Blood Glucose Regulation
Laura Armstrong & Joe Wolfensohn
Teachers


Contents
Recall Questions
This topic requires prior knowledge of the endocrine system and negative feedback.
Which gland controls blood glucose levels?
The pancreas.
Which hormones regulate blood glucose levels?
Insulin and glucagon.
What is negative feedback?
Any change away from the normal level is detected and a response is initiated to reverse the change.
Topic Explainer Video
Check out this @JoeDoesBiology video that explains blood glucose regulation, then read the study notes. Once you’ve gone through them, don’t forget to try the practice questions!
Recap: Homeostasis & Negative Feedback
-
Homeostasis is the regulation of the internal conditions of a cell or organism to maintain optimum conditions for function in response to internal and external changes.
-
Homeostasis maintains optimal conditions for enzyme action and all cell functions.
-
Negative feedback is a process that reverses a change in conditions to bring them back to normal.
Blood Glucose Regulation
Why Control Blood Glucose Is Important:
-
Glucose is needed by all cells for respiration, which releases energy.
-
Too much glucose in the blood (hyperglycaemia) → water would leave cells by osmosis and they would shrivel and shrink.
-
Too little glucose (hypoglycaemia) → not enough glucose for respiration and therefore not energy released for cells.
-
The body must maintain a constant blood glucose level.
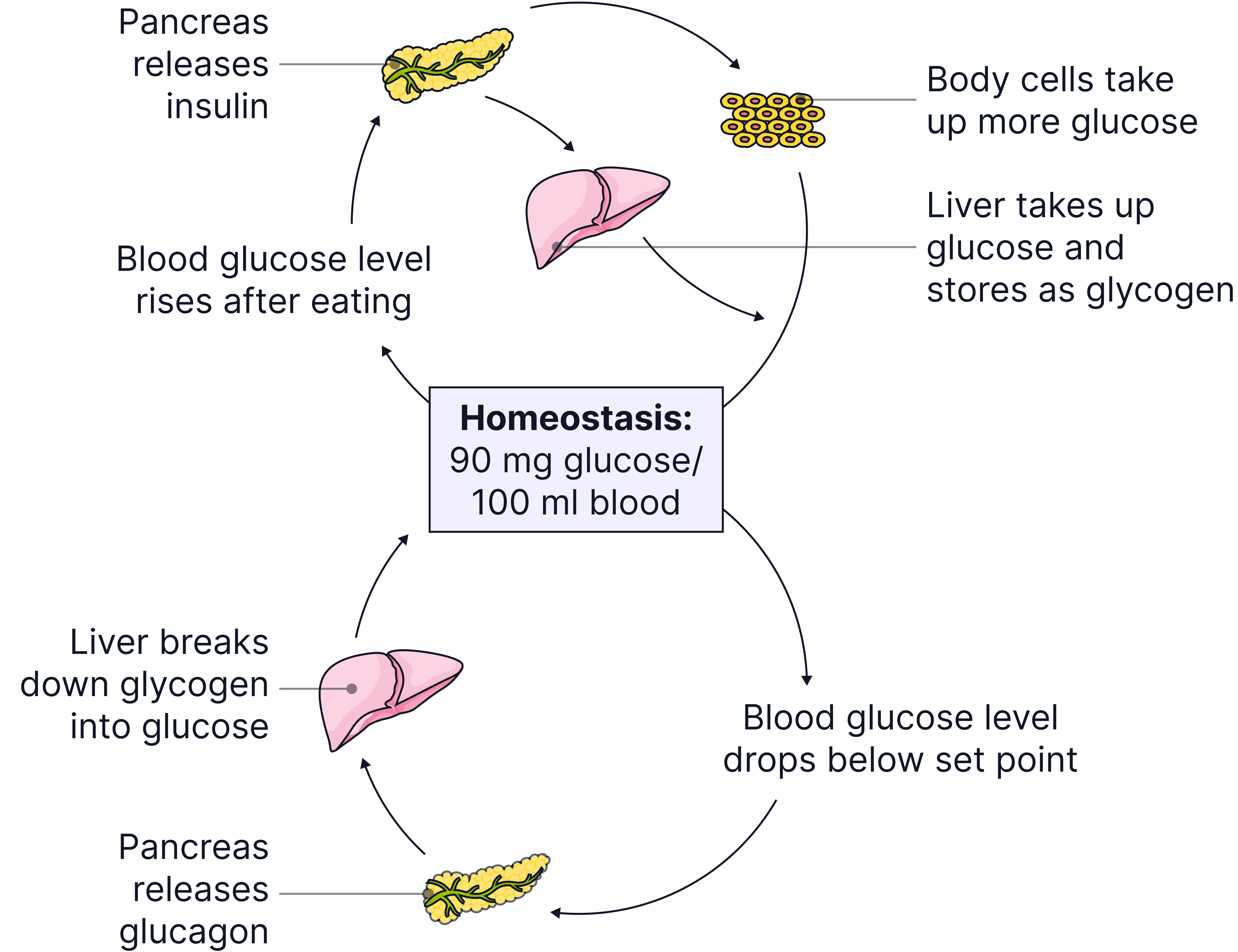
When Blood Glucose Rises:
-
After eating carbohydrates, glucose is absorbed into the blood via the small intestine.
-
The pancreas detects the rise and releases the hormone insulin.
-
Insulin causes:
-
Glucose to be taken up by cells.
-
Glucose to be stored in the liver and muscles as glycogen.
-
Blood glucose levels return to normal.
Higher Tier Only
When Blood Glucose Falls:
-
Between meals or after exercise, glucose levels drop.
-
The pancreas detects the fall and releases the hormone glucagon. (It stops releasing insulin).
-
Glucagon causes:
-
The liver to convert glycogen back into glucose.
-
Glucose diffuses back into the blood.
-
