Triple Science Only - The Eye
Laura Armstrong & Joe WolfensAssistant Head of Biologyohn
Teachers


Contents
Recall Questions
This topic requires basic prior knowledge of the eye and the nervous system.
Which part of the eye does light enter through?
The pupil.
What is a stimulus?
A change in the environment that is detected by a receptor (such as a change in light intensity).
What is the function of the retina?
The retina contains light-sensitive receptor cells that detect light and send electrical impulses to the brain.
Topic Explainer Video
Check out this @Lauradoesbiology video that explains the eye, then read the study notes. Once you’ve gone through them, don’t forget to try the practice questions!
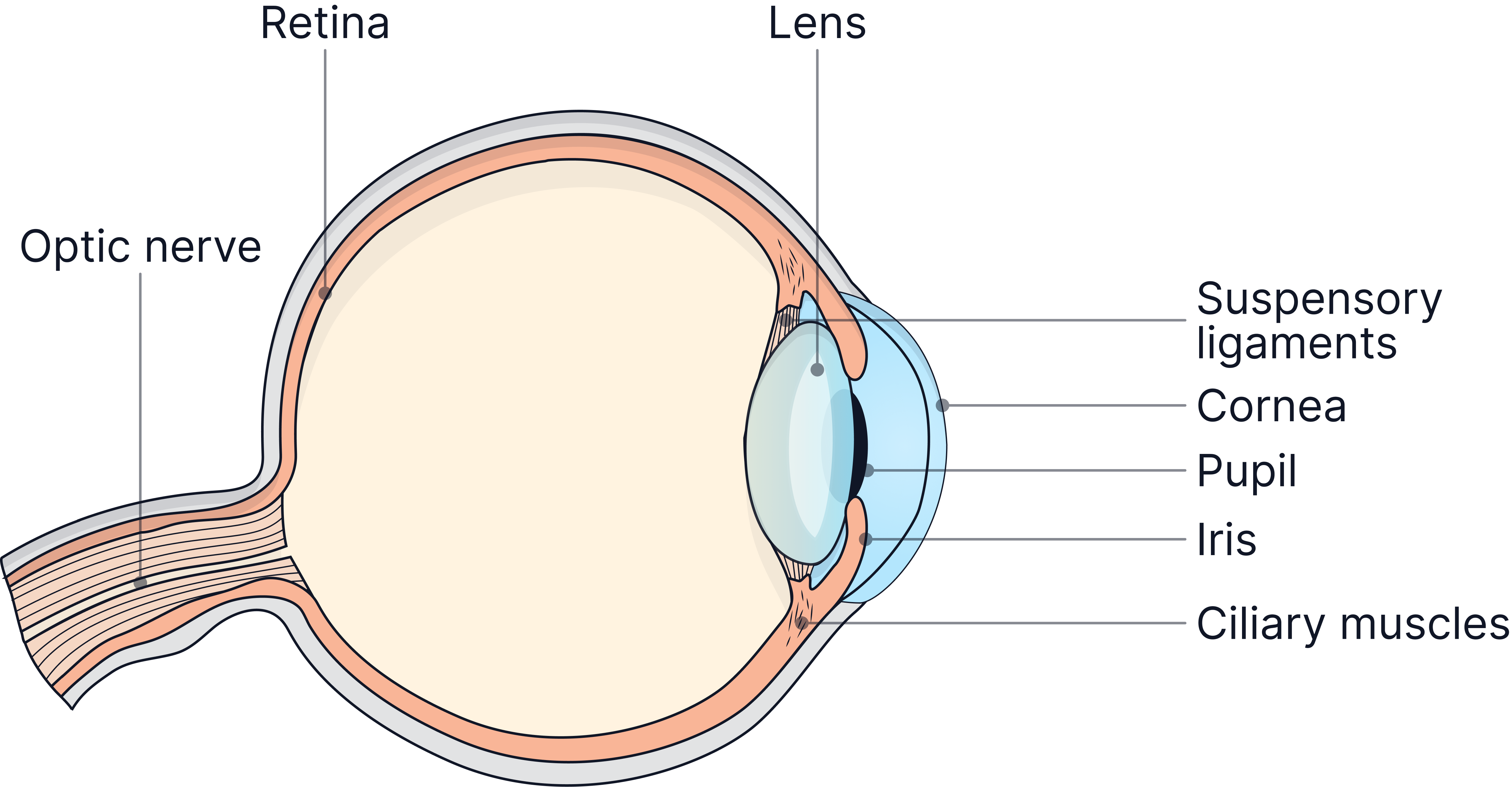
Structure of the Eye and Functions
|
Part |
Function |
|---|---|
|
Retina |
