Calculating The Gradient Of A Graph
Joe Wolfensohn
Teacher

Contents
Topic Explainer Video
Check out this @JoeDoesGCSEBiology video that explains calculating the gradient of a graph, then read the study notes. Once you’ve gone through them, don’t forget to try the practice questions!
Calculating Gradients on Graphs
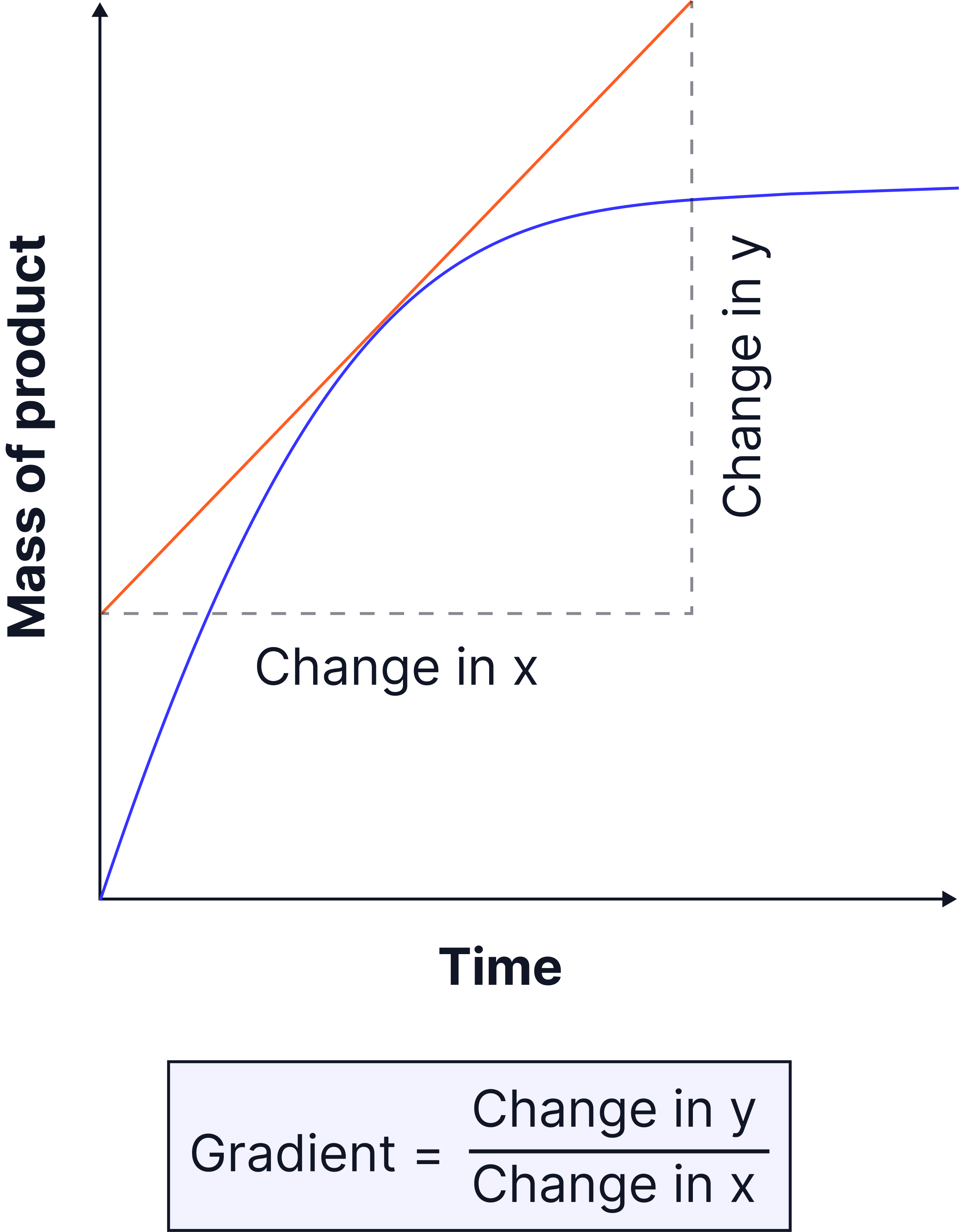
Gradient of a straight line
- Formula:
Gradient = change in y / change in x (Δy ÷ Δx)
- Steps:
-
- Identify two points on the straight line.
- Calculate the vertical change (Δy) and the horizontal change (Δx).
- Divide Δy by Δx.
- Include units (y-units per x-units).
Example:
Calculate the rate of reaction in the first 2 minutes.
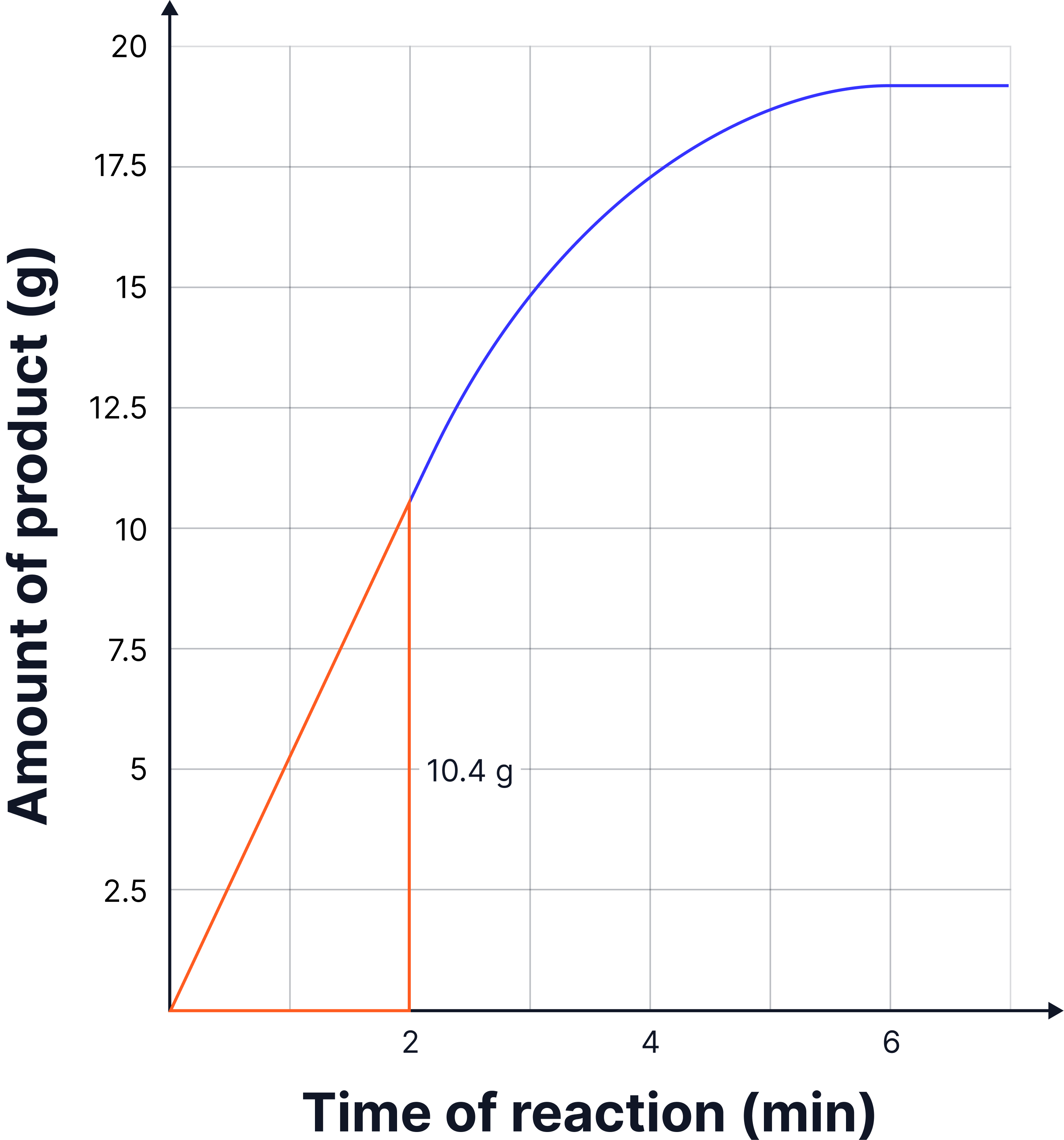
The change on the y axis is 10.4g and the change on the x axis is 2 minutes
Gradient = 10.4 ÷ 2 = 5.2 g / min
Gradient at a point on a curved graph
Used when the rate is not constant (e.g., enzyme activity curves).
- Steps:
-
- Choose the point where you want the gradient.
- Draw a tangent – a straight line that just touches the curve at that point and follows the curve’s slope without cutting through it.
- Pick two clear points on the tangent (widely spaced for accuracy).
- Calculate the gradient as for a straight line (Δy ÷ Δx).
- Include units.
When might this be used in biology?
- Enzyme rate of reaction at a specific moment.
- Population growth rate at a given time.
- Photosynthesis rate under changing light intensity.
