Waste Management
Laura Armstrong & Joe Wolfensohn
Teachers


Contents
Recall Questions
This topic requires prior knowledge of atmospheric pollutants from GCSE Chemistry.
Why is waste increasing?
Because the human population is growing and people use more resources as living standards rise.
Name one type of pollutant that causes air pollution.
Smoke or acidic gases (such as sulphur dioxide) from burning fossil fuels.
How does pollution affect biodiversity?
Pollution kills plants and animals, which reduces biodiversity.
Topic Explainer Video
Check out this @JoeDoesGCSEBiology video that explains waste management, then read the study notes. Once you’ve gone through them, don’t forget to try the practice questions!
Waste Management
Rapid growth in the human population and an increase in the standard of living mean that increasingly more resources are used and more waste is produced. Unless waste and chemical materials are properly handled, more pollution will be caused.
Types of pollution
1. Water Pollution
- Water pollution happens when waste enters rivers, lakes, or the sea.
- Examples:
- Sewage: Human waste and untreated sewage can enter rivers, adding bacteria that use up oxygen in the water. Fish and other aquatic animals can die due to lack of oxygen for aerobic respiration.
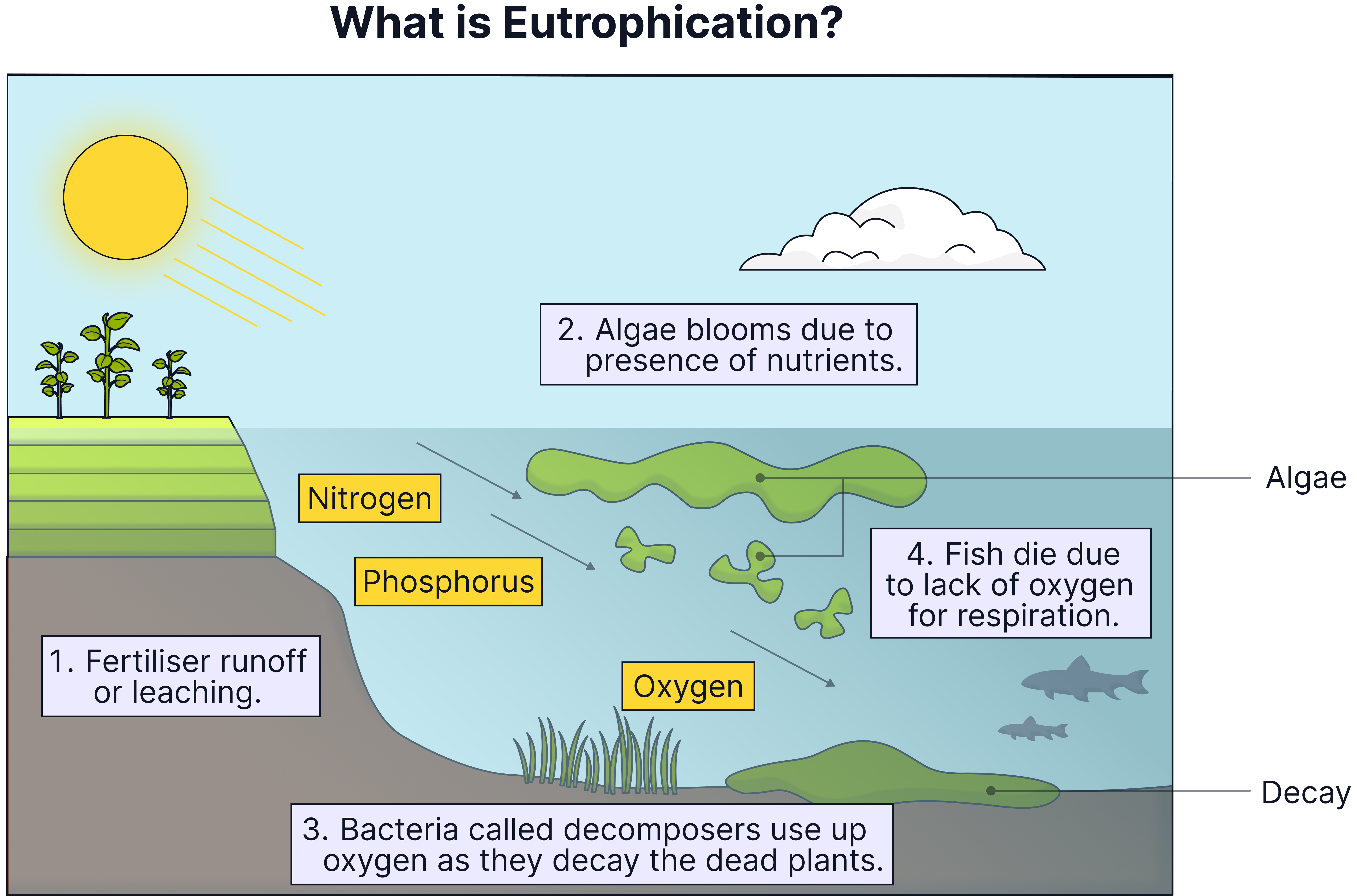
- Fertilisers: Leaching (run-off) from fields can wash fertilisers into water. This causes algal bloom which blocks sunlight. Plants will die from lack of photosynthesis, and decomposers decay the plants. These decomposers use up oxygen in aerobic respiration. This is called eutrophication.
