Evolution and Natural selection
Laura Armstrong & Joe Wolfensohn
Teachers


Recall Questions
This topic requires prior knowledge of variation.
What is variation?
The differences in characteristics between individuals in a population
What causes genetic variation?
Differences in inherited alleles and mutations
What is a mutation?
A change in the DNA that can create new alleles
Topic Explainer Videos
Check out these @JoeDoesBiology and @lauradoesbiology videos that explain evolution and natural selection, then read the study notes. Once you’ve gone through them, don’t forget to try the practice questions!
Evolution and Natural Selection
What Is Evolution?
- Evolution is the gradual change in the inherited characteristics of a population over time.
- It occurs due to the process of natural selection.
- It may lead to the formation of a new species.
The theory of evolution by natural selection states that all species of living things have evolved from simple life forms that first developed more than three billion years ago.
What Is Natural Selection?
- Natural selection is the process where organisms with the most advantageous characteristics survive and reproduce, passing their genes to the next generation.
- It is sometimes known as ‘survival of the fittest’.
Charles Darwin & His Theory
- Charles Darwin proposed the theory of natural selection after observing species, especially finches, during his voyage to the Galápagos Islands.
- In 1859, he published the book "On the Origin of Species" explaining natural selection and evolution.
Why Was Darwin’s Theory Not Accepted at First?
- He had no explanation for how inheritance worked (DNA was not yet discovered).
- It challenged religious beliefs that God created all life.
- There was not enough evidence at the time from fossils or genetics, so he did not have proof.
Examples of Natural Selection
1. Giraffes
- Ancestors had varying neck lengths due to genetic variation.
- This genetic variation is a result of mutations.
- There is competition between giraffes for food.
- In times of food shortage, giraffes with longer necks could reach more leaves.
- These giraffes are more likely to survive.
- And go on to reproduce.
