Diabetes
Laura Armstrong & Joe Wolfensohn
Teachers


Recall Questions
This topic requires prior knowledge of blood glucose regulation.
What is the role of insulin in the body?
Insulin lowers blood glucose levels by helping cells absorb glucose and encouraging the liver and muscles to store it as glycogen.
Which organ detects changes in blood glucose and releases insulin?
The pancreas.
What hormone is released when blood glucose is too low?
Glucagon.
Topic Explainer Video
Check out this @JoeDoesBiology video that explains diabetes, then read the study notes. Once you’ve gone through them, don’t forget to try the practice questions!
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a condition where blood glucose levels cannot be properly controlled.
There are two different types of diabetes, known as type 1 and type 2.
Types of Diabetes
|
Feature |
Type 1 Diabetes |
Type 2 Diabetes |
|
Cause |
Pancreas produces little or no insulin. |
Body cells stop responding to insulin or are not sensitive to insulin. |
|
Onset |
Usually develops in childhood or adolescence. |
Usually develops in adults and linked to obesity. |
|
Blood glucose levels |
Become very high without treatment. |
Also become high, but not as suddenly. |
|
Treatment |
Monitor blood glucose and take insulin injections for life. |
Low carbohydrate diet, regular exercise, and sometimes medication. |
|
Cure |
No known cure. |
Can sometimes be managed or reversed through lifestyle changes. |
Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes
A risk factor is something that increases the chance of developing a disease or health condition. Risk factors can be lifestyle-related (e.g. diet) or genetic. There are many risk factors for type 2 diabetes:
-
Obesity or being overweight (especially fat around the abdomen).
-
Lack of physical activity.
-
Poor diet (high in sugar and carbohydrates).
-
Family history of diabetes.
-
Age – risk increases with age (usually over 40).
-
Ethnicity – higher risk in people of South Asian, African-Caribbean, and Middle Eastern origin.
-
High blood pressure or cholesterol.
-
Smoking (may increase insulin resistance).
Interpreting data from a graph
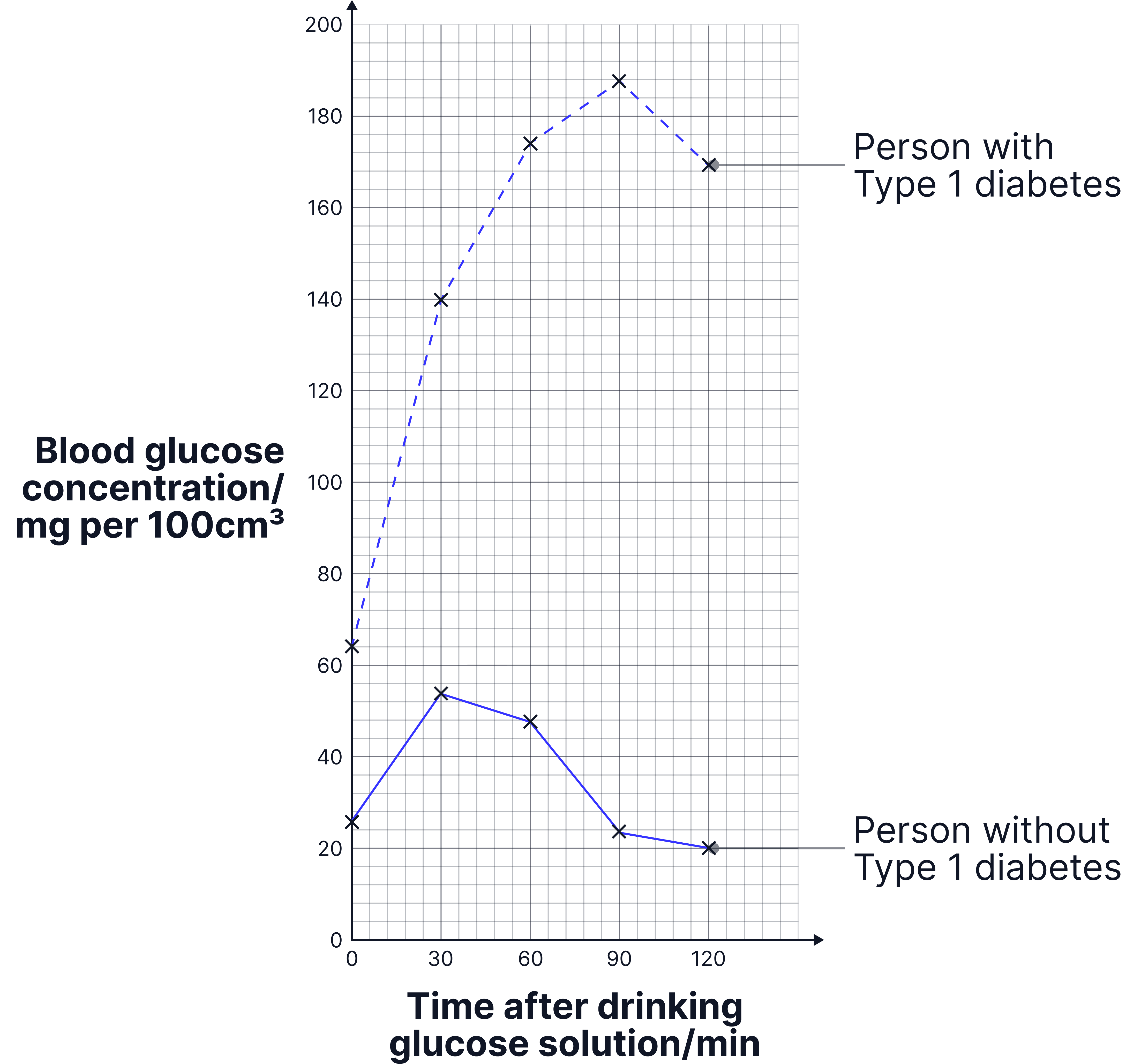
-
The person with type 1 diabetes always has a higher blood glucose concentration.
-
It is higher to begin with and rises much higher when they drink the glucose solution.
-
The concentration of glucose also rises more rapidly in the person with diabetes and the concentration stays high for longer.
-
The glucose concentration returns to the starting concentration by 90 minutes in the person without diabetes but it never returns to normal in the person with diabetes.
This is because when a person has type 1 diabetes, their pancreas is not producing insulin. This means glucose is not moving into their cells as quickly. Their muscle and liver cells are not storing glucose as glycogen!
Key Terms
-
Diabetes: A condition where blood glucose levels cannot be controlled.
-
Insulin: Hormone that lowers blood sugar.
-
Glucagon: Hormone that raises blood sugar.
-
Hyperglycaemia: High blood glucose.
-
Hypoglycaemia: Low blood glucose.
Exam Tips
- When comparing Type 1 and Type 2, be clear on the cause, treatment, and which type is lifestyle-related.
- For type 2 diabetes, make sure you give treatment options such as have a low carbohydrate diet and take regular exercise. Just saying ‘have a healthy diet’ or ‘have a balanced diet’ will not get you the mark!
Practice Question
Person A and person B both have diabetes. They had a test to measure the concentration of insulin in their blood when they were fasting. The table shows the results.
|
Person |
Fasting blood insulin concentration in arbitrary units |
|
A |
280 |
|
B |
20 |
|
Normal range |
50–175 |
Suggest which type of diabetes person A and person B have.
Give a reason for each answer. (2)
Person A has Type 2 diabetes
As their pancreas is producing (lots of) insulin but body cells cannot respond to it.
Person B has Type 1 diabetes
As their pancreas is not producing enough insulin (to control concentration of glucose in the blood)
More Practice
Try to answer these practice questions from the TikTok videos on your own, then watch the videos to see how well you did!