Resistivity
Brook Edgar
Teacher

Explainer Video
Resistivity
Resistivity is a property of a material. The lower the resistivity of a material, the lower the resistance of a component made from that material, and the better that component is able to conduct.
The resistance of a wire depends on the:
Length of the wire
Cross-sectional area of the wire
The material the wire is made of - its resistivity
Formula:
The resistivity of some common materials are shown below:
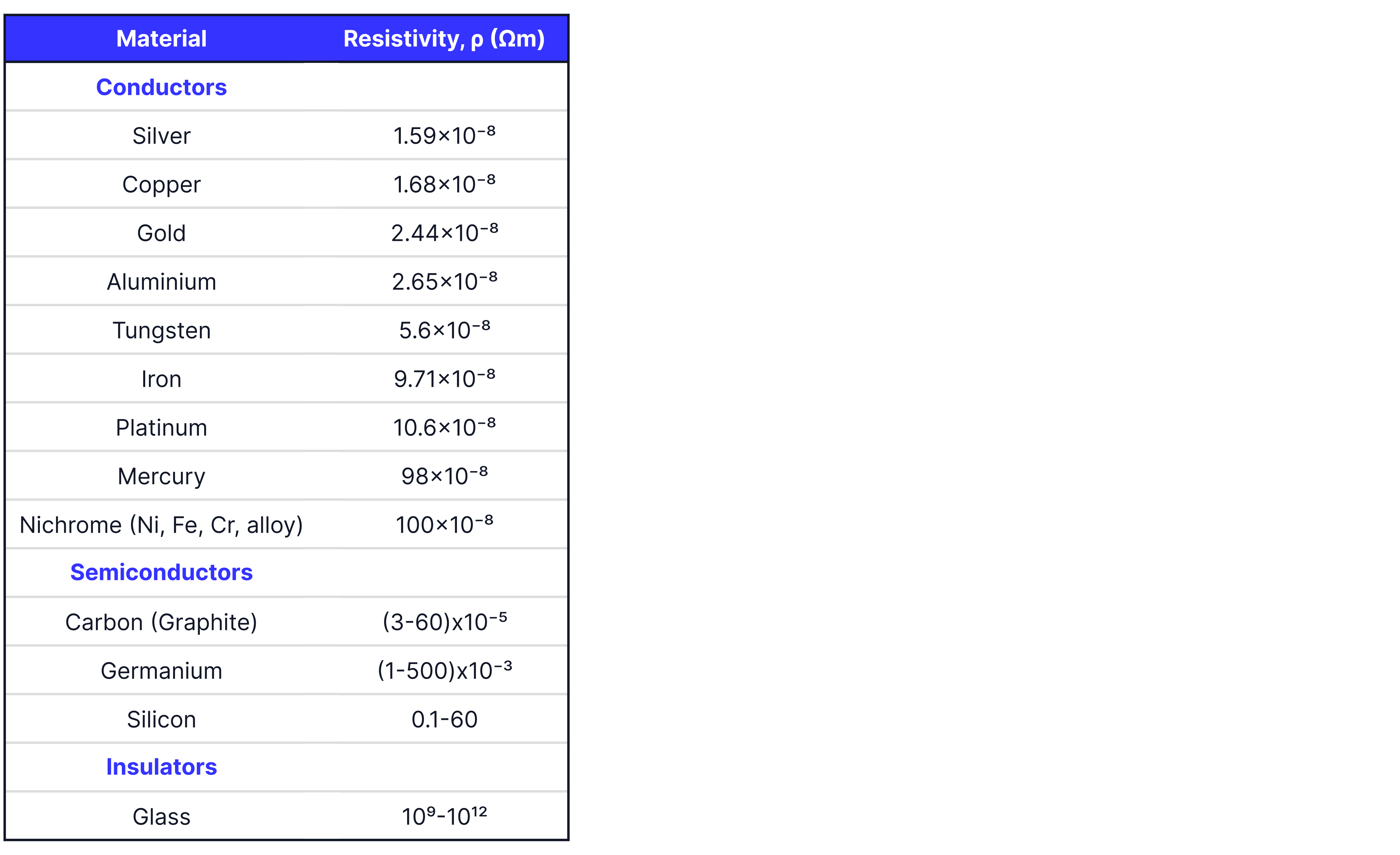
Modelled Example. To calculate the resistance of a piece of copper wire with a diameter of we need to know the resistivity of the wire. We can see from the table above that the resistivity of copper is .
