Using Quadrats To Estimate Population Size And Using Transects To Investigate Distribution
Laura Armstrong & Joe Wolfensohn
Teachers


Recall Questions
This topic requires prior knowledge of abiotic and biotic factors.
What is an abiotic factor?
A non-living factor that affects an ecosystem, e.g., light, temperature.
What is a biotic factor?
A living factor that affects an ecosystem, e.g., predators, disease, competition.
What is an ecosystem?
All the living organisms (community) and the non-living parts (abiotic factors) interacting together in an area.
Topic Explainer Video
Check out these @JoeDoesGCSEBiology videos that explain using quadrats and transects to investigate distribution, then read the study notes. Once you’ve gone through them, don’t forget to try the practice questions!
Sampling Using Quadrats And Transects
Why Do Ecologists Use Sampling?
- It’s often impossible to count every organism in an area.
- Sampling allows scientists to estimate population size and see how organisms are distributed.
- This helps show how abiotic and biotic factors affect communities.
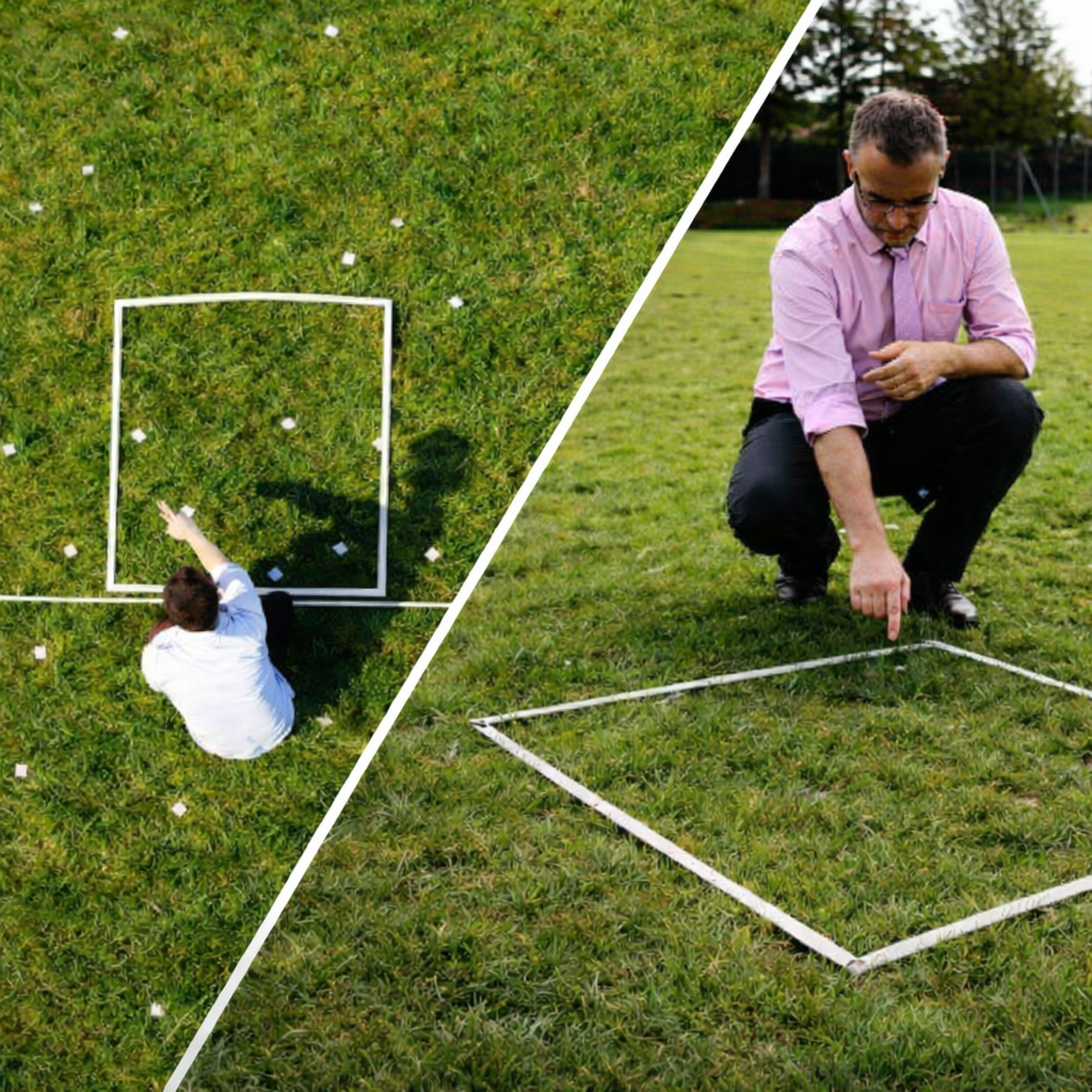
Using Quadrats
- A quadrat is a square frame of a known area (often 0.5 m x 0.5 m) used to mark out a sample area.
