Global Warming
Laura Armstrong
Teacher

Contents
Recall Questions
This topic requires prior knowledge of greenhouse gases from GCSE Chemistry.
What are greenhouse gases?
Gases in the atmosphere that trap heat energy and keep Earth warm.
Name two main greenhouse gases.
Carbon dioxide (CO₂) and methane (CH₄).
How does burning fossil fuels affect greenhouse gas levels?
It releases extra carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
Topic Explainer Video
Check out this @lauradoesGCSEbiology video that explains global warming, then read the study notes. Once you’ve gone through them, don’t forget to try the practice questions!
Global Warming
What Are Greenhouse Gases?
- Greenhouse gases are gases in the atmosphere that trap heat energy from the Sun.
- They act like a blanket, keeping the Earth warm enough to support life.
Main greenhouse gases:
|
Gas |
Where it comes from |
|
Carbon dioxide (CO₂) |
Burning fossil fuels like coal, oil, and gas; deforestation. |
|
Methane (CH₄) |
Cattle farming (digestion); decay of waste in landfill sites; rice paddies (rice fields). |
|
Water vapour |
Naturally present when water evaporates; not directly caused by humans. |
|
Nitrous oxide (N₂O) |
Fertilisers and some industrial processes. |
Why Are Greenhouse Gases Increasing?
Carbon dioxide:
- Burning fossil fuels for energy releases huge amounts of CO₂.
- Cutting down forests (deforestation) means fewer trees to absorb CO₂ by photosynthesis.
Methane:
- More cattle farming - cows produce methane during digestion.
- More rubbish in landfill - bacteria break down waste and release methane.
- Rice fields in warm, wet conditions also produce methane.
All of these things are on the rise, due to our population size increasing which increases the demand for food and energy.
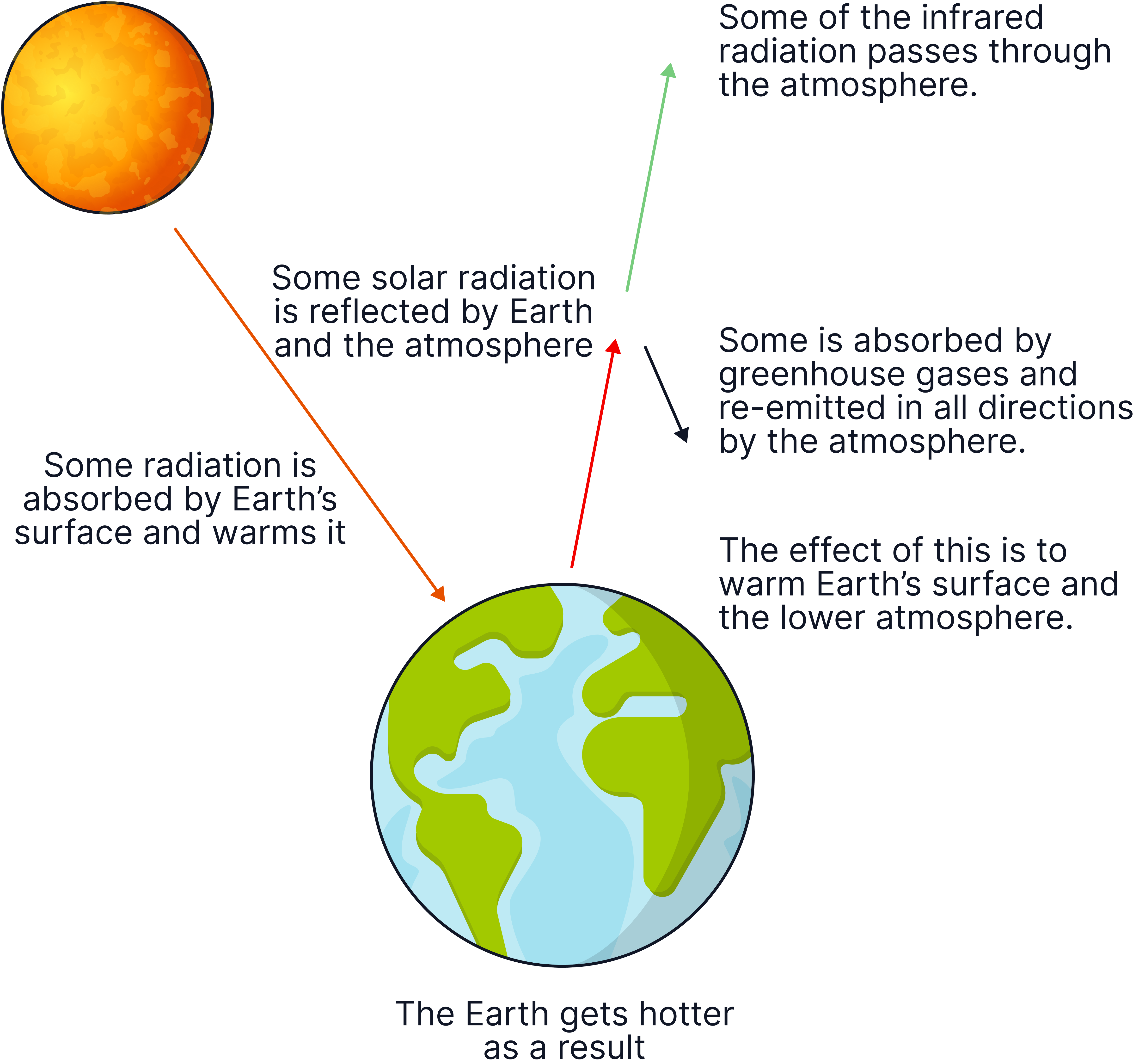
How the Greenhouse Effect Works
- The Sun’s heat energy reaches Earth.
- Some energy is absorbed by the Earth’s surface and warms it.
- The Earth radiates heat energy back into the atmosphere.
- Greenhouse gases trap some of this heat, stopping it escaping into space.
- This heat energy then gets re-radiated back to Earth.