Remember wires are cylindrical in shape, so their cross-sectional area is calculated as .
Worked Example
A pupil wants to make a resistor from a wire of length . The wire has a resistivity of . Calculate the required diameter of the wire.
Answer:
To find the diameter, we need to solve for the cross-sectional area first.
Superconductors
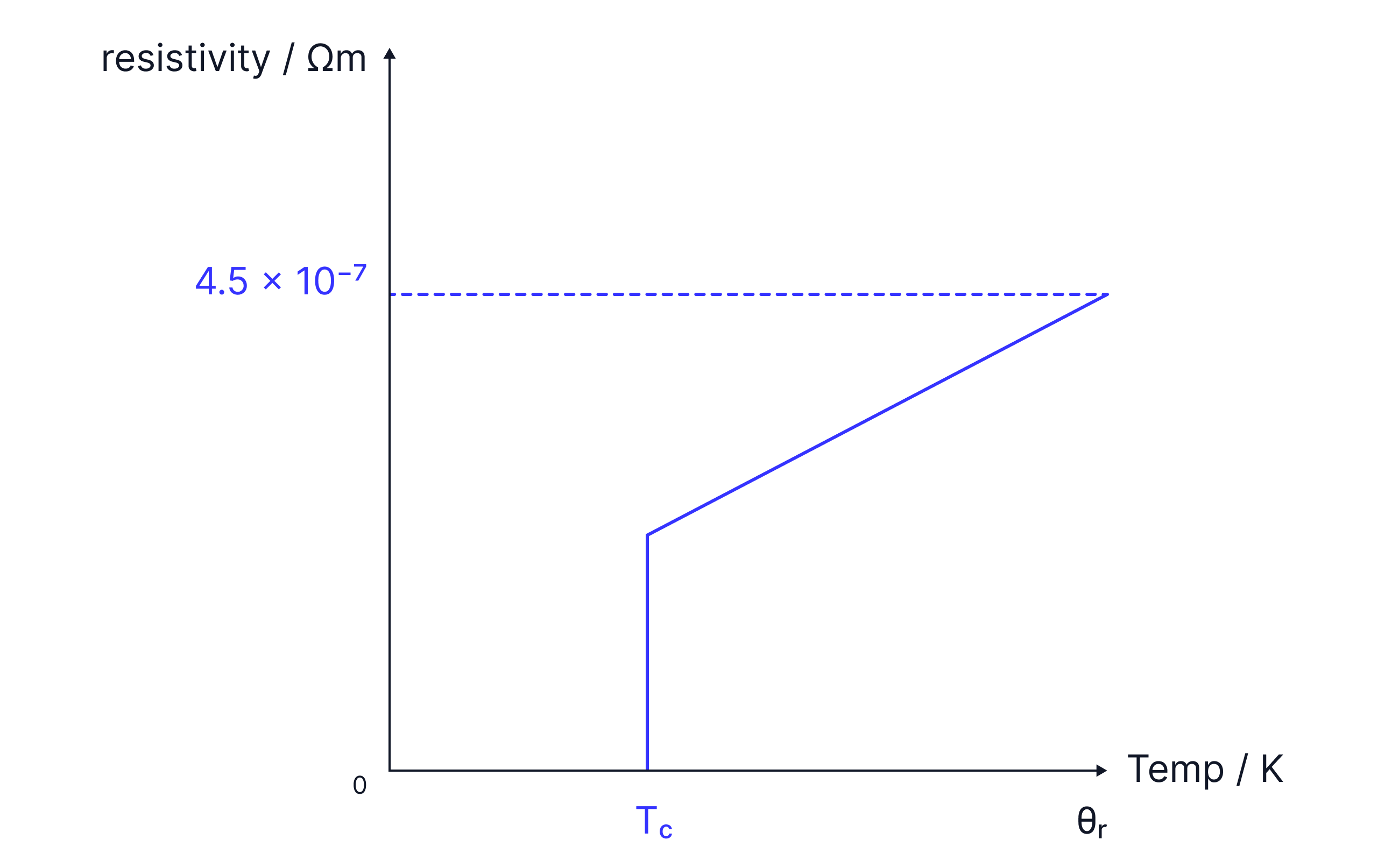
A superconductor is a material whose resistivity drops to zero when cooled to a temperature below the material’s critical temperature.
