Meiosis
Laura Armstrong & Joe Wolfensohn
Teachers


Contents
Recall Questions
This topic requires prior knowledge of mitosis, so you can compare mitosis with meiosis.
What is mitosis used for?
Growth, repair of tissues, and asexual reproduction.
What type of cells does mitosis produce?
Two genetically identical, diploid cells.
How many divisions occur in mitosis?
One cell division.
Topic Explainer Video
Check out this @JoeDoesBiology video that explains meiosis, then read the study notes. Once you’ve gone through them, don’t forget to try the practice questions!
Meiosis
What is Meiosis?
- Meiosis is a type of cell division that produces gametes (sex cells like sperm and egg).
- It occurs in the reproductive organs (testes and ovaries in humans).
- It results in four non-identical daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes (haploid).
Why is Meiosis Important?
- It ensures that the chromosome number is halved in gametes so that it returns to normal during fertilisation.
- It creates genetic variation due to the shuffling of genetic material.
- This variation is vital for evolution and survival of species.
Why Meiosis is Important – Chromosome Number Example
- A normal human body cell is diploid, meaning it has 46 chromosomes (or 23 pairs).
- If gametes (sperm and egg) were made by mitosis, they would also have 46 chromosomes each.
- When these gametes fuse during fertilisation, the resulting zygote would have 92 chromosomes, which is not viable.
Meiosis prevents this by halving the chromosome number:
- Meiosis in humans produces:
- Sperm (23 chromosomes)
- Egg (23 chromosomes)
- During fertilisation:
- 23 (sperm) + 23 (egg) = 46 chromosomes
This restores the correct diploid number in the zygote and ensures that the offspring has the right amount of genetic material.
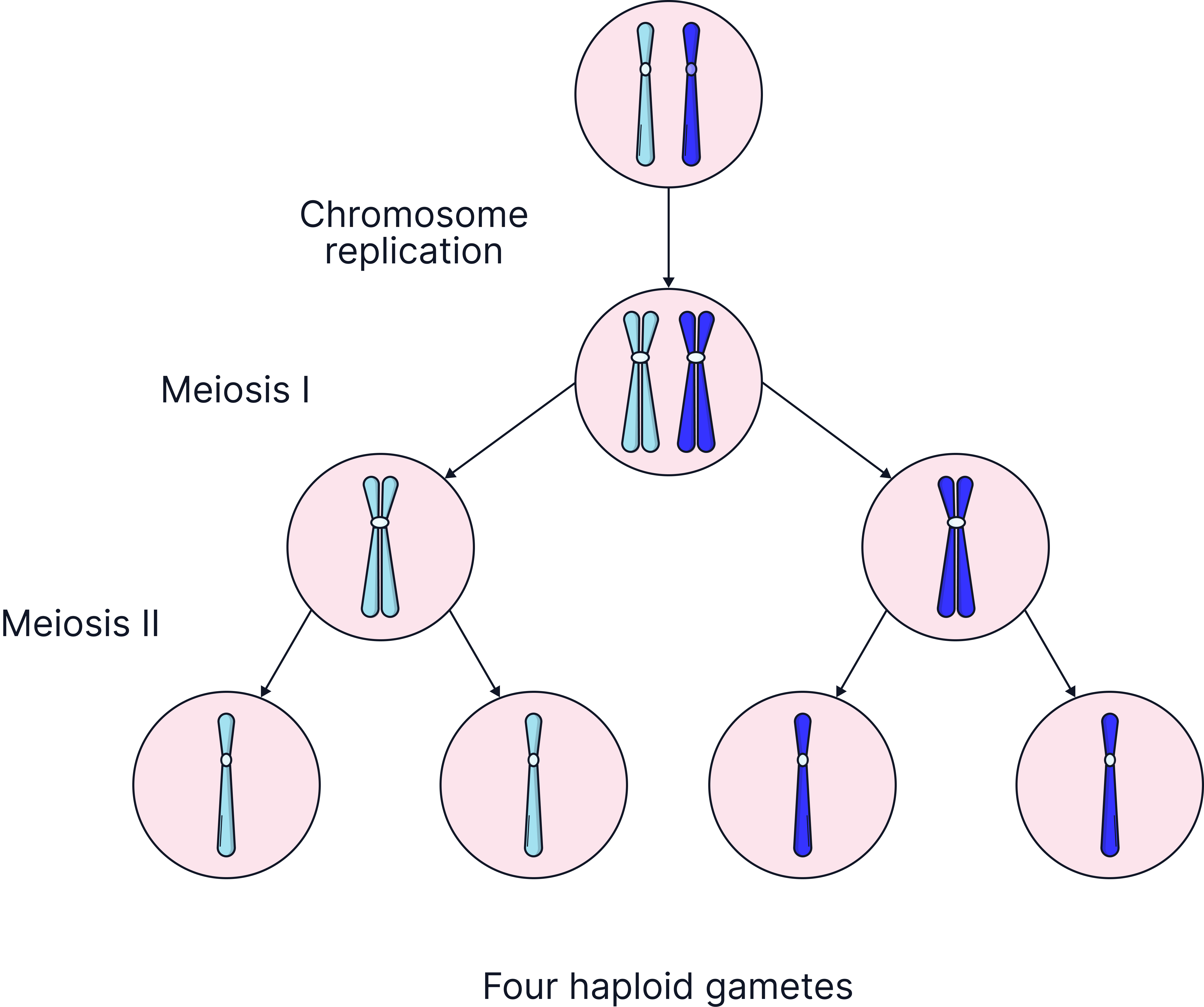
How Meiosis Works:
- DNA is replicated so chromosomes double before division.
- First Division – Chromosome pairs are separated, resulting in two daughter cells.
- Second Division – Chromosomes are separated, resulting in four daughter cells.
- The end result is 4 haploid cells, each genetically different. These haploid cells are gametes.
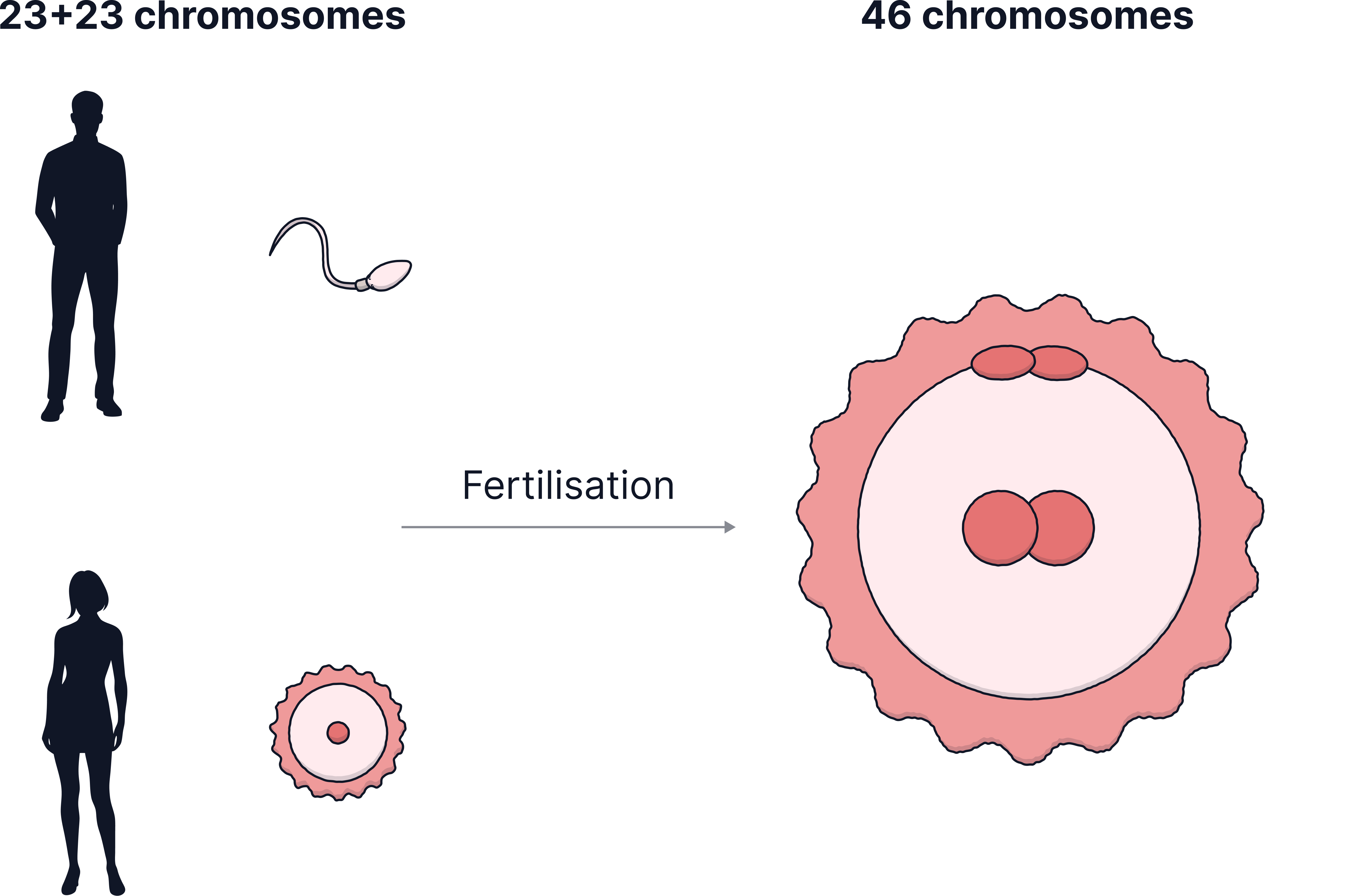
After meiosis:
- Two haploid gametes fuse at fertilisation to form a diploid zygote.
- The zygote then divides by mitosis to form an embryo.
Remember, meiosis only makes the gametes, all other cell division and growth will be via mitosis!
Comparison Table: Meiosis vs Mitosis
|
Feature |
Meiosis |
Mitosis |
|
Purpose |
Produces gametes. |
Growth, repair of tissues, asexual reproduction. |
|
Number of Divisions |
2 divisions. |
1 division. |
|
Cells Produced |
4 haploid cells, with half the number of chromosomes. |
2 diploid cells, with the full set of chromosomes. |
|
Genetic Variation |
Yes – all cells genetically different. |
No – all cells genetically identical. |
|
Used in |
Sexual reproduction. |
All other body cell processes, and for asexual reproduction. |
|
Occurs in |
The ovaries and testes. |
All parts of the body. |
Key Terms
- Meiosis – Cell division that produces genetically different gametes with half the normal number of chromosomes.
- Gametes – Sex cells (sperm and egg) that join in fertilisation.
- Haploid – A cell with half the number of chromosomes.
- Diploid – A cell with a full set of chromosomes.
- Genetic variation – Differences between individuals caused by the combination of genes.
- Zygote – The fertilised egg cell.
Exam Tips
When explaining the purpose of meiosis, always mention making gametes, halving the chromosome number, and introducing genetic variation. These are key words examiners look for.
Remember, meiosis only makes gametes- any other cell division will be mitosis!
