Equations Needed For GCSE Biology
Laura Armstrong
Teacher

Contents
Topic Explainer Video
Check out this @lauradoesGCSEbiology video that explains equations needed for GCSE Biology, then read the study notes. Once you’ve gone through them, don’t forget to try the practice questions!
Equations Needed For GCSE Biology
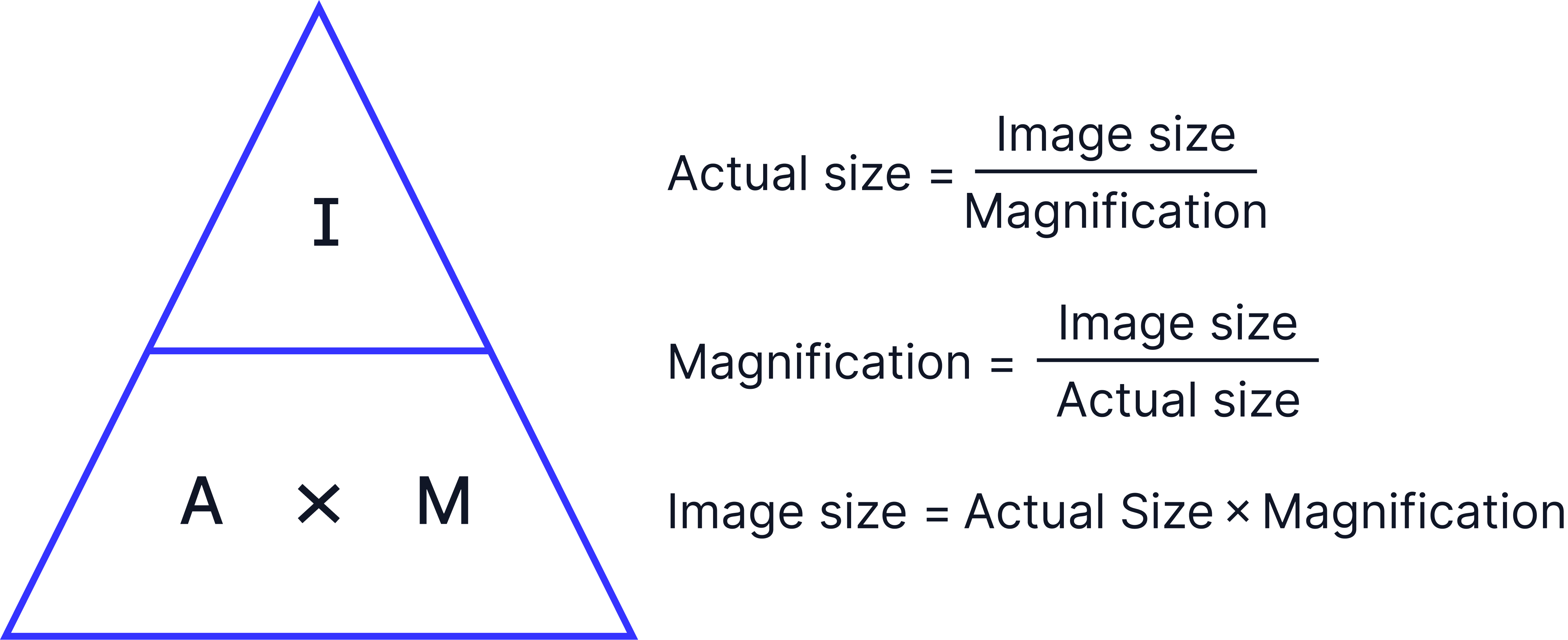
1. Magnification:
- Magnification = Image size / actual size
- You'll need to be able to measure the image size using a ruler, in mm, and convert this measurement to μm.
- You’ll need to be able to rearrange this equation. For example, to find the actual size you would use: Image size / magnification.
2. Total Magnification:
- Total Magnification = Eyepiece lens magnification x objective lens magnification.
- This equation helps calculate the total magnification when using a microscope with these two lenses.
3. Rates of Reaction:
- Rate of reaction = Change in value / Change in time.
- This formula is used to quantify how quickly a reaction is occurring, which can be applied to various biological processes, such as enzyme activity or decomposition.
- When finding rate from a graph use: change in y / change in x.
4. Body Mass Index (BMI):
- BMI = Weight / Height²
- Weight must be in kg and height must be in metres.
- BMI is a measure that helps assess whether someone's weight is healthy for their height.
5. Aerobic Respiration:
- Word equation: Glucose + Oxygen 🡪 Carbon dioxide + Water
- Chemical equation: C6H12O6 + 6O2 🡪 6CO2 + 6H2O
6. Anaerobic Respiration:
- Word equation (animals): Glucose 🡪 Lactic acid
- Word equation (plants and fungi): Glucose 🡪 Ethanol + Carbon dioxide
7. Photosynthesis:
- Word equation: Carbon dioxide + Water 🡪 Glucose + Oxygen (requiring light energy)
- Chemical equation: 6CO2 + 6H2O 🡪 C6H12O6 + 6O2
8. Higher tier only
The Inverse Square Law:
- Light intensity ∝ 1 / d2
Where:
- d = distance from the light source (in cm or m)
- Light intensity and distance are inversely related – when distance doubles, light intensity drops to a quarter.
