Food chains and webs
Laura Armstrong & Joe Wolfensohn
Teachers


Recall Questions
This topic requires prior knowledge of food chains from KS3 and photosynthesis.
What is always at the start of a food chain?
A producer.
What is a producer?
An organism that makes its own food by photosynthesis, usually a green plant or alga.
What do plants make during photosynthesis?
They make glucose, which can be used to produce proteins, starch, cellulose, lipids and is used in respiration.
Topic Explainer Video
Check out this @JoeDoesBiology video that explains food chains and webs, then read the study notes. Once you’ve gone through them, don’t forget to try the practice questions!
Producers and Feeding Relationships
Producers
-
The original source of energy for all food chains is the Sun
-
Photosynthetic organisms (green plants and algae) are called producers.
-
They make glucose using light energy from the sun, carbon dioxide and water in photosynthesis.
-
Glucose is turned into new plant material called biomass which is the source of energy for all other organisms in the ecosystem.
-
This means all life depends on producers to make food.
Feeding Relationships
-
Feeding relationships are shown as food chains.
-
Each stage of a food chain is called a trophic level.
-
All food chains start with a producer.
-
Next come consumers:
-
Primary consumers: herbivores that eat the producer (e.g. rabbits, caterpillars).
-
Secondary consumers: animals that eat the primary consumers.
-
