Triple Science Only - Maintaining water and nitrogen balance
Laura Armstrong & Joe Wolfensohn
Teachers


Recall Questions
This topic requires prior knowledge of osmosis and digestion of proteins.
What is osmosis?
The movement of water from a dilute solution to a more concentrated solution across a partially permeable membrane.
Why can too much water entering or leaving cells be dangerous?
Cells can swell and burst or shrink, so they can’t function properly.
What is the product of protein digestion?
Amino acids.
Topic Explainer Video
Check out this @Lauradoesbiology video that explains maintaining water and nitrogen balance, then read the study notes. Once you’ve gone through them, don’t forget to try the practice questions!
Water Balance and Osmosis
-
The body must maintain a constant water level for cells to function.
-
Water moves in and out of cells by osmosis.
-
If the concentration of water in the blood changes, it affects the water movement in and out of cells:
-
Too much water in the blood: water enters cells by osmosis → cells swell and may burst.
-
Too little water in the blood: water leaves cells by osmosis → cells shrink and become dehydrated.
-
Therefore, water levels must be carefully regulated.
How Water Is Lost from the Body
|
Route |
Type of Loss |
Can water loss be controlled? |
|---|---|---|
|
Lungs (exhalation) |
Water vapour is lost in exhaled breath. |
No |