- Toxic chemicals: Factories may leak harmful chemicals or heavy metals (like mercury) into water. This can poison animals and build up in food chains. Farmers may use harmful pesticides and herbicides which run-off into water, these can also build up in food chains.
- Litter and plastics: Thrown into water may be eaten by animals, or trap animals leading to death.
2. Air Pollution
- Air pollution happens when harmful gases or particles are released into the atmosphere.
- Examples:
- Smoke: Burning fossil fuels or wood produces smoke particles that can cause breathing problems (such as asthma) in humans.
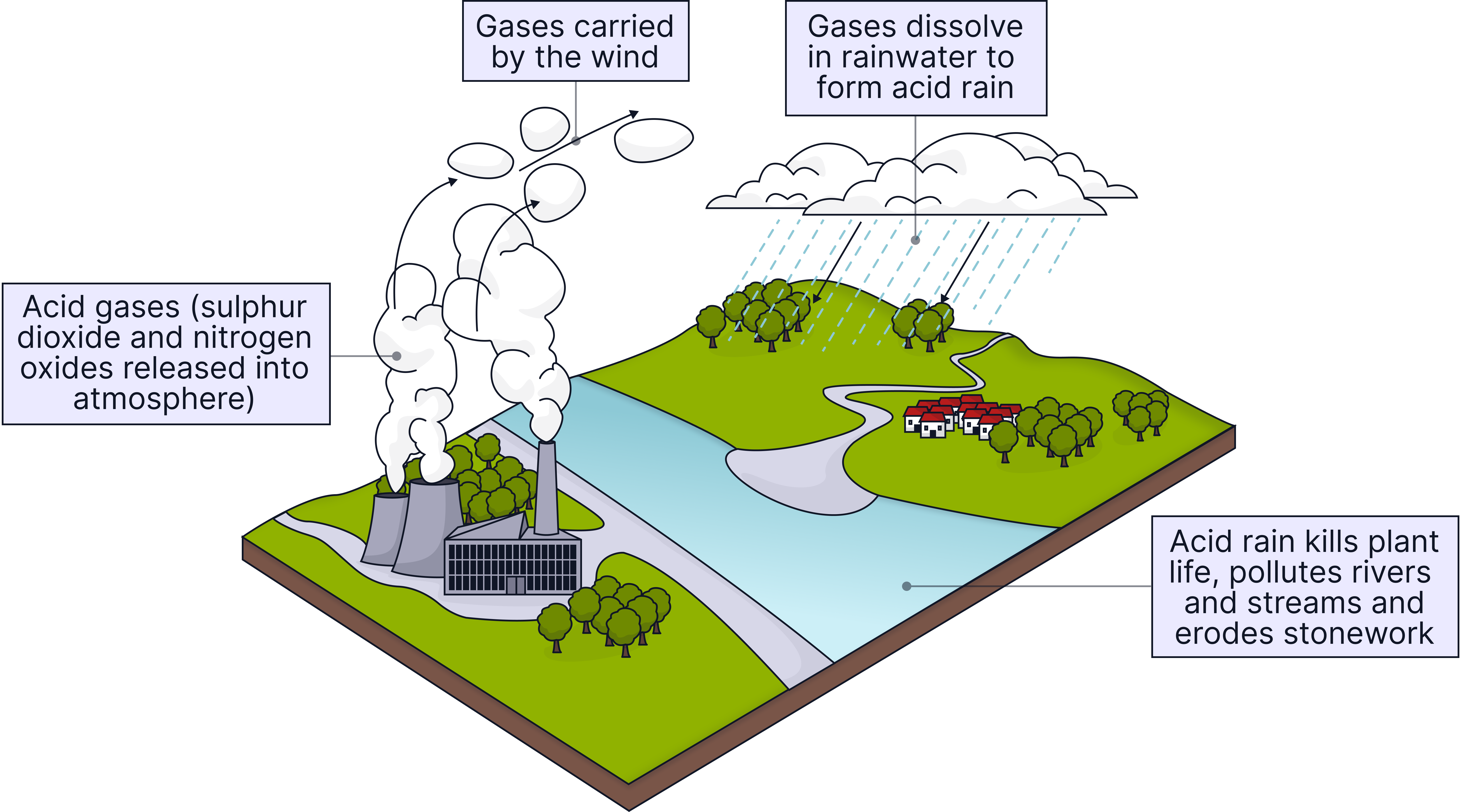
- Acidic gases: Sulphur dioxide from burning coal and oil can mix with rainwater to form acid rain.
- Acid rain damages leaves, causes acidification of lakes which kills fish, and erodes buildings.
3. Land Pollution
- Land pollution is caused by dumping waste or chemicals on the ground.
- Examples:
- Landfill sites: Large amounts of household waste end up in landfill, which can leak chemicals into the soil and groundwater. Methane is also released from landfill sites as food scraps and other organic material are decayed.
- Toxic chemicals: Industrial waste, pesticides, and chemical spills can poison soil, harming plants and animals.
- Some chemicals stay in the soil for a long time, affecting ecosystems for years.

Why Waste Management Matters
- Poor waste management leads to pollution.
- Pollution kills plants and animals, which can reduce biodiversity and disrupt food chains.
- Proper treatment of waste, recycling, and using fewer harmful chemicals help protect ecosystems.
Key Terms & Definitions
- Pollution - The addition of harmful substances to the environment.
- Eutrophication - When fertilisers cause excessive algal growth in water and the death and decay of plants, leading to oxygen depletion.
- Landfill - Large sites where waste is buried.
- Acid rain - Rain that is more acidic than normal due to air pollution from sulphur dioxide.
Exam Tip:
Always give specific examples for each type of pollution (e.g. name a gas or pollutant) and explain the effect on plants, animals, or biodiversity.
Practice Question
Water pollution is a problem for humans and wildlife.
Explain how human activities are polluting rivers, lakes and seas. (6 marks)
Model Answer:
There are many available marking points here. To score 5 or 6 marks you would need examples of a range of different types of water pollution, linked to explanations of their effects.
- more sewage released into rivers / lakes / seas
- leading to lack of oxygen in the water
- leading to animals dying from lack of oxygen for respiration
- fertilisers (used on farms to increase crop yield run into rivers / lakes / seas)
- causes algae to grow
- leading to lack of oxygen in the water
- herbicides / pesticides (used on farms to increase crop yield, run into rivers / lakes / seas)
- build-up in food chains
- toxic chemicals (run into rivers / lakes / seas)
- from factories / industry or power stations
- build-up in food chains
- acid rain formation
- acidification of lakes
- litter / plastics (thrown in rivers / lakes / seas)
- example of effect on living organisms, such as plastics consumed or plastics build up in stomach or plastics get stuck around beaks
- organisms living in rivers / lakes / seas are harmed / die
- oil spills from tankers in oceans
- oil may poison animals or damage their fur / feathers
More Practice
Try to answer these practice questions from the TikTok videos on your own, then watch the videos to see how well you did!