Tertiary consumers: animals that eat the secondary consumers.
What Do the Arrows in a Food Chain Represent?
-
The arrows in a food chain show the direction of energy flow.
-
They point from the food to the feeder - for example:
-
Grass → Rabbit
-
This means energy stored in the grass passes to the rabbit when it eats the grass.
-
Always draw your arrows the right way round in diagrams!
Example:
If you draw Grass → Rabbit → Fox, remember:
-
Sunlight gives energy to grass (producer).
-
Rabbits eat grass so energy from the grass is transferred to the rabbits.
-
Foxes eat rabbits so energy from the rabbits is transferred to the foxes.
Predators and Prey
-
A predator kills and eats other animals.
-
The animals that are eaten are called prey.
-
Predator and prey numbers are linked - if prey numbers drop, predator numbers usually drop too.
Food Webs
-
Food webs show many connected food chains in a community.
-
They show how species are interdependent - if one species is removed, it can affect the whole web.
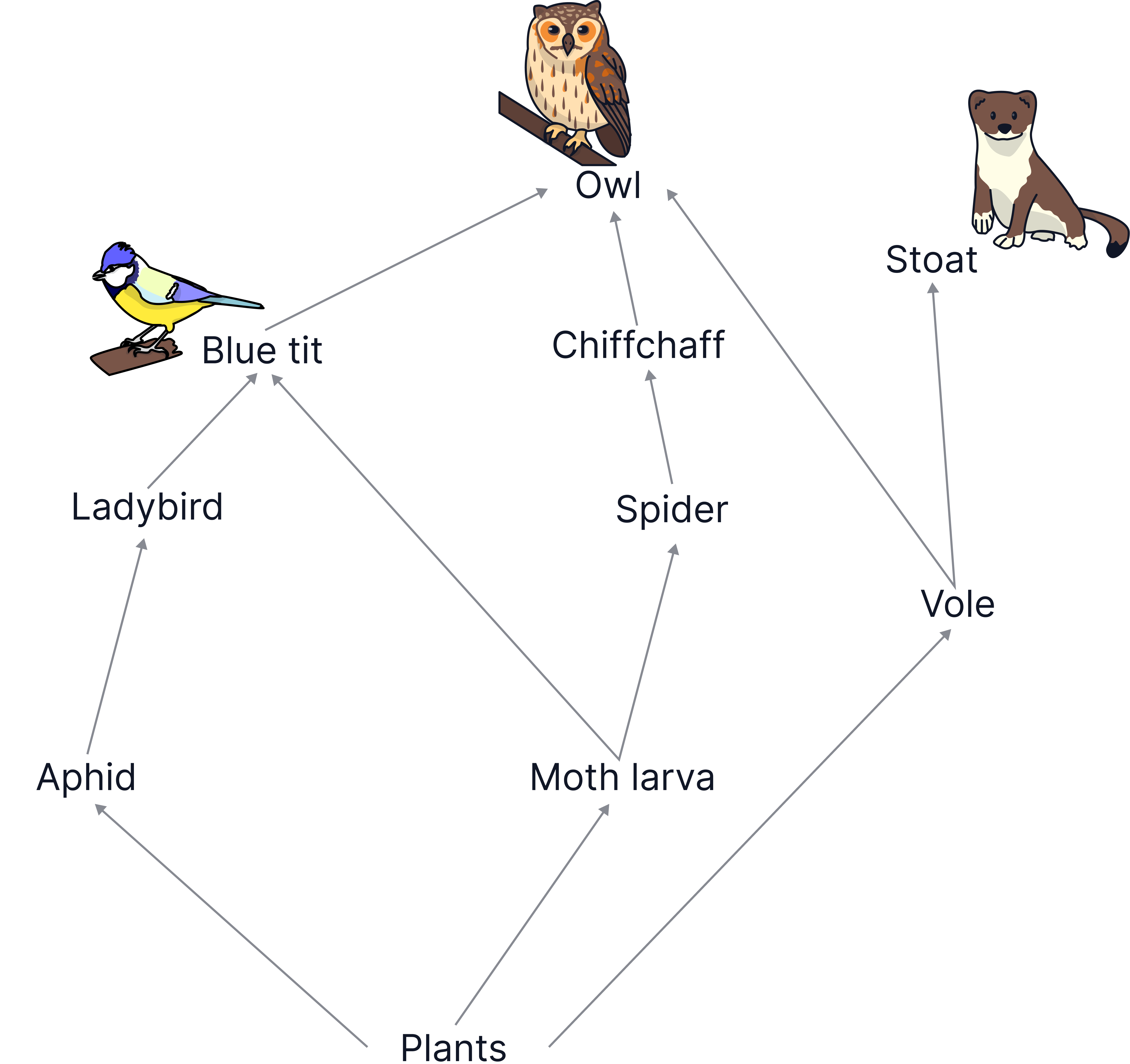
In this food web, the vole, the moth larva and the aphid are primary consumers (as they eat the plants (the producers).
The spider, the stoat, the ladybird and the blue tit are secondary consumers.
The blue tit is also a tertiary consumer, as is the chiffchaff.
The owl and the stoat could be described as top predators, or apex predators, as they are at the top of the food chain.
Interpreting food webs
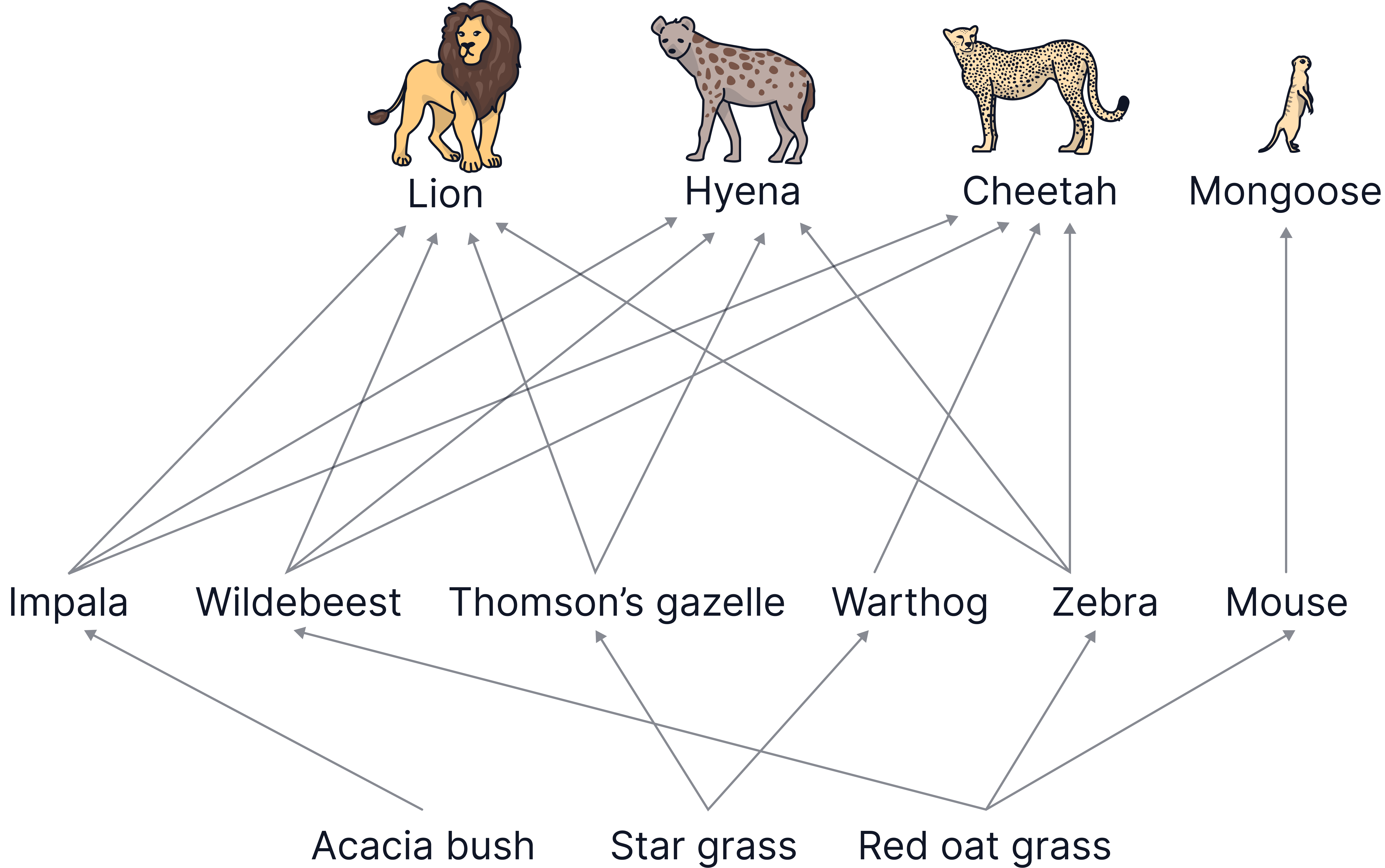
Here is a more complex food web.
You may be asked questions such as:
What would happen if you remove all the impala?
-
Numbers of acacia bushes may increase, as fewer impala are eating them. Numbers of lions, hyenas and cheetahs may decrease as they have less food to eat. However, they may just eat more of the other primary consumers, so their numbers may not change much.
The cheetah is an endangered species. If the number of lions increases this could affect the cheetah population. Why?
-
The cheetah population could decrease, as they are in competition with the lions for food. If there are more lions eating the zebra, the impala and the wildebeests, the cheetahs may starve.
Key Terms
-
Producer – An organism that makes its own food by photosynthesis.
-
Consumer – An organism that eats other organisms.
-
Predator – A consumer that kills and eats other animals.
-
Prey – An animal that is eaten by a predator.
-
Food chain – A diagram showing the transfer of energy in an ecosystem.
-
Food web – Lots of connected food chains showing feeding relationships.
-
Herbivore – An animal that only eats plants.
-
Carnivore – An animal that only eats other animals (meat).
-
Omnivore – An animal that eats both plants and animals.
Exam Tip
Always start food chains with a producer, then label the levels clearly (primary, secondary, tertiary consumer). Make sure your arrows are going the right way to show the transfer of energy.
Practice Question
Here is a food web.
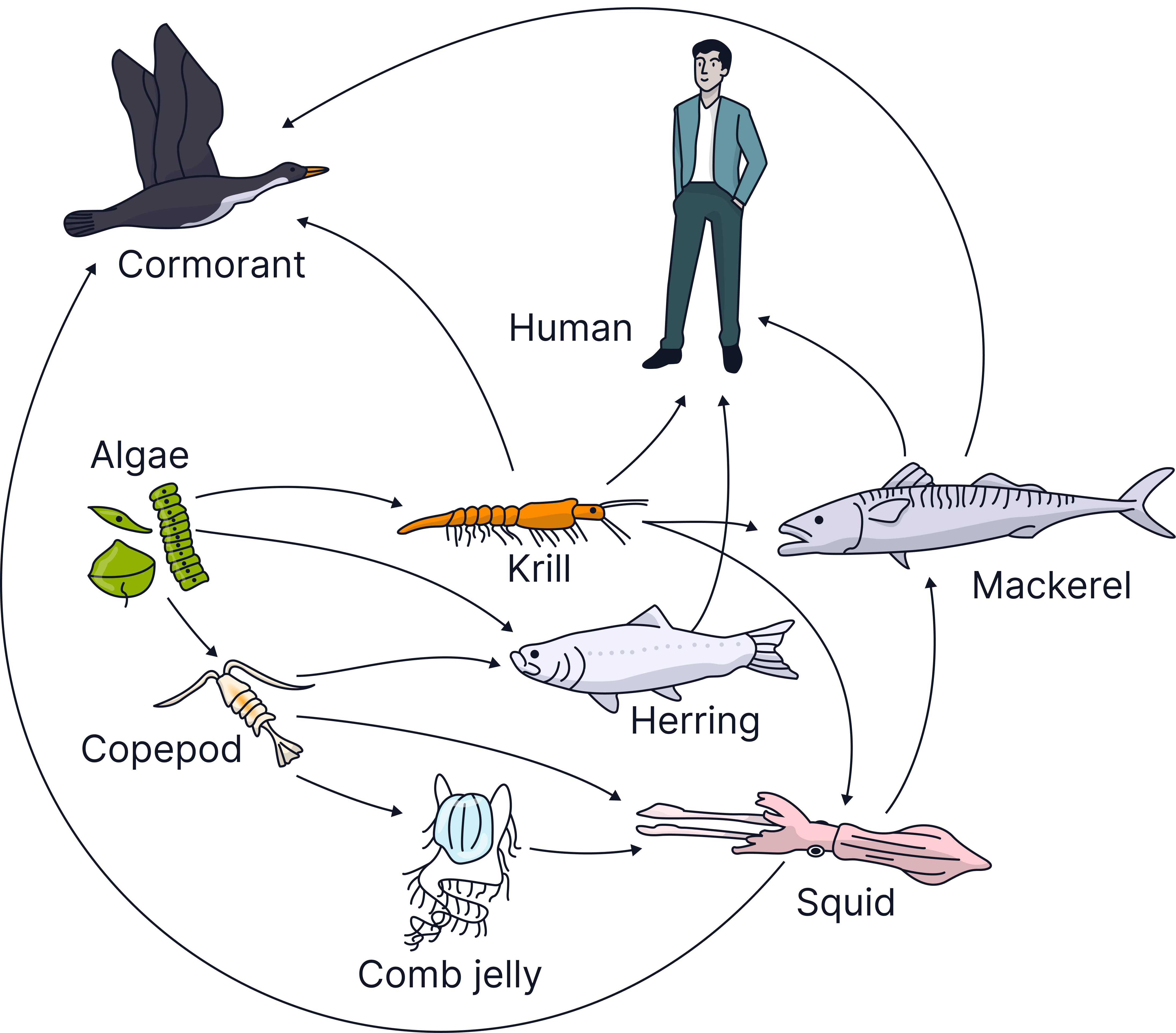
a) Describe how the algae get energy. (2 marks)
b) Name one primary consumer in the food web. (1 mark)
c) Name one producer in the food web. (1 mark)
d) The different food chains have different numbers of organisms. Use the food web to draw a food chain with five organisms, including the human. (1 mark)
a) From light / sunlight
Absorbed by chlorophyll / chloroplasts in photosynthesis
b) Krill / herring / copepod
c) Algae
d) algae 🡪 krill or copepod 🡪 squid 🡪 mackerel 🡪 human
More Practice
Try to answer these practice questions from the TikTok videos on your own, then watch the videos to see how well you did!