Practice Question
Determine the rate of water loss at 12:00.
Use the tangent on the graph.
Give your answer:
• in cm3 per minute.
• in standard form.
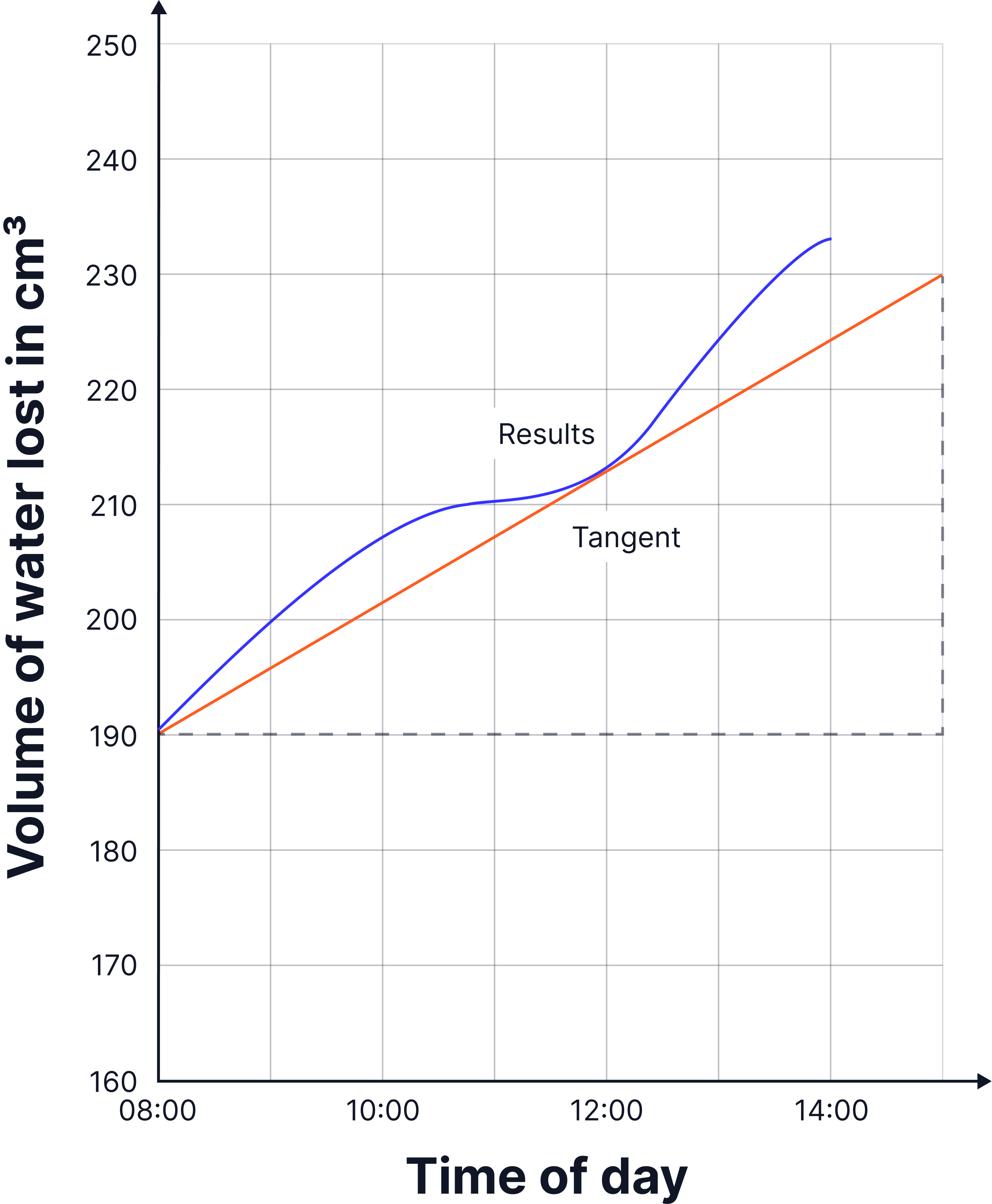
Model Answer:
- Use the tangent to make a triangle (use the widest range possible)
- Calculate the change on the x axis and y axis
- Δy = 230 − 190 = 40 cm³
- Δx = 7 hours (from 08:00 to 15:00 hours)
- Convert hours to minutes 7 x 60 = 420 minutes
- Gradient = 40 ÷ 420 = 0.095 cm³ / min
- Convert to standard form = 9.5 x10-2 cm3 / min
More Practice
Try to answer the practice question from the TikTok video on your own, then watch the video to see how well you did!