Variation And Mutations
Laura Armstrong & Joe Wolfensohn
Teachers


Recall Questions
This topic requires prior knowledge of alleles and genes.
What is an allele?
A different version of a gene
What is the genome?
The genome is the entire genetic material of an organism
What causes genetic variation?
Differences in the genes (alleles) individuals inherit and mutations
Topic Explainer Video
Check out this @JoeDoesBiology video that explains variation and mutations, then read the study notes. Once you’ve gone through them, don’t forget to try the practice questions!
Variation and Mutations
What Is Variation?
- Variation refers to the differences in characteristics between individuals in a population.
- It is essential for natural selection and evolution.
Causes of Variation
1. Genetic Causes
- Genes inherited from parents (different combinations of alleles).
- Examples: Eye colour, blood group, inherited disorders, being able to roll your tongue.
2. Environmental Causes
- Result from the environment.
- Examples: Language spoken, scars, your accent.
3. Combination of Both
- Example: Height and weight (influenced by both your genes and diet) and intelligence (influenced by your genes and how hard you work!)
There is usually extensive genetic variation in any population of a species.
What Are Mutations?
- A mutation is a change in DNA.
- Mutations occur randomly in DNA.
- All new alleles (versions of genes) arise from mutations.
Examples of mutations
DNA contains bases.
The order of these bases determines the order of amino acids in a protein.
So if bases are substituted, added or deleted- this can result in the amino acids being in the wrong order in a protein and the protein changing shape.
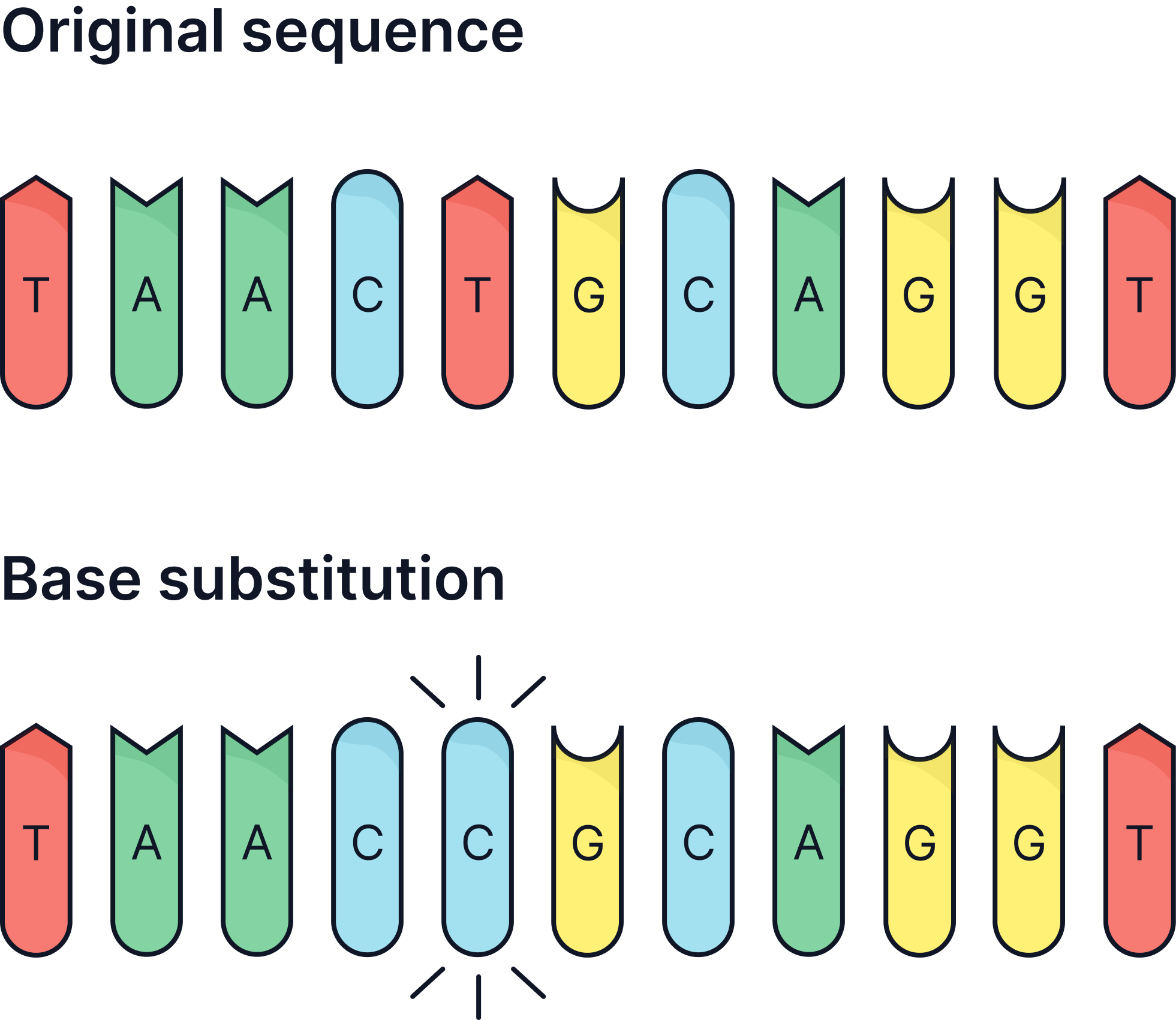
In this example, a T base in DNA has been substituted for a C base. This is a mutation as there has been a change in the DNA base sequence.
Effects of Mutations:
- Most mutations: Have no effect on the phenotype.
- Some mutations: May influence the phenotype slightly.
- Rare mutations: May change the phenotype significantly.
- If a mutation is beneficial and suited to environmental change, it may spread quickly through the population leading to evolution.
Example:
A mutation that gives bacteria resistance to antibiotics can lead to rapid spread of resistant strains through natural selection - leading to evolution.