They are used in electromagnets that require high currents, such as those found in MRI machines, transformers, generators, and maglev trains.
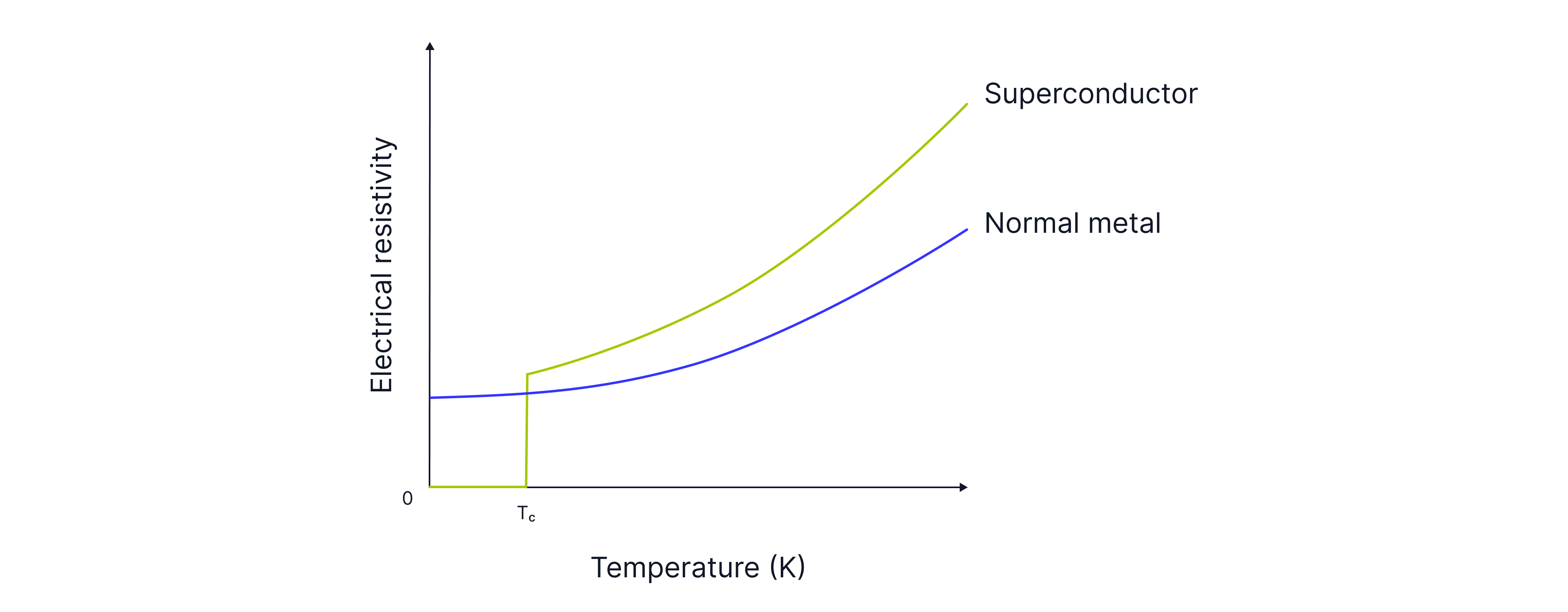
is the critical temperature. This is the point at which the resistivity of the material drops to .
Practice Questions
A resistor with resistance is made from a wire of resistivity and length . Which equation calculates the diameter of the wire?
-> Check out Brook's video explanation for more help.
Answer:
A rectangular metal bar, by and long, has a pd of across it and of current through it.
Find the resistivity of the material the metal bar is made from.
-> Check out Brook's video explanation for more help.
Answer:
The resistivity of the bar is .
At room temperature there is a wire that has a resistivity of . The radius of wire is .
Calculate the resistance of a length wire.
Calculate the power dissipated when the current is .
The wire becomes superconducting as cooled. Sketch a graph of resistivity against temperature for this wire. Use to represent room temperature.
-> Check out Brook's video explanation for more help.
Answer: