Specialised animal cells
Laura Armstrong & Joe Wolfensohn
Teachers


Contents
Recall Questions
This topic requires prior knowledge of the structure and function of a typical animal cell to understand how adaptations relate to specific functions.
What is the function of the mitochondria?
Aerobic respiration to release energy.
What is the function of the ribosome?
Protein synthesis.
What is the role of the nucleus?
Controls the activity of the cell and contains the DNA.
Topic Explainer Video
Check out this @JoeDoesBiology video that explains specialised animal cells or read the full notes below. Once you've gone through the whole note, try out the practice questions!
Specialised Animal Cells
Specialised cells have adaptations that allow them to perform their specific roles effectively. Differentiation is the process by which a cell becomes specialised. Here are five key examples:
Sperm Cell
Function=>To swim to the egg for fertilisation.
Adaptations:
-
Long tail (flagellum) – for swimming to the egg.
-
Lots of mitochondria – provides energy for movement.
-
Acrosome (enzyme sac) – contains enzymes to break down the egg cell membrane.
-
Haploid nucleus – contains half the number of chromosomes (23).

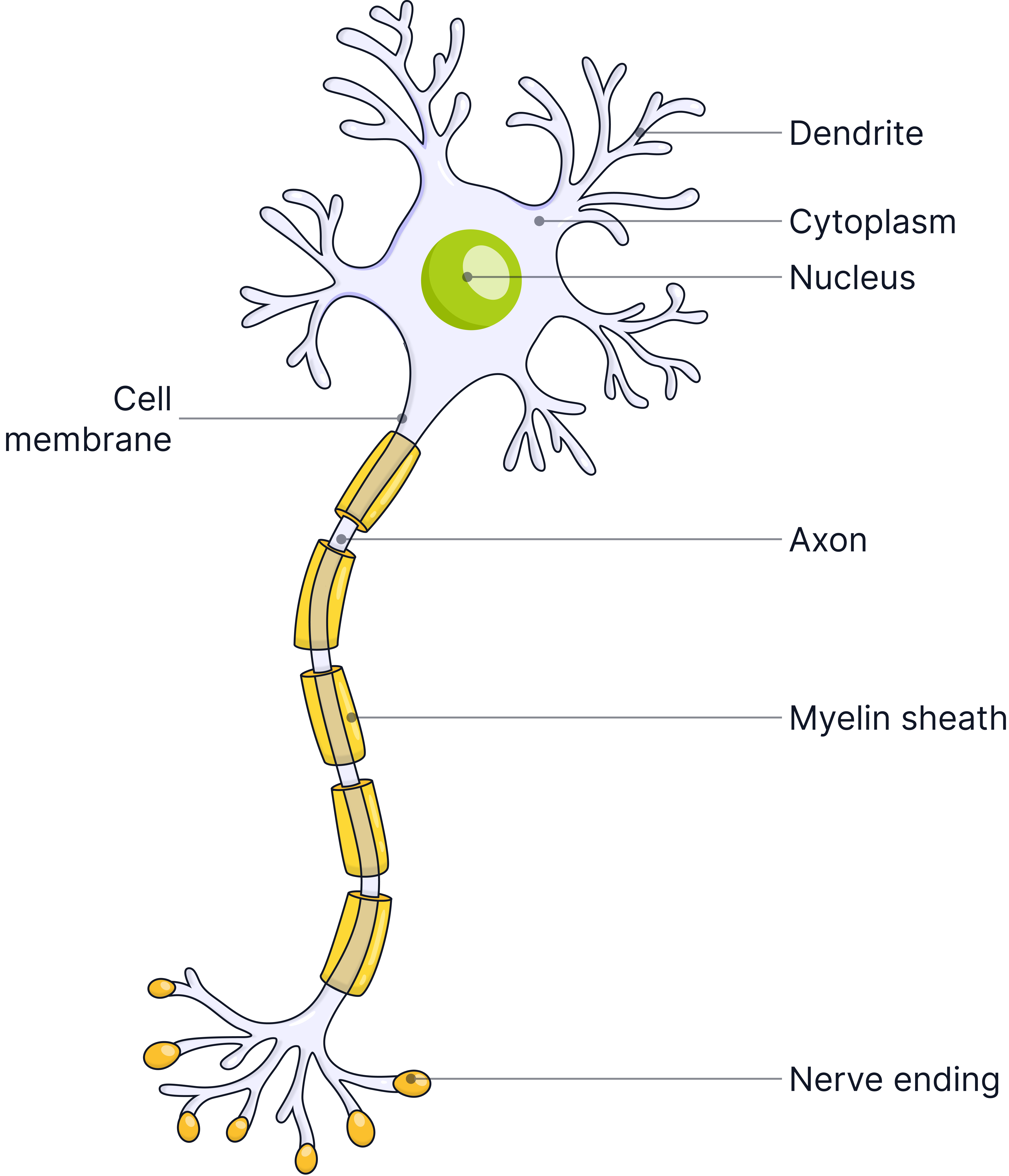
Nerve Cell (Neurone)
Function=>To carry electrical impulses around the body.
Adaptations:
-
Long axon – allows signals to travel long distances.
-
Branched end/Dendrites – connect with other neurones forming a network.
-
Myelin sheath – insulates the axon, speeds up transmission of electrical impulses.
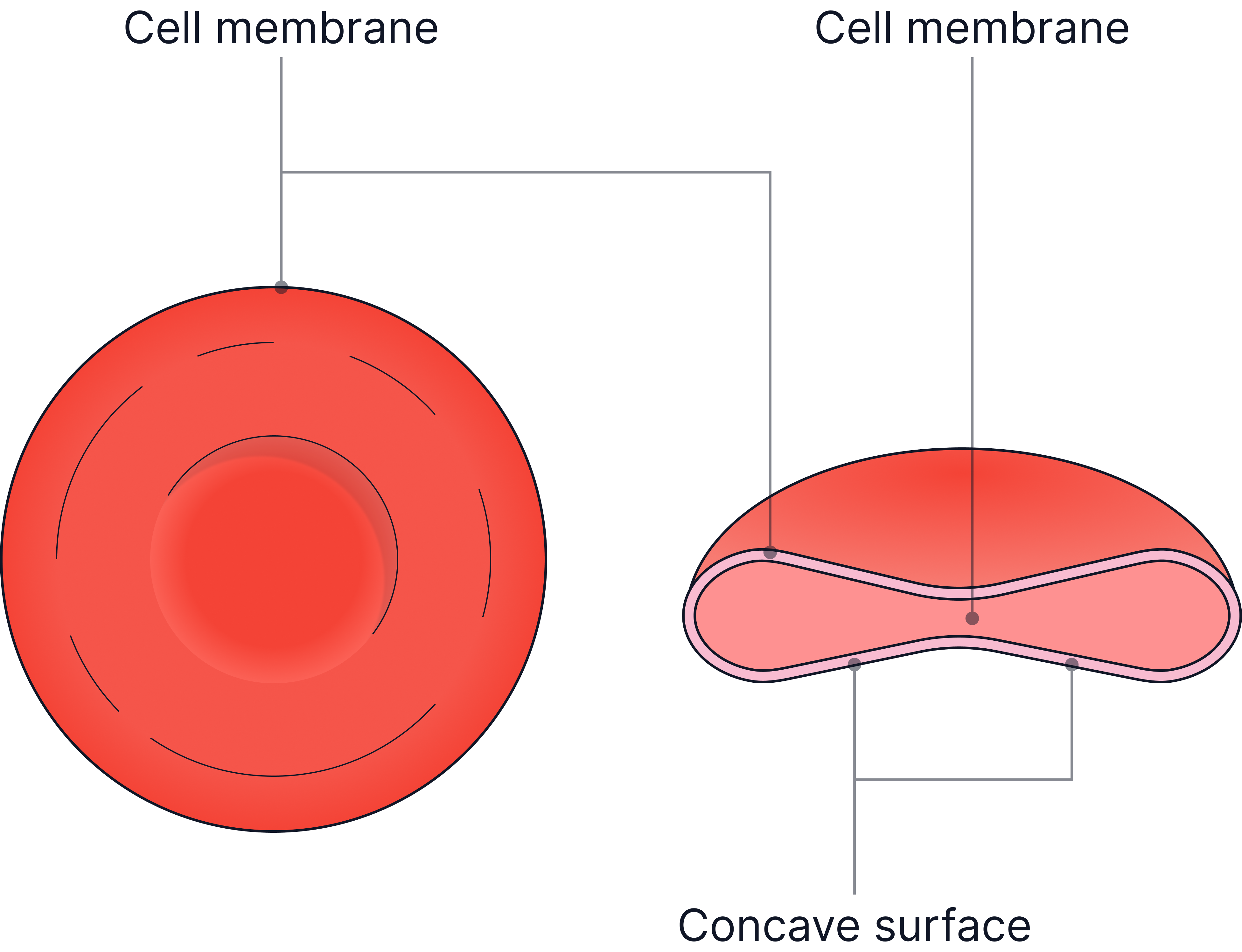
Red Blood Cell
Function=>To carry oxygen from the lungs to tissues.