- Scientists place quadrats randomly to estimate the population size of plants or slow-moving animals like limpets.
How to use quadrats:
- Place quadrats randomly in the study area to avoid any bias.
- This can be achieved by drawing a grid over a map of the area and assigning co-ordinates.
- A random number generator can then be used to select co-ordinates to sample.
- Place the quadrat at the sample site and count the number of organisms in each quadrat.
- Calculate the mean number of organisms per quadrat.
- Multiply the mean number per metre2 by the total area of the habitat to estimate the whole population size.
- Remember to use many quadrats (at least 10), this will make the estimate more representative of the true population size.
Using a Gridded Quadrat & Percentage Cover
What is a gridded quadrat?
A gridded quadrat is a square frame divided into smaller squares - for example, a 0.5 m x 0.5 m quadrat with a 5 × 5 grid gives 25 smaller squares.
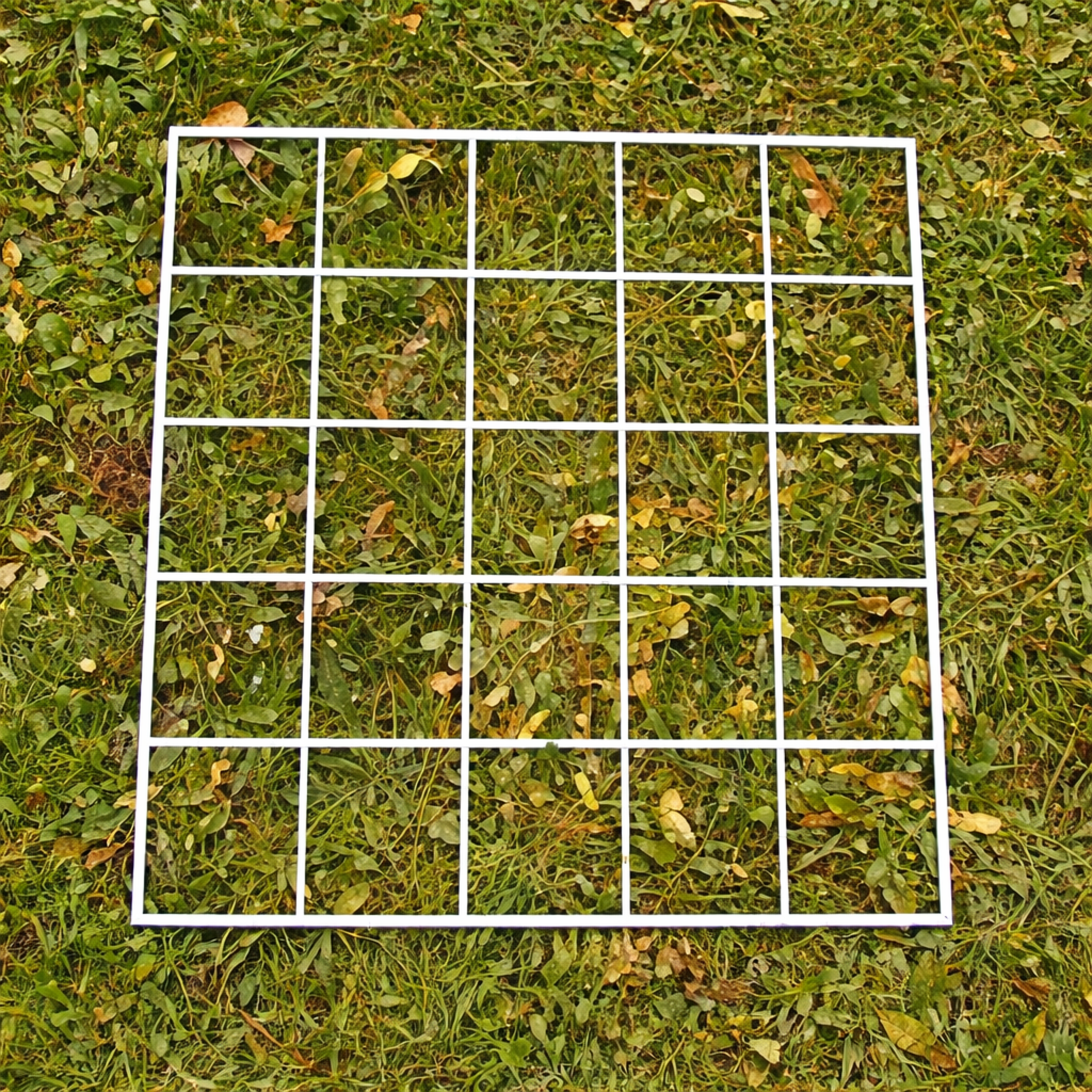
Gridded quadrats can be used to estimate percentage cover.