- Passing on the advantageous gene for their longer neck.
2. Peppered Moths
- Moths had different colours due to genetic variation.
- This genetic variation is a result of mutations.
- Originally, pale-coloured moths camouflaged better against light trees.
- As pollution darkened trees, darker moths were better camouflaged from predators.
- Dark moths were more likely to survive.
- And go on to reproduce.
- Passing on the advantageous gene for their darker colour.
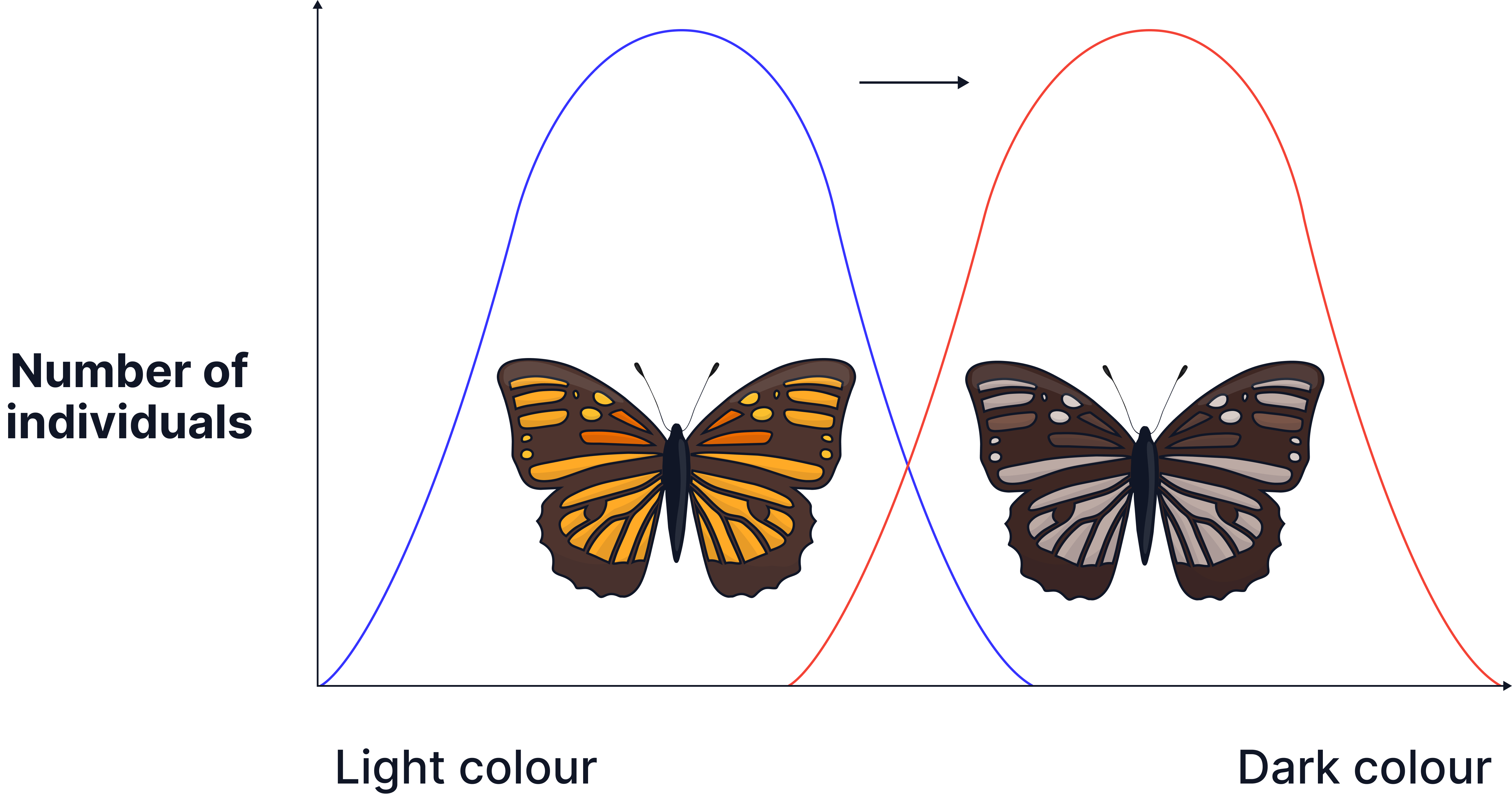
Natural selection takes place gradually, over many generations. This means that over time, a population will become better suited to its environment.
Natural Selection may lead to Speciation
Speciation is the process by which new species are formed.
If two populations of one species become so different in phenotype (characteristics) that they can no longer interbreed to produce fertile offspring they have formed two new species.
Details of speciation are not required for Combined Science, but are included on the Separate Science specification.
Key Terms
- Evolution – The gradual change in the inherited traits of a population over time.
- Natural Selection – Survival and reproduction of organisms best suited to the environment.
- Mutation – A change in DNA that can give rise to new alleles.
- Adaptation – A trait that helps an organism survive.
- Species – A group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring.
- Speciation - is the process by which new species are formed.
Exam Tips:
In a question about natural selection, always mention:
- Genetic variation due to mutation.
- The advantage in a specific environment.
- Survival and reproduction.
- Passing on beneficial genes or alleles (don’t just say characteristics).
Try to tailor your answer to the organism in the question, for example, giraffes with longer necks could reach more food and therefore did not starve.
Darker coloured moths were better camouflaged and therefore less likely to be seen and eaten by predators/ birds.
Practice Question
These birds use their beaks to reach nuts inside the bird feeder.

The graph shows the mean beak length of this species of bird in the UK.
