Triple Science Only - Plant cloning
Laura Armstrong & Joe Wolfensohn
Teachers


Contents
Recall Questions
This topic requires prior knowledge of types of reproduction.
What is a clone?
A clone is a genetically identical copy of an organism.
Which type of reproduction produces clones?
Asexual reproduction.
What are the key differences between sexual and asexual reproduction?
Sexual reproduction involves two parents, fertilisation and produces genetically different offspring. Asexual reproduction involves one parent and produces genetically identical offspring.
Topic Explainer Video
Check out this @JoeDoesBiology video that explains plant cloning, then read the study notes. Once you’ve gone through them, don’t forget to try the practice questions!
What is Plant Cloning?
Plant cloning is the process of creating genetically identical copies of plants using asexual reproduction methods. It ensures that offspring inherit the same desirable traits as the parent plant.
Examples of Desirable Traits in Plants
|
Trait |
Why It’s Desirable |
|---|---|
|
Disease resistance |
Reduces crop loss from fungi, bacteria, or viruses. |
|
Pest resistance |
Less need for pesticides. |
|
Drought tolerance |
Survives in low water conditions. |
|
High yield |
Produces more food per plant. |
|
Faster growth |
Quicker harvests. |
|
Improved taste or texture |
More appealing to consumers. |
|
Longer shelf life |
Reduces food waste. |
|
Uniform appearance |
Makes harvesting and selling easier. |
|
Better nutrient content |
Healthier for consumers. |
Two Common Methods of Plant Cloning
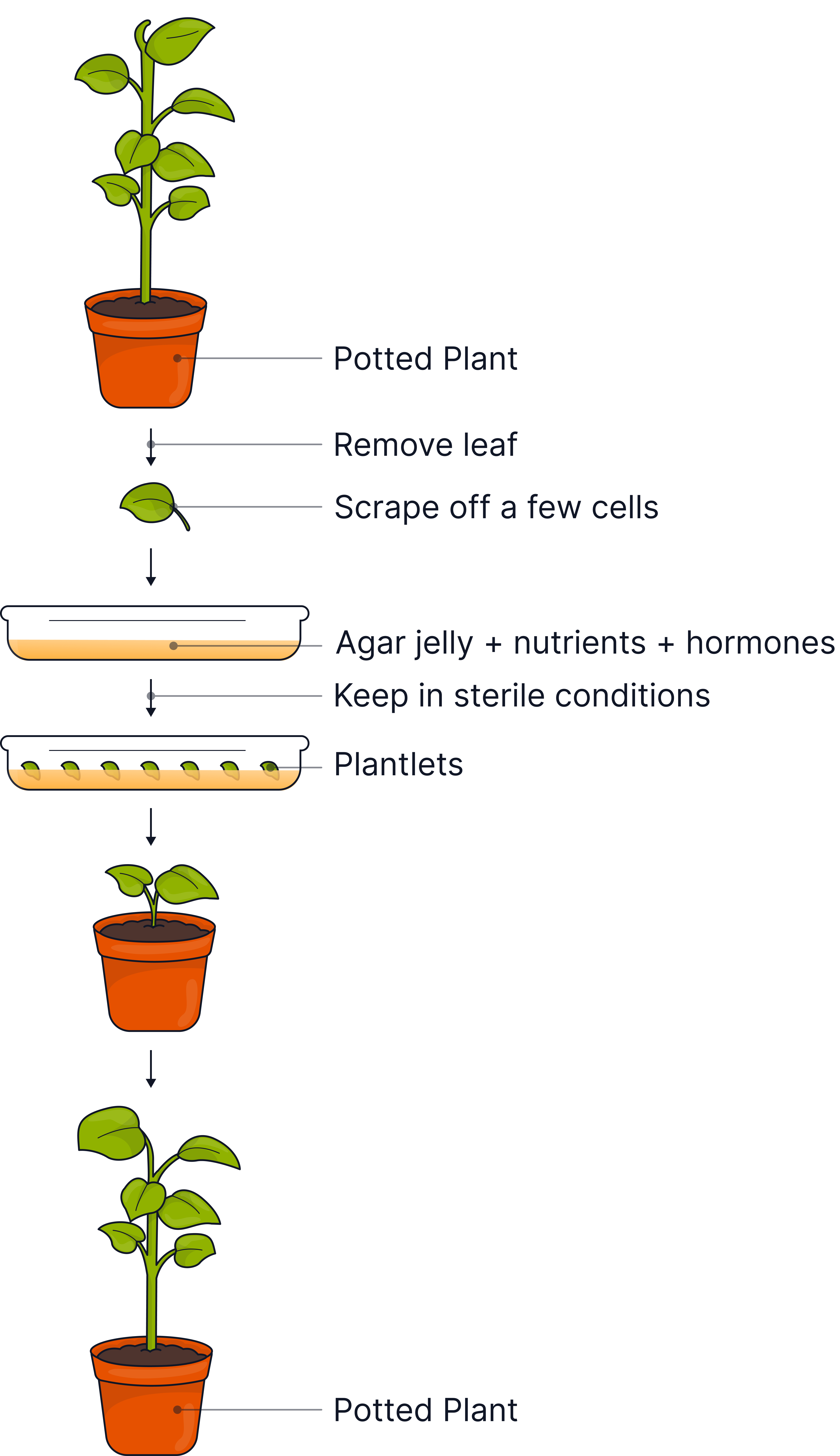
Tissue Culture (Lab-based)
-
Involves using a small group of cells from part of a plant to grow a whole new plant.
-
These cells are grown in sterile conditions on a nutrient-rich jelly (agar) containing hormones such as auxin to stimulate growth.
-
The cells develop into tiny identical plantlets.
-
Once large enough the plantlets will be transferred to moist soil where they will continue to grow.
-
The new plants will be genetically identical to the parent plant from which the cells were taken.
Used for:
-
Preserving rare species.
-
Producing large numbers of identical plants quickly and efficiently.
-
Commercial plant growing in nurseries.
Advantages of tissue culture
-
Offspring plants are genetically identical to the parent plant so will have the same desirable traits.
-
Can produce many offspring plants from one parent plant.
-
There will be less damage to the parent plant compared to taking cuttings.
Cuttings (Garden-based)
-
A simple and traditional method.
-
A section of a plant (e.g. a side shoot with a few leaves) is cut from the parent plant.
-
The cut stem is dipped in rooting powder containing hormones such as auxin to stimulate root growth.
-
It is then planted into moist soil.
-
Sometimes a transparent plastic bag is placed over the growing shoot to trap water vapour and reduce water loss by transpiration. It also helps to keep the plants warm and keep pests away.
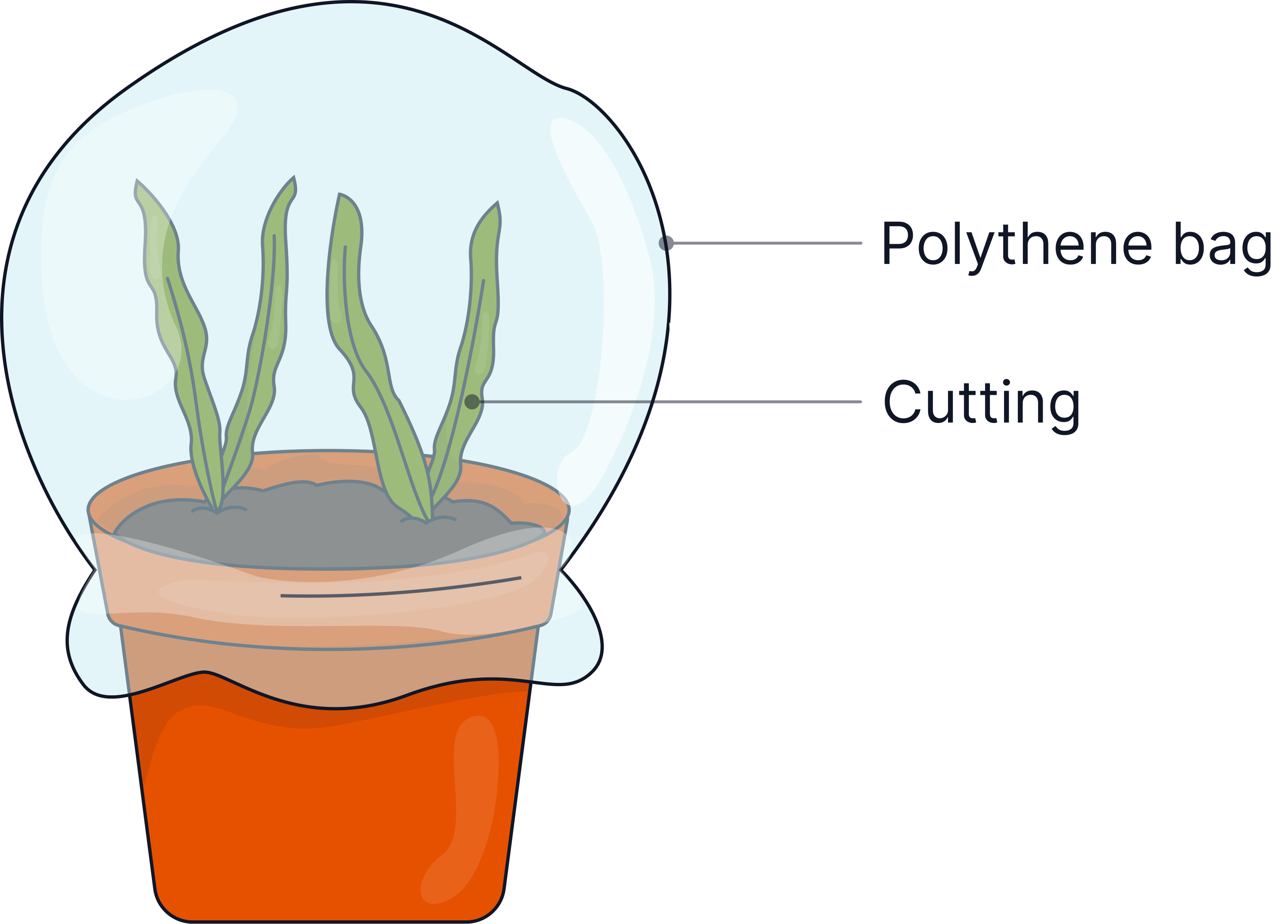
- It grows into a new plant that will be genetically identical to the parent plant from which the shoot was taken.

Used by:
-
Gardeners.
-
Quick, cheap, and easy to do at home.
Advantages of taking cuttings
-
Offspring plants are genetically identical to the parent plant so will have the same desirable traits.
-
Cheap and easy to do.
-
Quicker than growing plants from seeds.
Benefits & Risks of Plant Cloning in Agriculture
|
Benefits |
Risks |
|---|---|
|
Can help preserve endangered plant species. |
All clones are genetically identical → no genetic variation. |
|
Plants all have desired characteristics of the parent plants. |
If one plant is vulnerable to disease, all clones are. |
|
Can be done year-round in controlled environments. |
Reduces genetic diversity (important for survival). |
Key Terms
- Clone - An organism that is genetically identical to another organism.
- Asexual reproduction - Reproduction involving one parent and producing clones.
- Tissue culture - Growing new plants from a small group of cells in lab conditions.
- Cutting - A piece of a plant used to grow a new plant naturally.
- Genetic variation - Differences in DNA between individuals.
Exam Tip
Common mistake: Saying clones are “identical” without explaining what that means genetically. Use the phrase “genetically identical” to be precise. These cloning methods require one parent plant so are both examples of asexual reproduction.
Practice Questions
Question 1
Suggest two advantages of using tissue culture and not using cuttings to produce plants. (2)
- more / many offspring / plants produced from one parent plant.
- less damage to parent plant.
Question 2
Give two advantages to a gardener of producing geraniums from cuttings rather than from seeds (2)
-
quicker than growing from seeds.
-
cheap / more plants can be produced from one parent plant.
-
cuttings produce plants genetically identical (to parents).
More Practice
Try to answer the practice question from the TikTok video on your own, then watch the video to see how well you did!