Contains light receptor cells (photoreceptors) that detect a change in light intensity and convert light energy into electrical impulses. |
|
Cornea |
Transparent front layer that bends (refracts) light into the eye. |
|
Iris |
Contains muscles that control the diameter of the pupil. |
|
Pupil |
Hole in the centre of the iris through which light enters. |
|
Lens |
Focuses light onto the retina by changing shape. |
|
Ciliary muscles |
Contract or relax to change the shape of the lens. |
|
Suspensory ligaments |
Hold the lens in place and work with ciliary muscles during accommodation. |
|
Optic nerve |
Carries electrical impulses from the retina to the brain. |
|
Sclera |
Tough outer layer that protects the eye. |
Adjusting to Bright and Dim Light (Pupil Reflex)
This involves muscles in the iris- there are two sets of muscles in the iris, the radial muscles and the circular muscles.
-
In bright light:
-
Radial muscles relax, circular muscles contract → pupil constricts (gets smaller) to let in less light.
-
-
In dim light:
-
Radial muscles contract, circular muscles relax → pupil dilates (gets larger) to let in more light.
-
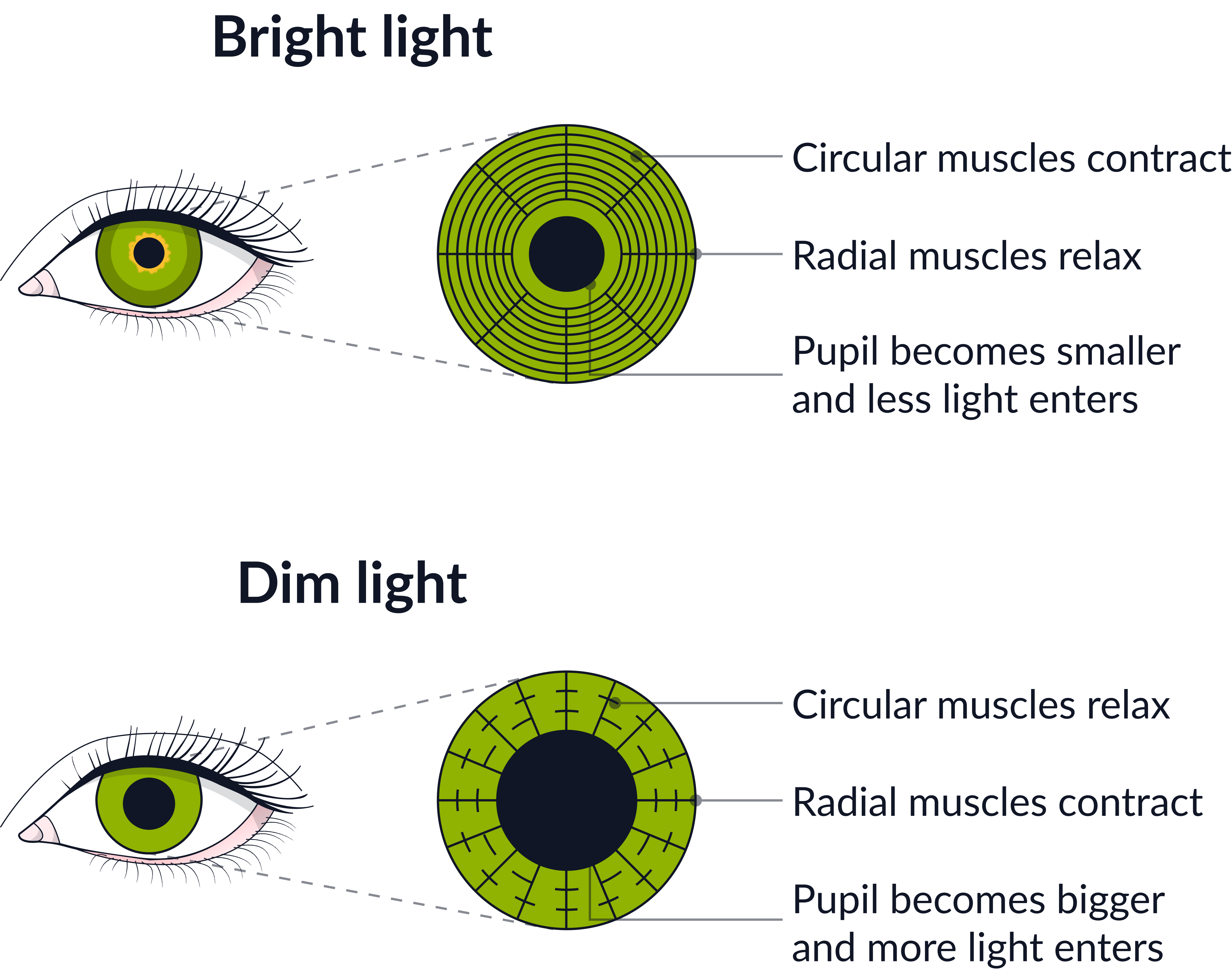
This protects the retina and helps you see in different light conditions.
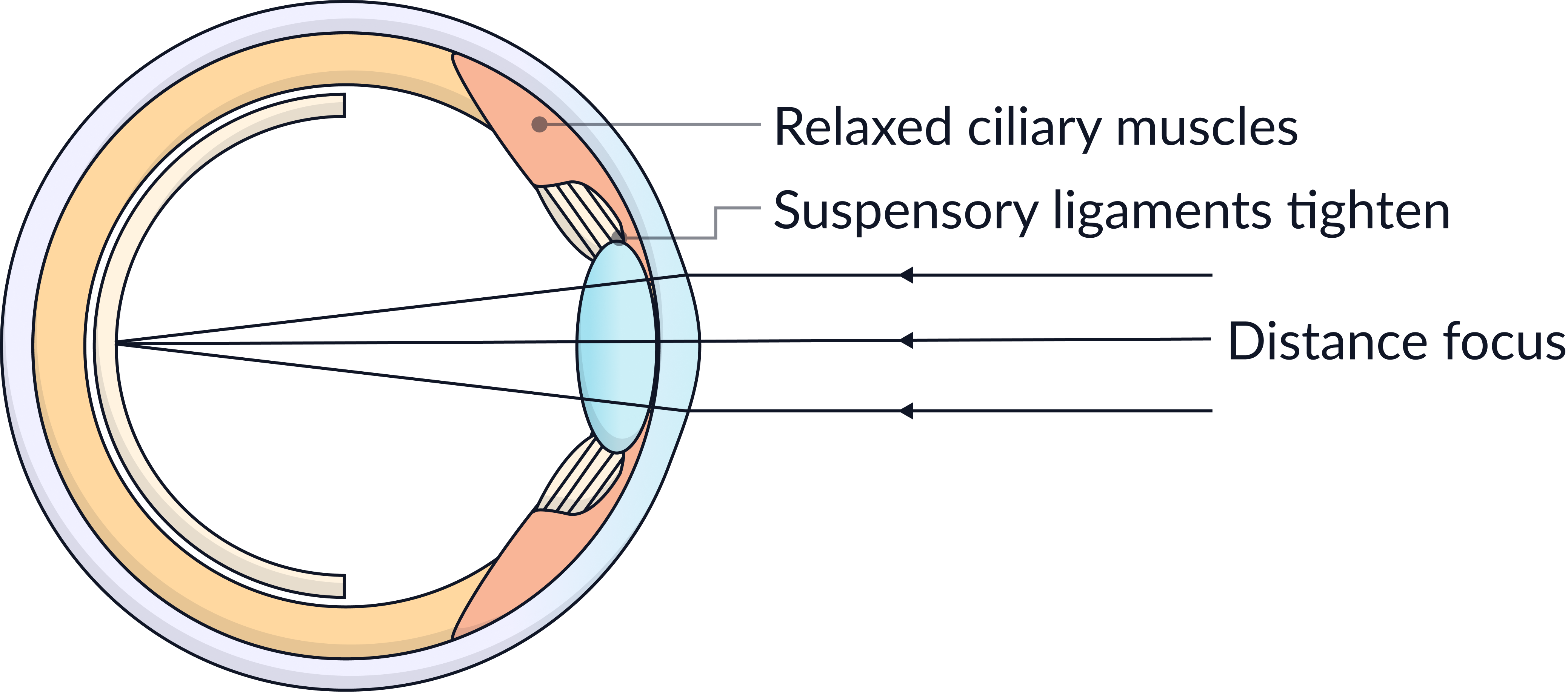
Accommodation – Focusing on Near and Distant Objects
The eye can change the shape of the lens to help focus on near or distant objects. This is called accommodation. This process involves the suspensory ligaments and the ciliary muscles that are connected to the lens.
To focus on distant objects
1. Ciliary muscles relax.
2. Suspensory ligaments tighten.
3. The lens becomes less curved.
4. Light is refracted by a lesser amount so it focuses on the retina.
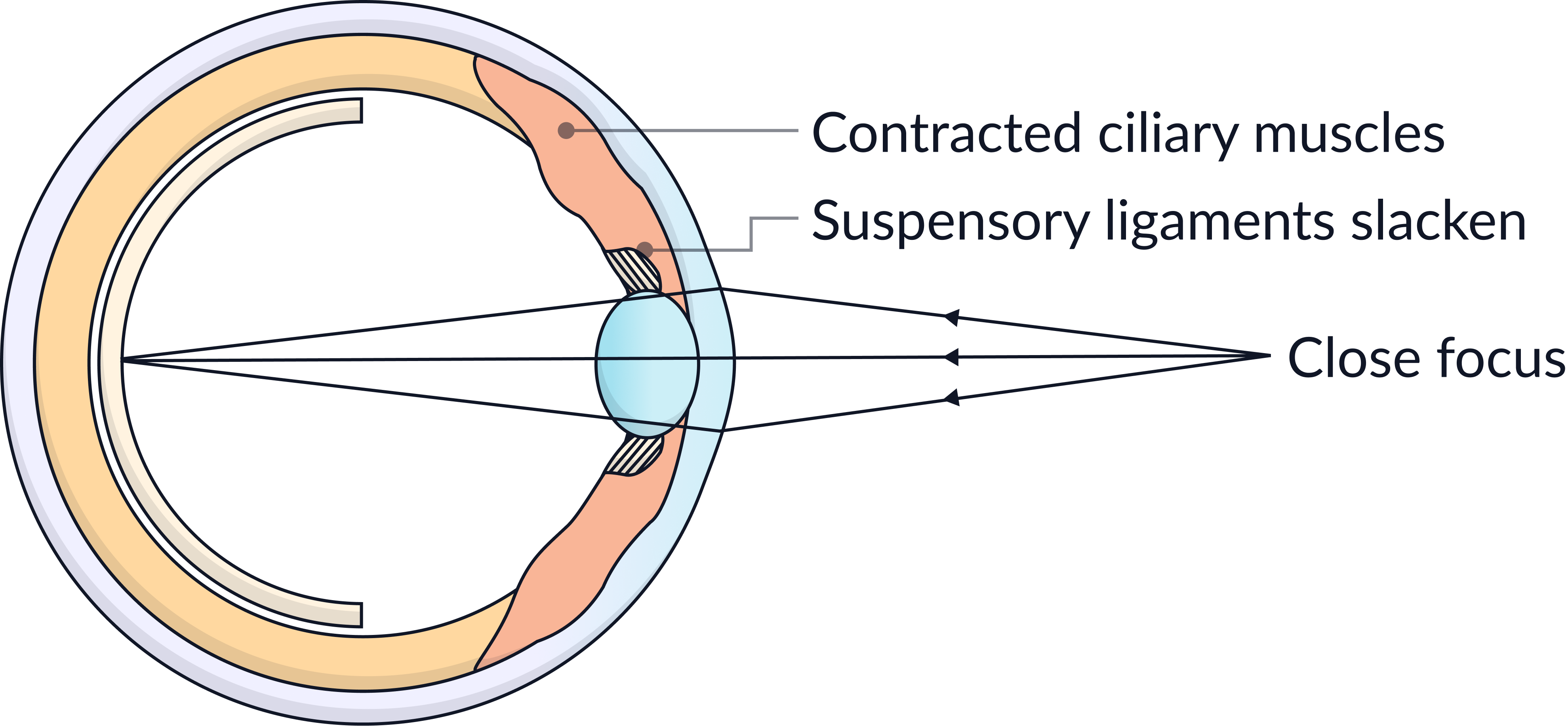
To focus on near objects
1. Ciliary muscles contract.
2. Suspensory ligaments slacken / loosen.
3. The lens becomes more curved.
4. Light is refracted by a greater amount so it focuses on the retina.
Accommodation in summary
|
Object Distance |
Ciliary Muscles |
Suspensory Ligaments |
Lens Shape |
Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Distant |
Relaxed |
Tight |
Thinner / Less curved |
Light is refracted less |
|
Near |
Contracted |
Slack |
Fatter / More curved |
Light is refracted more |
Vision Defects and Treatment
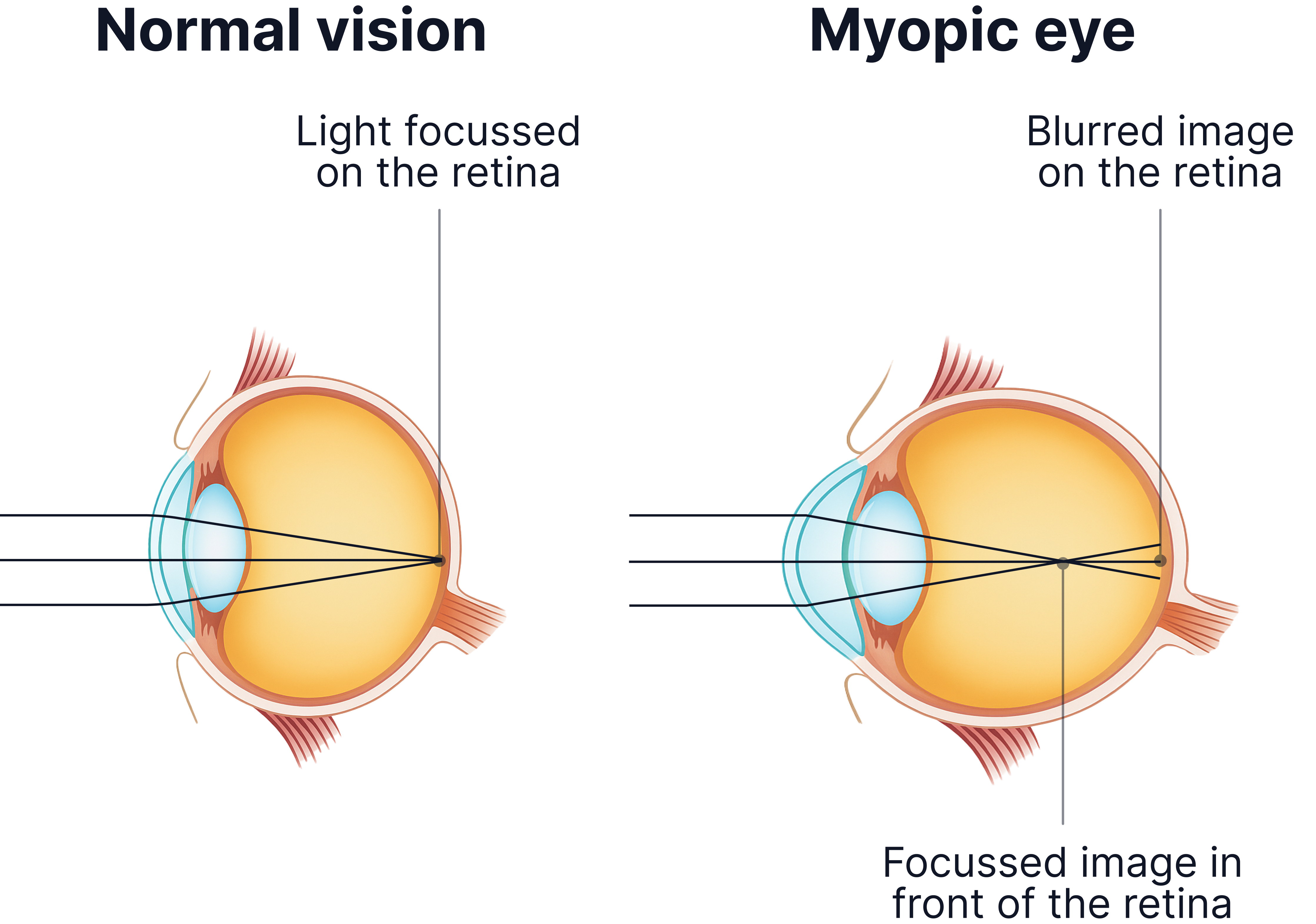
1. Myopia (Short-sightedness)
-
Can see near objects clearly but distant objects are blurry.
-
Light focuses in front of the retina.
-
Caused by the eyeball being too long or the lens being too curved (so light is refracted too much)
-
Corrected with a concave lens (spreads out light rays) so light is focused on the retina.