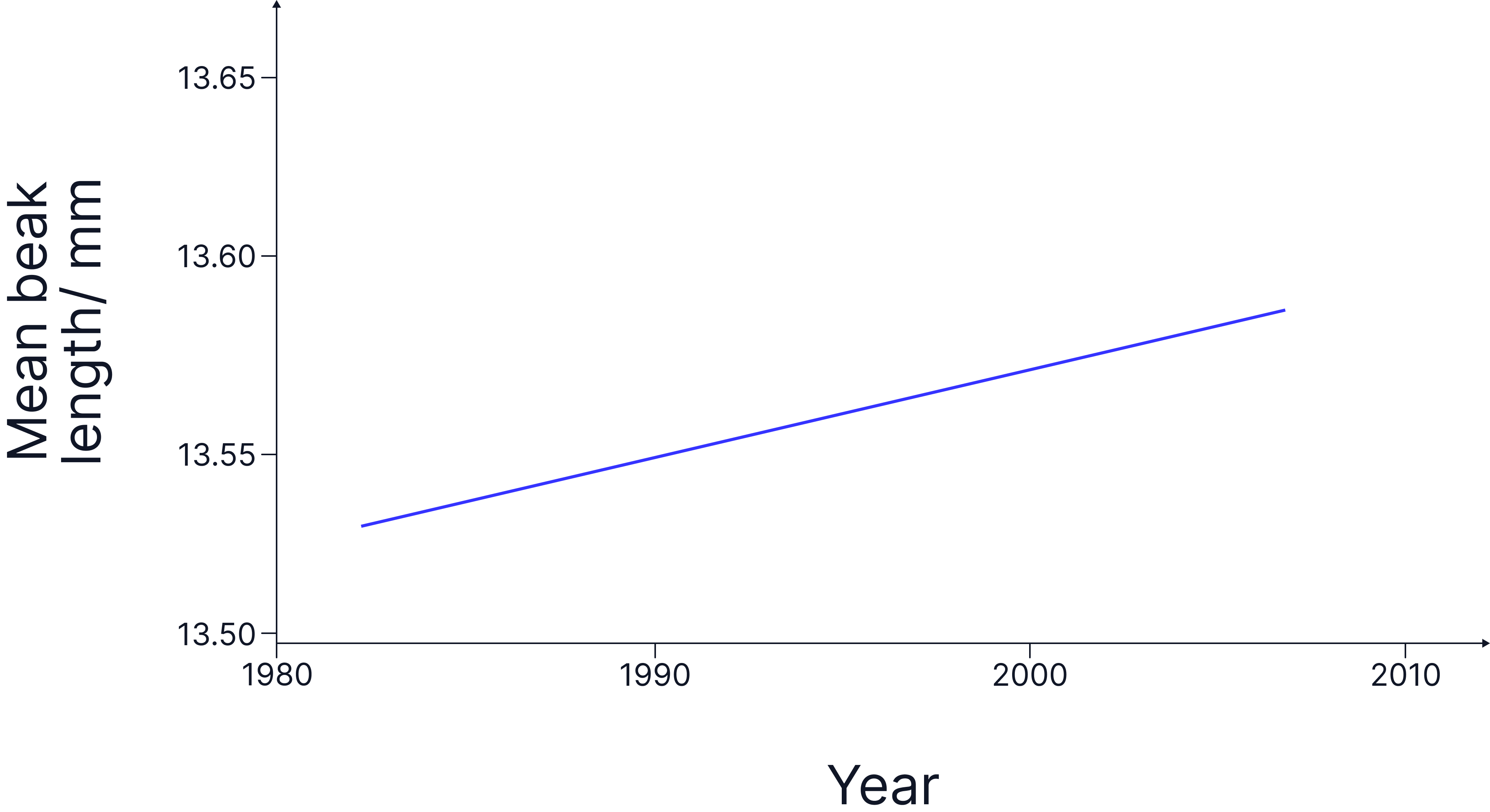
Explain the process of evolution that could cause the trend in the graph. (6 marks)
Model Answer:
- there is genetic variation in beak length (in this bird population).
- variation is due to mutations.
- birds with longer beaks can reach more nuts / food or birds with longer beaks can fight with or outcompete birds with shorter beaks.
- so can survive and reproduce.
- pass gene / allele (for long beak) on.
- which is natural selection.
- repeated over many generations.
- birds are evolving to have longer beaks.
More Practice
Try to answer these practice questions from the TikTok videos on your own, then watch the videos to see how well you did!