Adaptations:
-
Biconcave shape – increases surface area for gas exchange.
-
No nucleus – more room for haemoglobin.
-
Contains haemoglobin – binds to oxygen.
-
Small and flexible – fits through narrow capillaries.
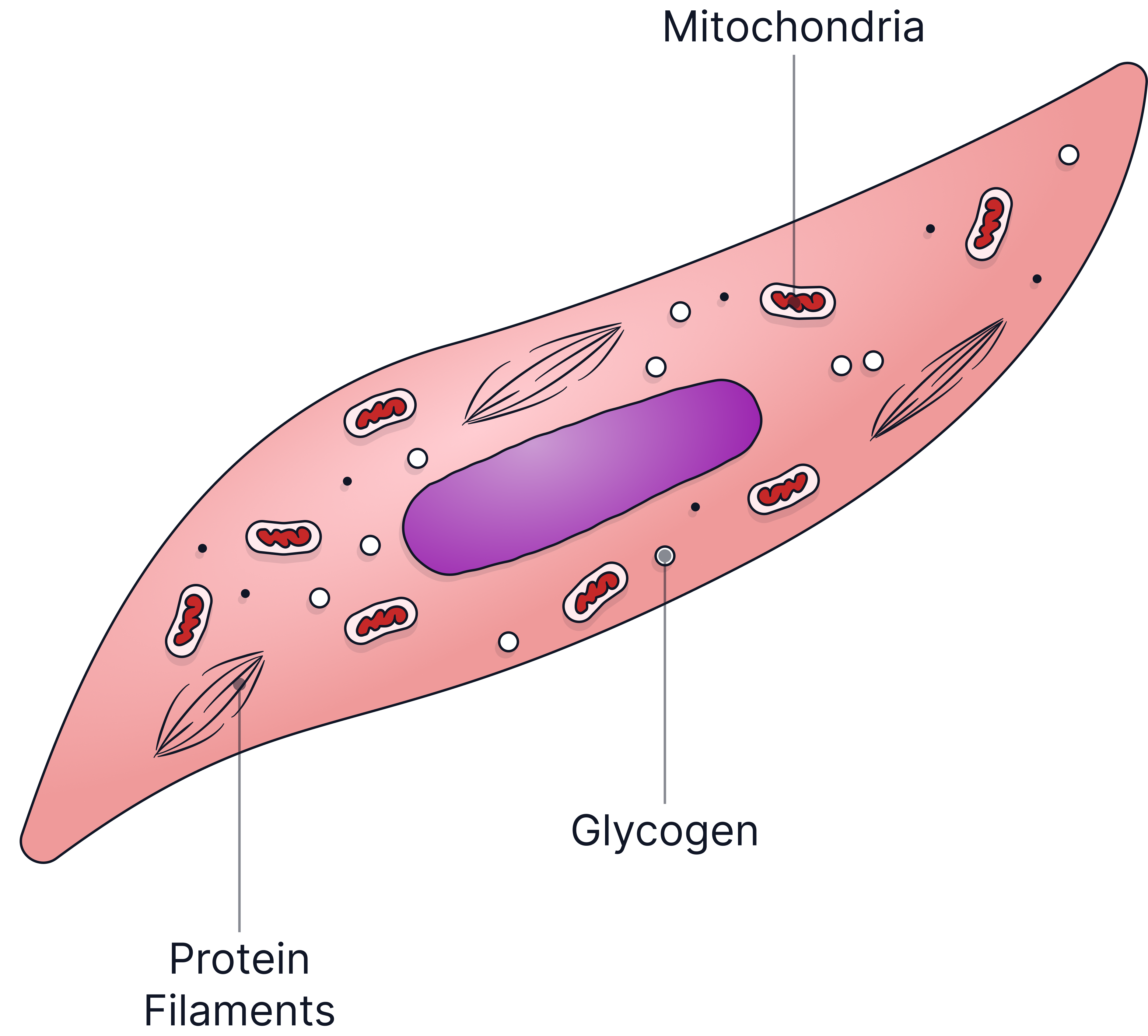
Muscle Cell
Function=>To contract and relax to produce movement in the body.
Adaptations:
-
Long and thin – allows muscle fibres to contract efficiently.
-
Contains many mitochondria – provides lots of energy for contraction.
-
Store glycogen – can be broken down into glucose and used in respiration to release energy.
-
Special protein filaments (actin and myosin) – slide over each other to shorten the cell and cause contraction.