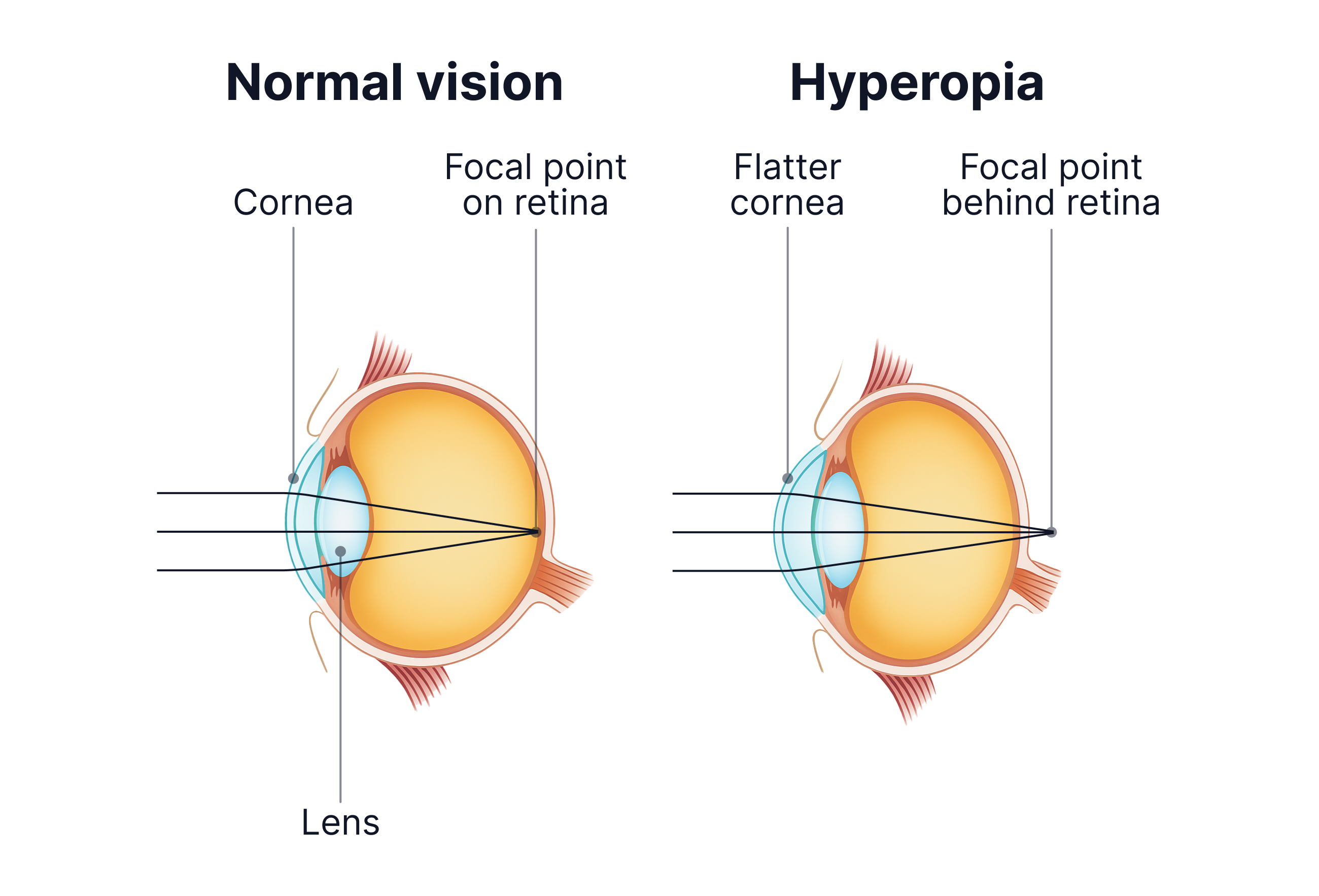
2. Hyperopia (Long-sightedness)
-
Can see distant objects clearly but near objects are blurry.
-
Light focuses behind the retina.
-
Caused by the eyeball being too short or the lens being too thin (so light is not refracted enough).
-
Corrected with a convex lens (brings light rays together) so light is focused on the retina.
Treatments for Vision Defects
-
Spectacle lenses – concave for myopia, convex for hyperopia.
-
Contact lenses – worn directly on the eye surface. Lightweight, almost invisible, convenient e.g. when playing sport, comfortable. However there is a risk of eye infection and they are an ongoing expense.
-
Laser eye surgery – reshapes the cornea to change how much light is refracted and improve focus. Can completely correct vision so no need for contacts or glasses. Long term solution. However