|
Skin (sweat) |
Water evaporates from the skins surface to cool the body. |
No |
|
Kidneys (urine) |
Water is lost in urine produced the kidneys |
Yes (controlled by kidneys) |
Only the kidneys can regulate how much water is removed from the body.
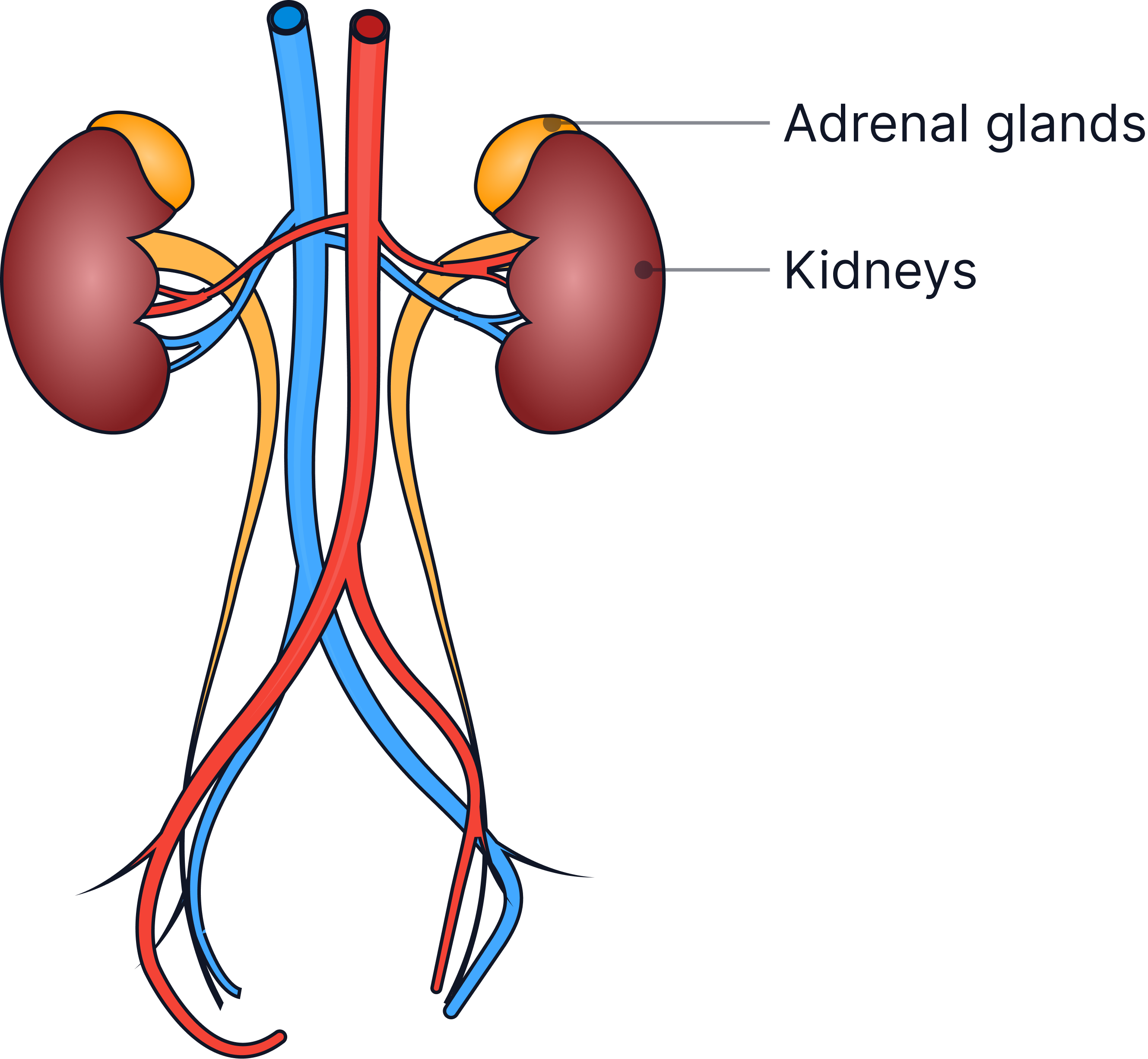
The Role of the Kidneys
The kidneys filter the blood and produce urine.
-
They filter the blood to remove:
-
Urea
-
Mineral ions (such as sodium ions)
-
Water
-
Glucose
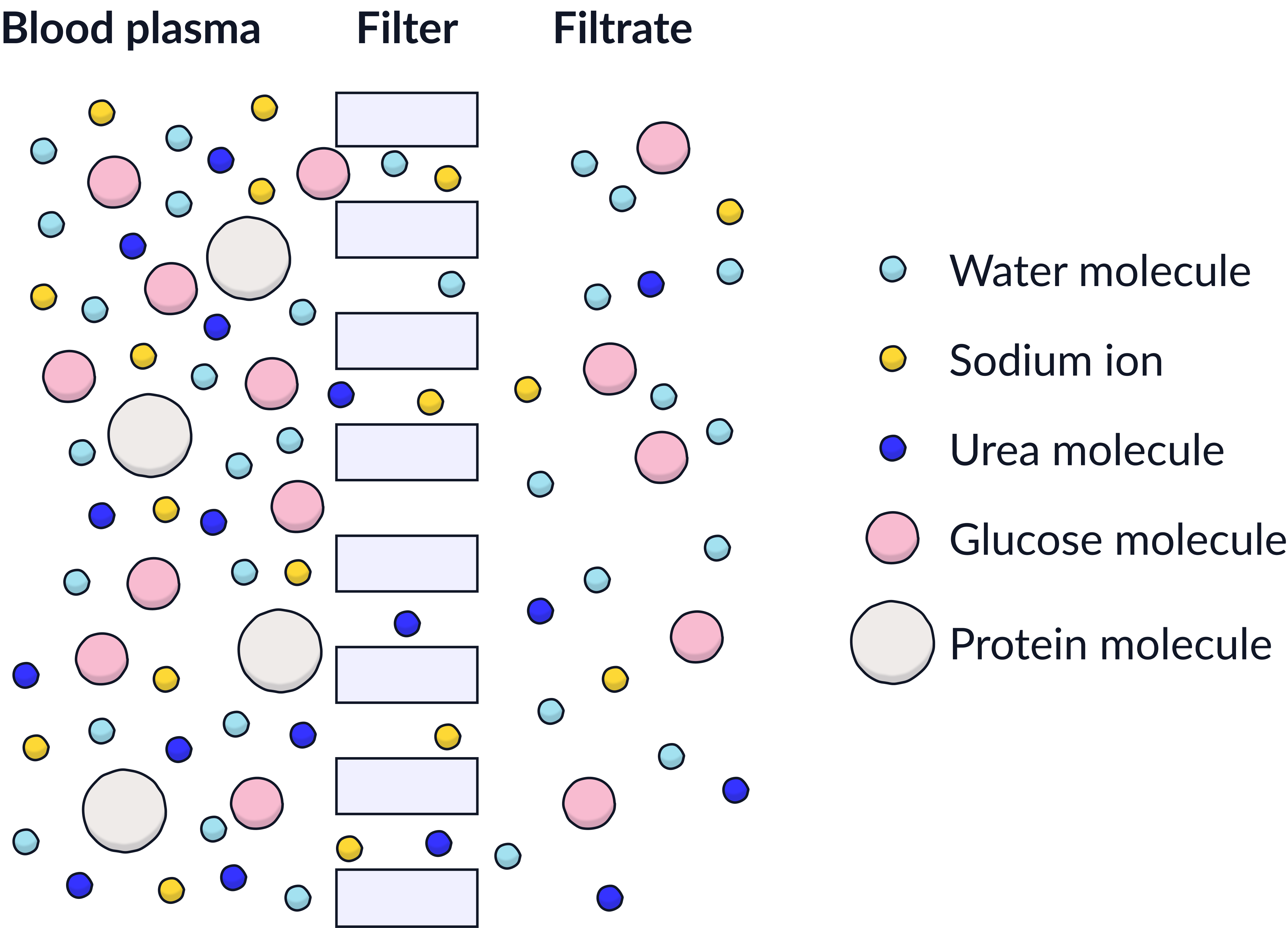
These substances are small enough to pass through the filters in the kidneys. They will leave the blood and pass into the kidneys tubules, forming the filtrate.
Substances such as proteins and blood cells are too large to pass through the filters in the kidneys so these substances will remain in the blood.
-
They perform selective reabsorption:
-
All glucose is reabsorbed (goes back into the blood from the filtrate).
-
The amount of water and ions reabsorbed varies depending on the body’s needs.
-
They produce urine, which is sent to the bladder.
-
Urine will contain
-
Urea
-
Excess mineral ions
-
Excess water
-
Higher Tier Only
Nitrogen Balance and Urea
-
Proteins are broken down into amino acids during digestion.
-
The body cannot store excess amino acids.
-
In the liver, excess amino acids are deaminated:
-
The amino group is removed to form ammonia.
-
Ammonia is highly toxic, so it's immediately converted into urea.
-
Urea is transported to the kidneys where it is filtered from the blood and excreted in urine.
-
Urea is still toxic in large amounts, but less so than ammonia.
Key Terms
- Osmosis - The movement of water from a dilute to a concentrated solution across a partially permeable membrane.
- Selective reabsorption - Process in the kidneys where useful substances (like glucose and some water/ions) are reabsorbed into the blood.
- Deamination - The process in the liver where excess amino acids are broken down into ammonia, which is then converted into urea. (HT only)
- Urea - A toxic waste product formed in the liver from the breakdown of excess amino acids.
- Urine - A liquid produced by the kidneys that contains urea, excess water, and excess ions for excretion.
Exam Tips
- Don’t confuse the roles of the liver and the kidneys.
- The liver produces urea from excess amino acids.
- The kidneys filter the blood to remove urea and produce urine.
Practice Question
Describe what happens to glucose, protein and urea in the kidneys. (4 marks)
-
glucose and urea are filtered out of the blood.
-
protein is not filtered out of the blood as it is too large.
-
all glucose reabsorbed / goes back into the blood.
-
urea passes out in urine.
More Practice
Try to answer the practice question from the TikTok video on your own, then watch the video to see how well you did!