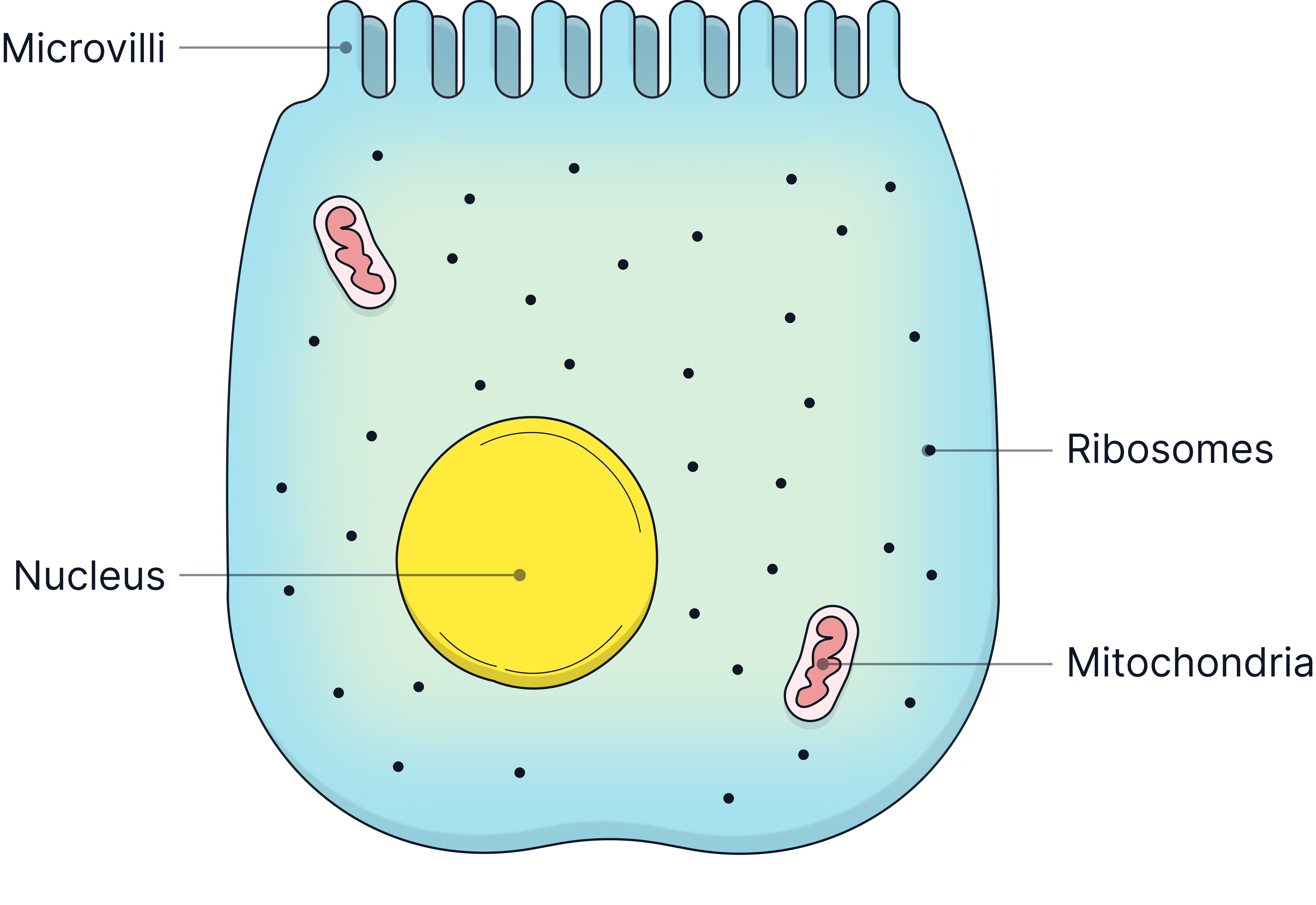
Epithelial Cell of the Small Intestine
Function=>To absorb nutrients from digested food.
Adaptations:
-
Microvilli (folded cell membrane) – increase surface area for maximum absorption.
-
Lots of mitochondria – to release energy for active transport.
-
Lots of ribosomes – To make proteins, eg. enzymes needed for digestion.
Key Term
- Differentiation – the process by which cells become specialised.
Exam Tip
- Always match the adaptation to the function – this is how marks are awarded in exam questions.
Practice Question
Explain two ways in which red blood cells are adapted for their function. (2 marks)
- Red blood cells have no nucleus, allowing more space for haemoglobin.
- Their biconcave shape increases surface area for faster diffusion of oxygen.
More Practice
Try to answer these practice questions from the TikTok videos on your own, then watch the videos to see how well you did!