Command Words
Laura Armstrong
Teacher

Topic Explainer Video
Check out this @lauradoesGCSEbiology video that explains some common command words, then read the study notes. Once you’ve gone through them, don’t forget to try the practice questions!
GCSE Biology Command Words - with Real Examples
Command words are the words and phrases used in exams and other assessment tasks that tell you how you should answer the question.
State (or Give / Name)
Meaning: A short, precise fact - no explanation needed.
Example:
State the organ that produces insulin.
- Answer: Pancreas.
Describe
Meaning: Say what happens, or what something is like - step-by-step or in order.
Examples:
Describe the pathway of a reflex action.
- Answer: A stimulus is detected by a receptor, an electrical impulse travels along a sensory neurone to the spinal cord, crosses a synapse to a relay neurone, then to a motor neurone which causes a muscle (effector) to contract.
Describe what happens to the diaphragm when you breathe in.
- Answer: The diaphragm contracts and moves downwards. This increases the volume of the lungs.
When describing a graph, you must say what the trend is:
Describe the effect of increasing light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis.
- The rate increases steadily until it levels off at a maximum.
- Try to include key data from a graph if the axes have a numbered scale.
Explain
Meaning: Say why or how something happens - use ‘because’ to show cause and effect.
Examples:
Explain why leaves have a large surface area.
- Answer: Because it increases the area available for light absorption, which increases the rate of photosynthesis.
Explain why the stomach has an acidic pH.
- Answer: Because hydrochloric acid kills bacteria and provides the optimum pH for protease enzymes to work at their fastest rate.
Compare
Meaning: Say similarities AND differences. Use words like whereas, both, but, however.
Examples:
Compare the structure of veins and arteries.
- Answer: Both are blood vessels with muscle and elastic tissue in their walls. Arteries have thicker muscular walls and a narrower lumen, whereas veins have thinner muscular walls and a wider lumen. Veins have valves, arteries do not.
Compare aerobic and anaerobic respiration in humans.
- Answer: Both release energy from glucose, but aerobic respiration uses oxygen and produces carbon dioxide and water, whereas anaerobic does not use oxygen and produces lactic acid.
Evaluate
Meaning: Give strengths and weaknesses. Say what’s good and what could be a problem.
Examples:
Evaluate the use of vaccinations to control disease.
- Answer:
- Advantages: Vaccination can prevent the spread of disease, protect vulnerable people (herd immunity), and reduce deaths.
- Disadvantages: Some people may have side effects, vaccines can be expensive, and not everyone chooses to be vaccinated.
Evaluate the use of IVF in treating infertility.
- Answer:
- Advantages: IVF helps couples who cannot have children naturally to conceive.
- Disadvantages: IVF is expensive, has a low success rate, and can lead to multiple births which have health risks to mother and babies. It can be considered unethical because spare embryos may be destroyed which some people disagree with.
Suggest
Meaning: Make an educated guess based on what you know.
Examples:
Suggest why fewer insects are found under trees.
- Answer: Less light reaches the ground so fewer plants grow, meaning fewer insects have food or shelter.
A scientist finds bacteria growing near a hot spring. Suggest how the enzymes in these bacteria might be adapted.
- Answer: They might have a higher optimum temperature so they do not denature at high temperatures.
Calculate
Meaning: Use data to get a numerical answer. Always show your working and include units if needed.
Example:
A student counted 20 bubbles of oxygen in 1 minute during a photosynthesis experiment. Calculate the rate of bubble production per hour.
- Answer: 20 bubbles x 60 minutes = 1200 bubbles per hour.
Complete
Meaning: Finish a diagram, table or sentence using what you know.
Examples:
Complete the sentence: “The _______ carries oxygenated blood away from the heart.”
- Answer: aorta
Complete the table by naming the products of anaerobic respiration in animals.
|
Type of Respiration |
Products |
|
Aerobic |
Carbon dioxide + water |
|
Anaerobic (animals) |
___________ |
- Answer: Lactic acid
Sketch
Meaning: Draw a simple diagram or graph showing the main features. It does not have to be perfect - it’s about shape and labels.
Example:
Sketch a graph to show how enzyme activity changes with temperature.
- Answer: A sketch showing a curve that rises to an optimum, then falls sharply after the enzyme denatures.