Exam Tips:
Units are always really important in Biology calculation questions.
Pay close attention to the units used in a question (e.g., μm, mm, kg, m, etc.) and ensure you convert them correctly when needed for your answer.
Check out the study note on converting units for more help with this!
Practice Questions
The graph shows the total volume of water lost from a plant over 6 hours.
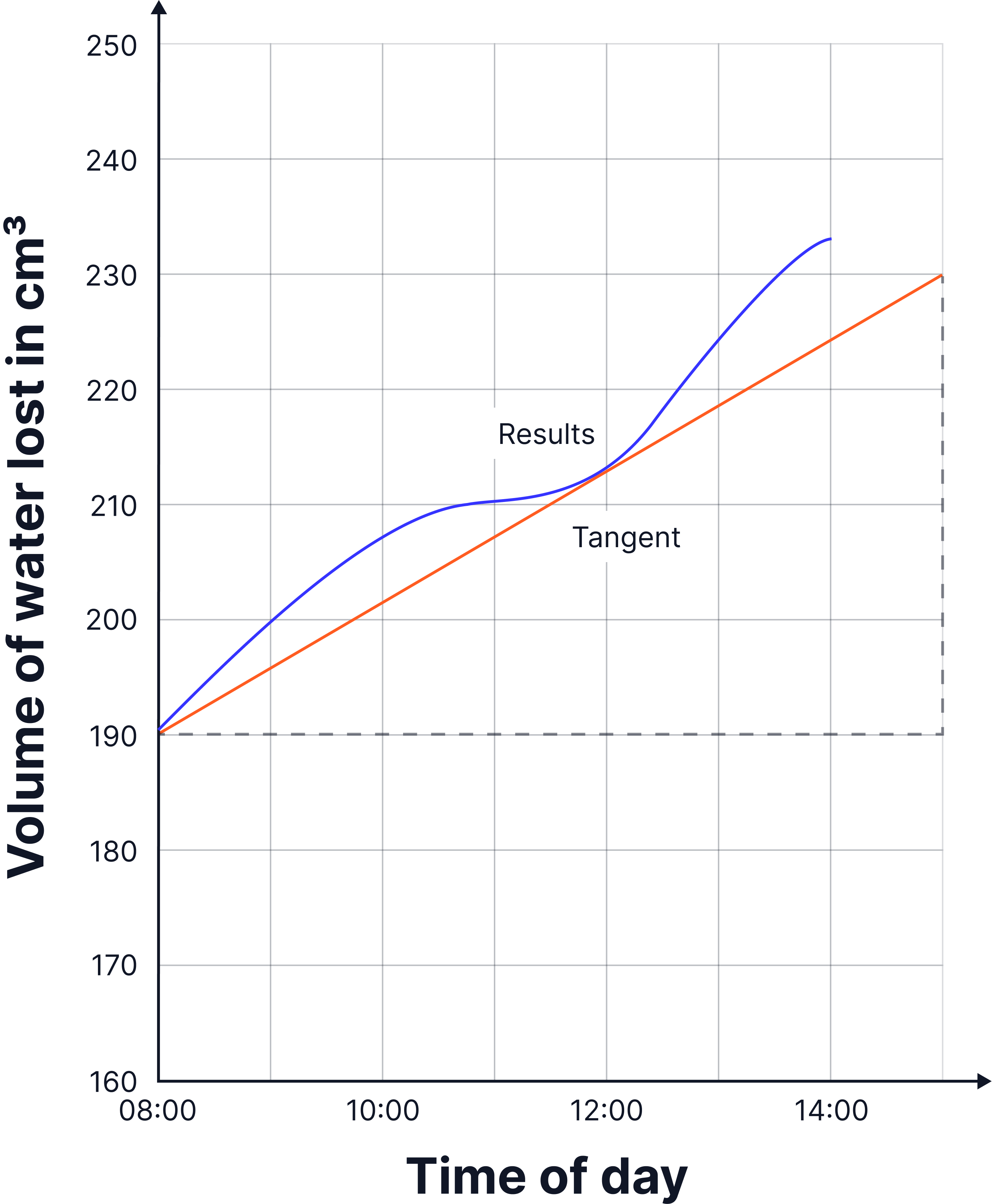
Determine the rate of water loss at 12:00.
Use the tangent drawn on the graph above. (4 marks)
Give your answer:
• in cm3 per minute
• in standard form
Model answer:
Use the equation change in y / change in x
Change in y = 230 – 190 = 40
Change in x = 8am to 3pm = 7 hours
40 ÷ 7 (in hours)
5.71 (per hour)
Correct conversion to minutes 5.71 / 60 = 0.0952
answer in standard form = 9.5 x 10-2
More Practice
Try to answer the practice question from the TikTok video on your own, then watch the video to see how well you did!