- This keeps Earth’s temperature warm enough for life - but too many greenhouse gases cause too much warming.
Impacts of Global Warming
Global warming means the gradual increase in Earth’s average temperature due to rising greenhouse gas levels.
Possible effects include:
- Ice melting: Polar ice caps and glaciers melt, causing sea levels to rise → flooding of low-lying areas.
- Warmer oceans expand: raising sea levels → leading to coastal flooding.
- Climate change: More extreme weather - heatwaves, storms, droughts, floods.
- Loss of habitats: Animals like polar bears lose sea ice; coral reefs die due to warmer temperatures.
- Changes in species distribution: Some animals and plants may move to cooler areas.
- Reduced biodiversity: Some species may become extinct if they can’t adapt.
- Impact on food production: Some areas may become too hot or dry for crops – this could lead to food shortages.
- Changes to migration patterns: Some birds may move to cooler regions if their usual habitats get too warm.
Key Terms & Definitions
- Greenhouse gas - Gas that traps heat in the atmosphere (e.g., CO₂, CH₄).
- Fossil fuels - Coal, oil, and gas formed from dead organisms millions of years ago.
- Greenhouse effect - The natural process that warms the Earth’s surface.
- Global warming - The rise in Earth’s average temperature due to increased greenhouse gases.
Exam Tip:
Always link human activities (burning fossil fuels, farming) to specific gases (CO₂, methane) and explain how these gases trap heat energy. Use clear examples of impacts.
Practice Question
Explain how increased burning of fossil fuels contributes to global warming and describe two impacts of global warming. (4 marks)
Model Answer:
- Burning fossil fuels releases more carbon dioxide, which is a greenhouse gas.
- This traps more heat energy in the atmosphere, causing global warming.
- One impact is melting ice caps, which raises sea levels and causes flooding.
- Another impact is more extreme weather, like droughts and heatwaves.
More Practice
Try to answer these practice questions from the TikTok videos on your own, then watch the videos to see how well you did!