% cover is a way to estimate how much of an area is covered by a particular plant or organism without counting each individual.
This is useful when:
- Plants are too small or too numerous to count easily - like grass, moss, or tiny clover plants.
- When you want a quick estimate of how much ground a species covers.
How to calculate percentage cover
Place the quadrat randomly.
Look inside the quadrat and count how many squares contain the species you’re sampling.
Calculate percentage cover:
Percentage cover = (Number of squares covered / Total number of squares) x 100
Example:
- You use a quadrat with 25 squares.
- 7 squares contain clover.
- Percentage cover of clover = (7 / 25) x 100 = 28% cover
When a plant or organism only partly covers a square, you need a consistent rule to avoid double counting or missing squares:
The standard rule:
• If more than half the square is covered, count it in.
• If less than half the square is covered, leave it out.
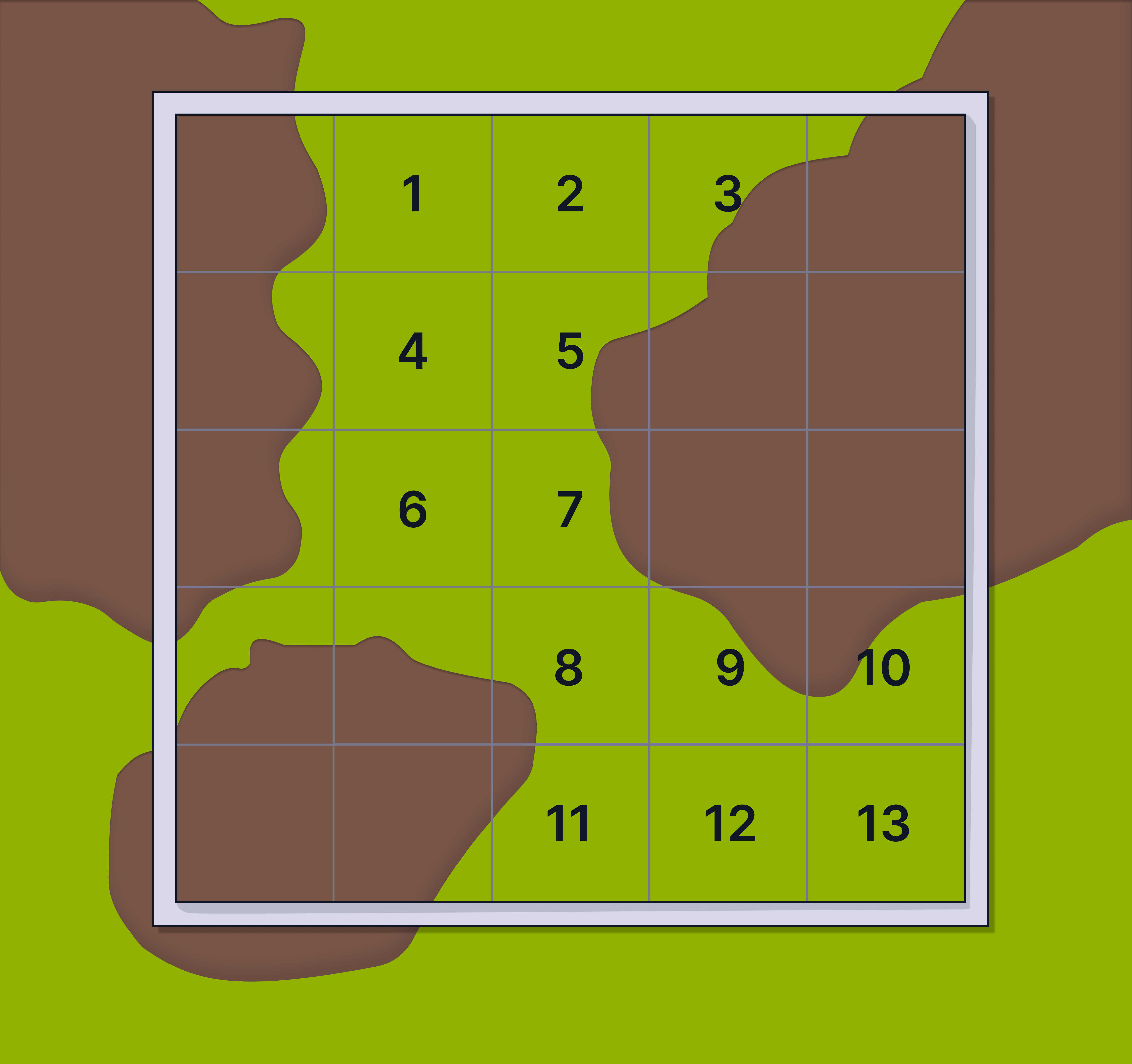
In this quadrat, only 13 squares are counted, as only 13 are at least half covered by the green plant.
% cover = (13 / 25) x 100 = 52 % cover
Why this rule matters:
- It keeps the method fair and repeatable.
- It avoids overestimating or underestimating the true coverage.
- All ecologists should use the same rule when working in a team.
Using Transects
- A transect is a line (e.g., tape measure or string) across a habitat.
- It is used to investigate how distribution changes across an area - for example, how plants change from a path into a woodland, or from the coast line to inland.
How to use a transect:
- Stretch a tape measure between two points.
- Place quadrats at regular intervals along the line (e.g., every 1 m). This is called systematic sampling, it is not random.
- Count or record the species in each quadrat.
- Measure abiotic factors in each quadrat (e.g., light, soil moisture) to explain changes.
Example:
- If you run a transect from a path into a woodland, you could:
- Use a light meter to see how light levels drop under trees.
- Use a soil pH probe to check if the soil becomes more acidic under trees.
- Use a soil moisture probe to see if shaded soil holds more water.
5. Repeat the transect several times and place many quadrats along the transect to get representative data.

Using a transect, placing quadrats at regular intervals.
Why Does It Matter?
- Quadrats and transects help ecologists link distribution and abundance to abiotic factors (like light, soil pH) and biotic factors (like competition).
- For example, fewer plants may grow closer to a path because they are trampled - a biotic factor.
Key Terms & Definitions
- Quadrat - A square frame with a known area used for sampling organisms in a habitat.
- Transect - A line across a habitat used to study how organisms are distributed.
- Distribution - Where organisms are found within a habitat.
- Abundance - The number of organisms present.
- Bias in Sampling - The way a sample is collected means the estimate for population size is not representative of the overall population size.
Exam Tips:
- Use many quadrats to get representative data.
- When trying to estimate population size, calculate the mean number of plants per quadrat and show clear working out to estimate population size.
Practice Question
A student places 5 quadrats in a field. The number of daisies in each quadrat is: 4, 5, 3, 6, 2. Each quadrat is 0.5 m². Estimate how many daisies are in a field of 100 m². [3 marks]
Model Answer:
- Mean number of daisies per quadrat = (4 + 5 + 3 + 6 + 2) ÷ 5 = 20 ÷ 5 = 4. (1 mark)
- Each quadrat is 0.5 m², so there are about 4 daisies per 0.5 m².
This means there are 8 daisies per 1 m2 (1 mark) - Total area = 100 m².
Estimated total = 8 x 100 = 800 daisies. (1 mark)
More Practice
Try to answer these practice questions from the TikTok videos on your own, then watch the videos to see how well you did!