there are risks of complications- vision may be worse than before. There is a risk of infection from surgery and surgery is expensive.
-
Replacement lens surgery –artificial lens made of clear plastic replaces own lens- long term solution- no need for glasses or lenses. However this is high risk as it requires surgery inside the eye- could potentially damage retina- leading to loss of sight. Risk of infection and an expensive procedure.
Key Terms
- Accommodation - The automatic adjustment of the lens to focus on near or distant objects.
- Pupil Reflex - The adjustment of pupil size in response to light levels.
- Myopia - Short-sightedness; difficulty seeing distant objects clearly.
- Hyperopia - Long-sightedness; difficulty seeing near objects clearly.
- Concave lens - A lens that diverges light rays, used to correct myopia.
- Convex lens - A lens that converges light rays, used to correct hyperopia.
- Refract - To bend light as it passes through a different medium (e.g., from air to cornea or lens).
Exam Tips
- Make sure you don’t confuse the muscles involved in adjusting to light and accommodation.
- When adjusting the size of the pupil to light, it is the circular muscles and the radial muscles in the iris that are used.
- When adjusting the shape of the lens in accommodation, it is the ciliary muscles and the suspensory ligaments that are used.
Practice Question
Explain how the eye focuses on a near object. (4 marks)
-
The ciliary muscles contract.
-
The suspensory ligaments loosen.
-
The lens becomes thicker/more curved.
-
This causes light to be refracted more so it focuses on the retina.
More Practice
Try to answer these practice questions from the TikTok videos on your own, then watch the videos to see how well you did!