Continuous vs. Discontinuous Variation
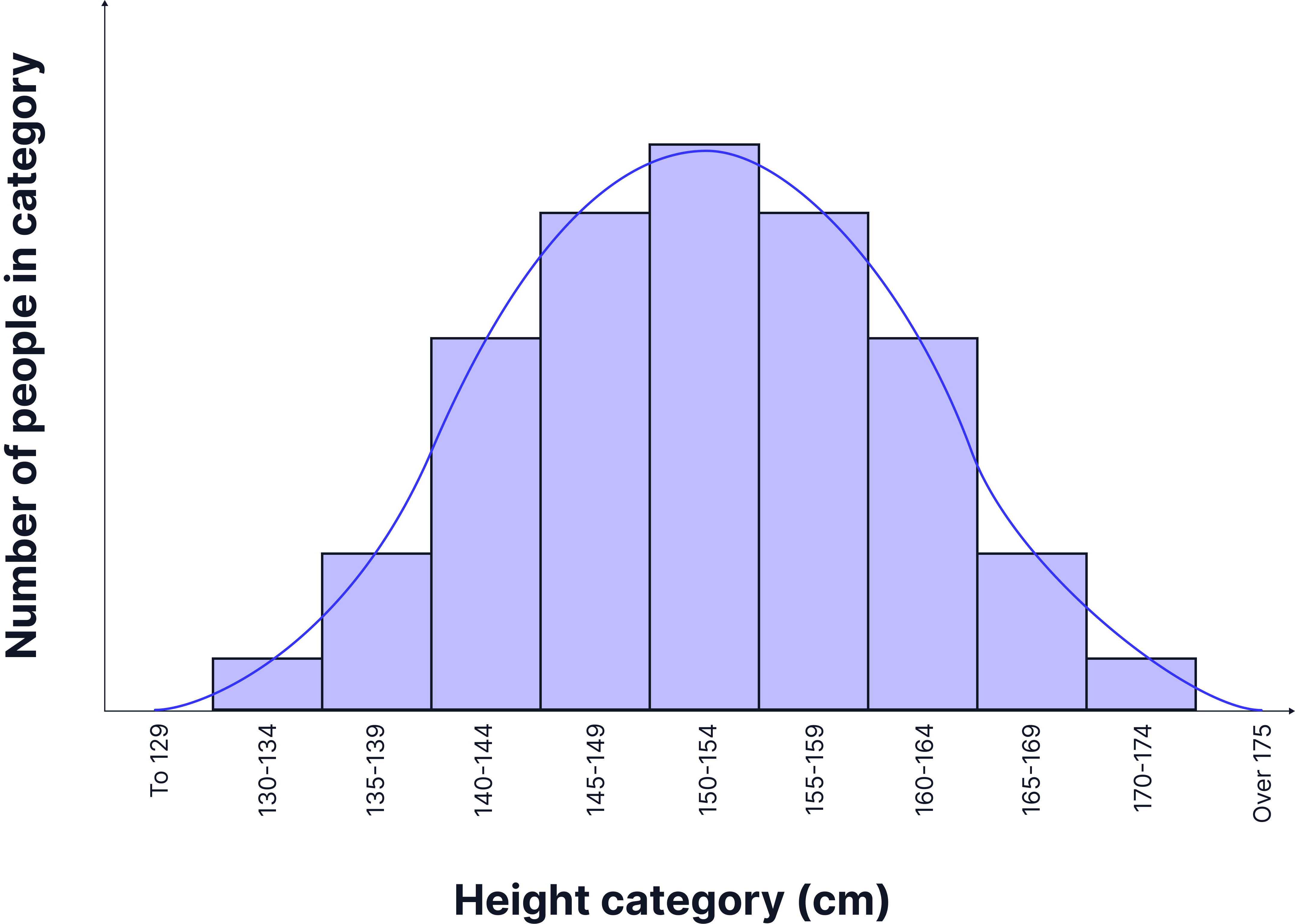
Continuous Variation
- Definition: Variation that shows a range of values.
- No distinct categories – individuals can fall anywhere along a scale.
- Controlled by many genes and often influenced by the environment.
Examples of continuous variation:
- Height in humans.
- Body mass.
- Leaf length in plants.
Graph Used:
- A histogram with a smooth curve (often bell-shaped, called a normal distribution)
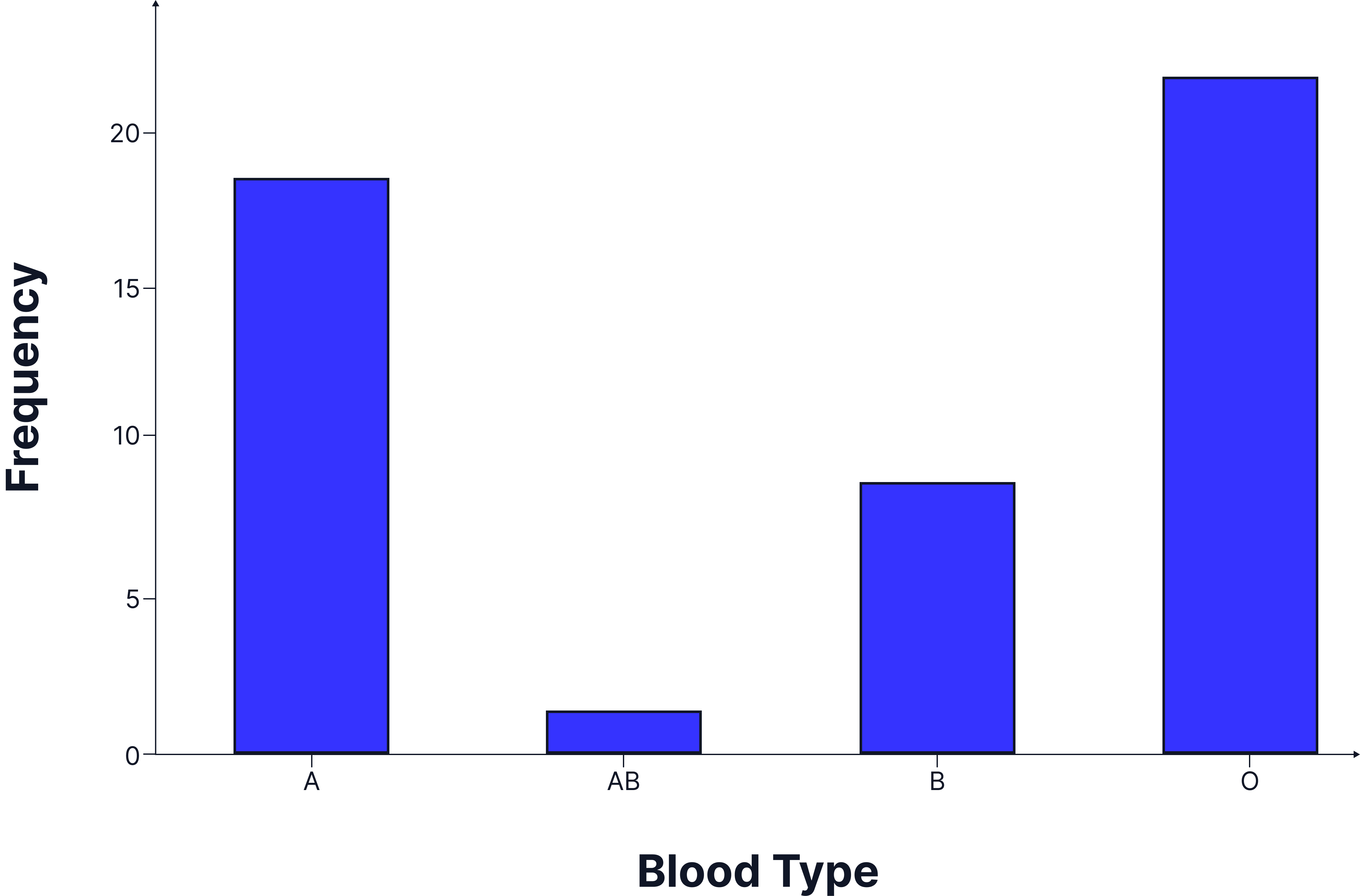
Discontinuous Variation
- Definition: Variation with a limited number of distinct categories.
- Usually controlled by a single gene.
- Not influenced by the environment.
Examples:
- Blood group (A, B, AB or O)
- Tongue rolling (can roll or can’t roll)
- Ear shape (lobed or unlobed)
Graph Used:
- Bar chart (each category shown separately with gaps between bars).
Quick Comparison Table
|
Feature |
Continuous Variation |
Discontinuous Variation |
|
Type of data |
Range of values. |
Distinct categories. |
|
Control |
Many genes + environment. |
Usually one gene. |
|
Examples |
Height, mass. |
Blood group, tongue rolling. |
|
Graph type |
Histogram. |
Bar chart. |
Key Terms
- Variation – Differences between individuals in a population.
- Mutation – A change in the DNA.
- Allele – Different versions of genes.
- Environmental factor – A non-genetic influence, like diet or climate.
- Discontinuous variation – Variation with a limited number of distinct categories / groups.
- Continuous variation – Variation that shows a range of values.
Exam Tips:
When drawing graphs, possibly linked to variation, remember to label the X and Y axis, include any units and plot all points or bars accurately!
You should also use sensible scales and make sure your graph takes up over half of the gridded space provided.
Practice Question
Describe how variation in a species can arise. (4 marks)
Model Answer:
- Variation can be caused by differences in the genes inherited from parents (genetic variation).
- This includes different alleles that individuals carry.
- Variation can also be caused by environmental factors, such as diet or climate.
- Most individuals show a combination of both genetic and environmental variation.
More Practice
Try to answer the practice question from the TikTok video on your own, then watch the video to see how well you did!