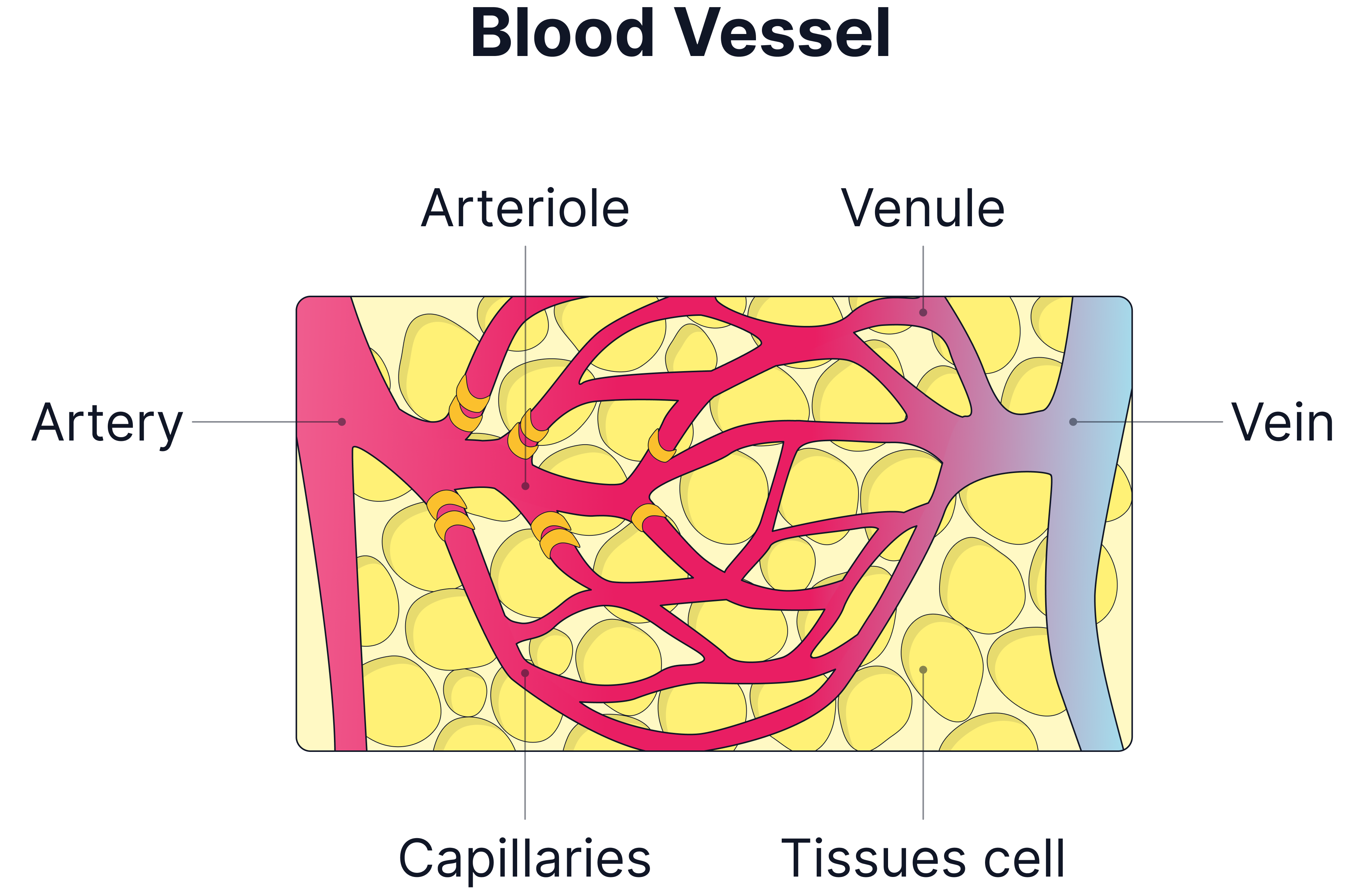
Types of Blood Vessels and Their Functions
Arteries
-
Carry oxygenated blood away from the heart (except the pulmonary artery which carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs).
-
Have thick muscular walls to withstand high pressure.
-
Contain many elastic fibres allowing them to stretch and recoil. They stretch when the ventricles contract and recoil when the ventricles relax to maintain blood pressure..
-
Narrow lumen also helps to maintains high pressure.
-
Smooth endothelium reduces friction for easier blood flow.
The aorta
The aorta is the artery with the highest blood pressure, this is because it is closest to the heart and connected to the left ventricle which contracts with the greatest force.
The aorta is an artery that does contain valves. The aortic valves are a type of semi-lunar valve found at the base of the aorta.
The fluctuations in pressure seen on the graph below represent the increase in pressure when the ventricles contract and the decrease in pressure when the ventricles relax. Pressure is maintained so there are no large surges by the stretch and recoil of elastic fibres in the blood vessel walls.

The pressure decreases in the blood vessels as you move further away from the heart and further from the contractions of the left ventricle.
The pressure also decreases as the cross-sectional area of the blood vessels increases as you get further from the heart.
Veins
-
Carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart (except the pulmonary vein which carries oxygenated blood from the lungs into the heart).
-
Have thin walls with less muscle and fewer elastic fibres as they carry blood under low pressure.
-
Contain valves to prevent backflow of blood.
-
Large lumen reduces resistance to blood flow.
-
Blood flow is assisted by skeletal muscle contraction.
-
Smooth endothelium reduces friction for easier blood flow.

Capillaries
-
Site of exchange of substances between blood and tissues.
-
One cell thick walls allow rapid diffusion. The wall is called the endothelium.
-
Small lumen ensures red blood cells are in close contact with the walls of the capillaries providing a short diffusion pathway for oxygen. It also means that blood travels slowly through a capillary, providing more time for exchange of substances to take place.
-
A large network increases surface area for diffusion and exchange of substances.

Role of Arterioles in Vasoconstriction and Vasodilation
-
Arterioles are small arteries that control blood flow to tissues.
-
Vasoconstriction: Smooth muscle in arteriole walls contracts, reducing lumen diameter and restricting blood flow to certain tissues.
-
Vasodilation: Smooth muscle relaxes, widening the lumen and increasing blood flow.
-
Helps regulate blood pressure and temperature (e.g., vasodilation of arterioles near to the skin’s surface increases heat loss via the skin in warm conditions).
Key Terms
-
Lumen: The central cavity of a blood vessel through which blood flows.
-
Vasoconstriction: Narrowing of blood vessels to reduce blood flow.
-
Vasodilation: Widening of blood vessels to increase blood flow.
Exam Tip
When describing adaptations, always link structure to function e.g., the capillary wall is a single layer of endothelium cells allowing efficient diffusion.
Explain how the structure of arteries is related to their function. (4 marks)
-
Thick muscular walls withstand high blood pressure.
-
Elastic fibres allow stretch and recoil, maintaining blood pressure and blood flow.
-
Narrow lumen maintains high pressure for efficient transport.
-
Smooth endothelium reduces friction for easier blood flow.
Practice Question 1
Try to answer the practice question from the TikTok on your own, then watch the video to see how well you did!
Practice Question 2
If you want to try out another one, check this video out and see how you do!