Blood glucose levels return to normal.
This is an example of a negative feedback loop – the body detects a change and triggers a response to restore the normal level.
Using a graph to explain changes in blood glucose concentration

-
Meal eaten- blood glucose remains stable as carbohydrates take time to be digested and glucose needs to be absorbed into the bloodstream.
-
Blood glucose concentration rises above normal as glucose is absorbed into the blood via the small intestine.
-
The pancreas is secreting insulin- this causes blood glucose concentration to fall as glucose moves into cells (where it is used for respiration) and is stored in the liver and muscles as glycogen.
-
Blood glucose concentration returns to normal.
-
Played hockey- blood glucose concentration falls below normal as muscles cells are using lots of glucose in respiration to release energy.
-
Higher tier only: The pancreas is secreting glucagon- this causes glycogen in the liver to be broken down into glucose. Glucose diffuses into the blood so blood glucose concentration rises back to normal.
Only higher tier students need to know about glucagon- but foundation tier students should be able to explain the effects of insulin.
Key Terms
-
Glucose: A sugar used for respiration.
-
Pancreas: Endocrine gland that releases insulin and glucagon.
-
Insulin: Hormone that lowers blood glucose.
-
Glucagon: Hormone that raises blood glucose.
-
Glycogen: Storage form of glucose in the liver and muscles.
Exam Tip
Don’t mix up glucagon and glycogen. Remember, glucagon is a hormone released by the pancreas when blood glucose falls. Glycogen is a storage form of glucose, stored in the liver and muscles.
Practice Question
Explain how blood glucose levels are controlled after a meal. (4 marks)
-
After a meal, blood glucose levels rise.
-
The pancreas detects the increase and secretes insulin.
-
Insulin causes cells to absorb glucose from the blood.
-
It also causes the liver / muscle cells to convert glucose into glycogen for storage, reducing blood glucose levels.
More Practice
Try to answer these practice questions from the TikTok videos on your own, then watch the videos to see how well you did!