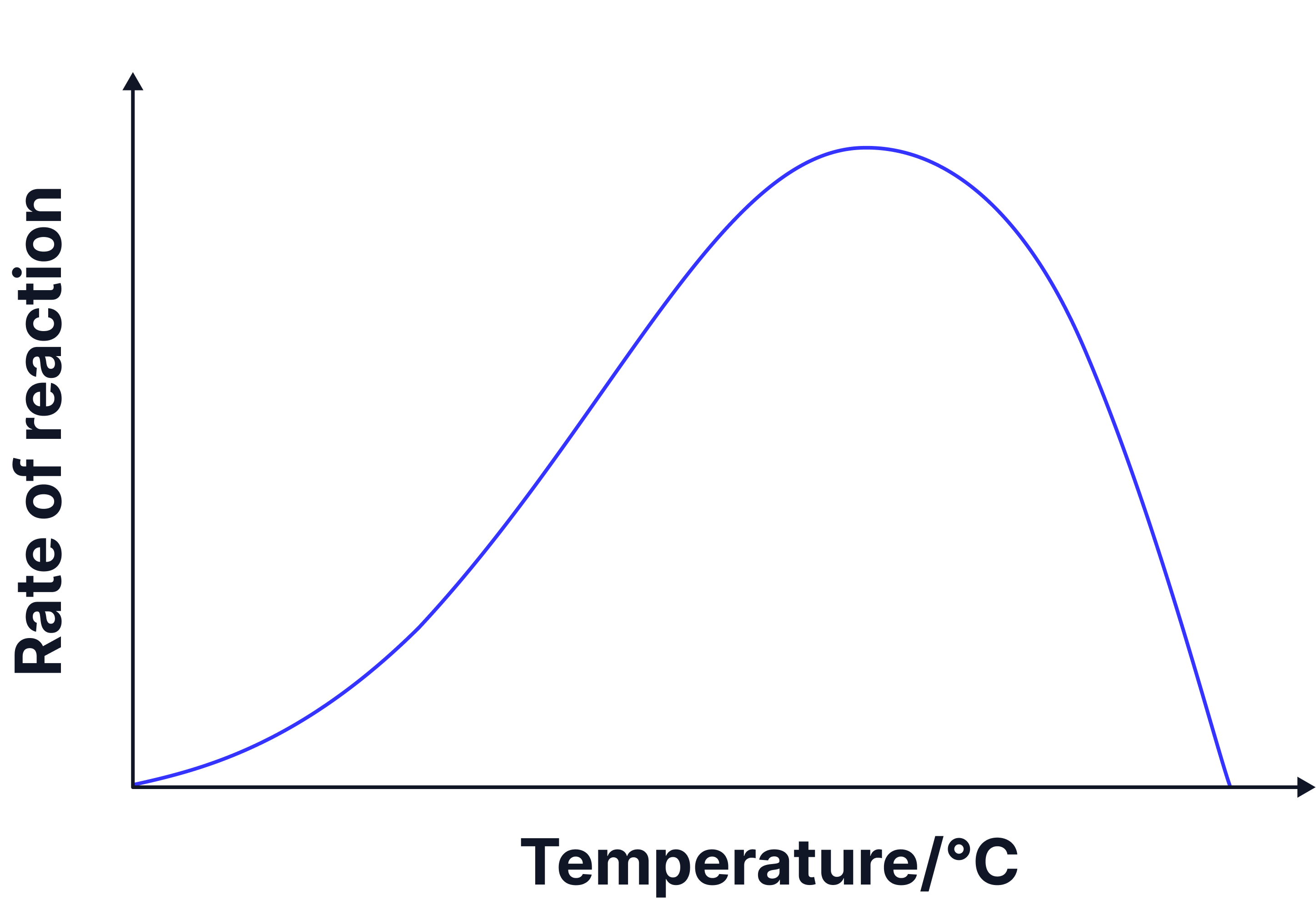
Label axes: e.g. ‘Temperature (°C)’ on the x-axis, ‘Rate of reaction’ on the y-axis.
Design
Meaning: Plan an experiment. You must include method, variables, apparatus, and how to make it valid (control variables and repeats).
Example:
Design an experiment to investigate the effect of pH on amylase activity.
Answer:
- Add amylase and starch solution into test tubes with different pH buffers (e.g. pH 3, 5, 7, 9 and 11).
- Keep temperature, enzyme concentration, and substrate volume the same.
- Measure the time taken for the substrate to be broken down.
- This can be done using iodine solution.
- Take a sample of the enzyme and substrate mixture every 30 seconds and drop into iodine solution.
- When the iodine stops going blue / black and remains yellow – this tells us all the starch has been broken down into glucose.
- Repeat at least 2 further times and calculate a mean time taken.
Tip: Always name the independent, dependent, and control variables.
Predict
Meaning: Use your science knowledge to say what you think will happen. You do not always have to explain (unless it says ‘Explain your prediction’).
Example:
Predict what will happen to the rate of photosynthesis if the light intensity is increased.
- Answer: The rate will increase.
Predict what will happen to a plant cell placed in pure water.
- Answer: It will swell and become turgid.
More Practice
Try to answer these practice questions from the TikTok videos on your own, then watch the videos to see how well you did!