Practice Questions
Use the diagram to answer the following questions:
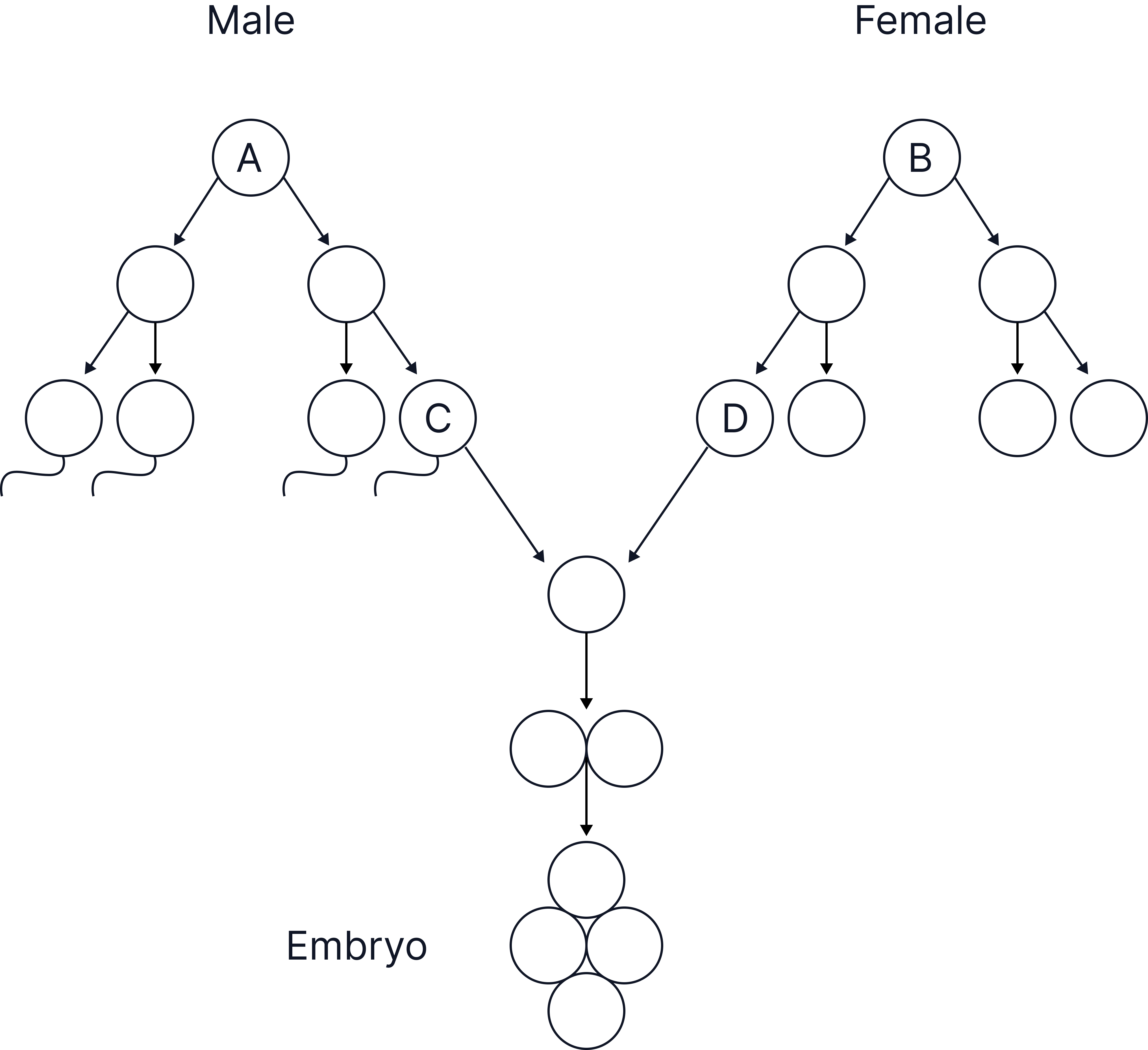
a) Name the type of cell division that produces cell D from cell B. (1)
b) Which organ in the male body produces cell C from cell A? (1)
c) Cells A and B contain 46 chromosomes, how many chromosomes would there be in cell C? (1)
d) Why is it important that cell C has this number of chromosomes? (2)
Model Answers:
a) Meiosis.
b) The testes.
c) 23 chromosomes.
d) Cell C fuses with cell D / with the egg cell or is used in fertilisation
Having half the number of chromosomes prevents doubling of chromosome number / restores original number of chromosomes/ makes sure the zygote has 46 chromosomes / the correct number of chromosomes.
More Practice
Try to answer these practice questions from the TikTok videos on your own, then watch the videos to see how well you did!